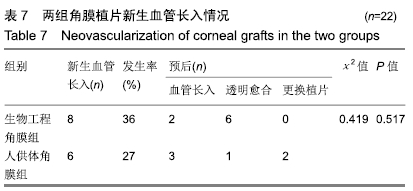
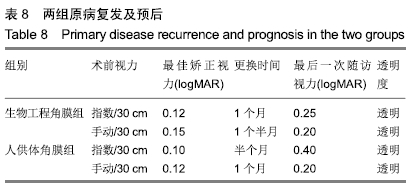
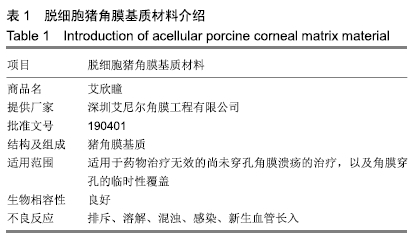
[1] AUGSTEN PR, DAWCZYNSKI J, PFISTER W, et al. Fusarium-Keratitis.Ophthalmologe.2008;105(11):1043-1045.
[2] 易先金,朱顺清.角膜真菌病的临床与实验研究[J].国外医学:眼科学分册,1989,13(5):264-269.
[3] 谢立信.角膜移植学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2000:77-88,262.
[4] 胡建章,谢立信.真菌性角膜炎板层角膜移植术后复发的临床研究[J].中华眼科杂志,2008,44(2):111-115.
[5] 陈金鹏,徐辉勇,章剑,等.甘油保存角膜行深板层角膜移植治疗真菌性角膜溃疡的临床观察[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2014,32(5): 630-633.
[6] 蓝平,高明宏,孟彤柏,等.长期低温保存角膜方法的建立和临床应用[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2001,19(2):135-138.
[7] 唐勋伦,文智伟,伍俊,等.板层角膜移植术治疗真菌性角膜溃疡穿孔的临床观察[J].临床眼科杂志,2010,18(3):242-243.
[8] WANG X, WANG W, XU J, et al. Pretreatment of rapamycin before allogenic corneal transplant promotes graft survival through increasing CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Exp Clin Transplant.2013;11(1):56-62.
[9] XIE L, SHI W, LIU Z, et al.Lamellar keratoplasty for the treatment of fungal keratitis.Cornea. 2002;21(1):33-37.
[10] XIE L, DONG X, SHI W.Treatment of fungal keratitis by penetrating keratoplasty.Br J Ophthalmol.2001;85(9): 1070-1074.
[11] GAIN P, JULLIENNE R, HE Z, et al.Global Survey of Corneal Transplantation and Eye Banking. Jama Ophthalmol. 2016; 134(2):167.
[12] TERRY MA.The evolution of lamellar grafting techniques over twenty-five years.Cornea.2000;19(5):611-616.
[13] 潘东艳,柳林.板层角膜移植术手术方式及植片材料研究进展[J].国际眼科杂志,2005,5(4):738-741.
[14] 吴振中,蒋幼芹.眼科手术学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1994: 127-177.
[15] 龚岚,朱澄,邱孝芝,等.反板层角膜移植的临床应用研究[J].眼科新进展,2001,21(3):203-204.
[16] 伍桂军,丁伟,杨方耀.环行板层巩膜瓣联合全板层角膜移植术治疗严重眼部化学伤临床及免疫学探讨[J].眼科新进展,2000, 20(6):397-399.
[17] ZHANG MC, LIU X, JIN Y, et al.Lamellar keratoplasty treatment of fungal corneal ulcers with acellular porcine corneal stroma.Am J Transplant.2015;15(4):1068-1075.
[18] 郑钦象,华闪闪,赵泽林,等.生物人工角膜治疗感染性角膜炎的安全性和有效性[J].中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志, 2016,18(4): 215-218.
[19] 谢立信.108例真菌性角膜炎的临床和组织病理学研究[J].中华实验眼科杂志,1999,20(4):283-285.
[20] 姜剑,毕宏生,王兴荣,等.羊膜移植联合羊膜覆盖治疗真菌性角膜炎分析[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2010,28(9):992-994.
[21] MEYER RF, BOBB KC.Corneal Epithelium in Penetrating Keratoplasty.Am J Ophthalmol.1980;90(2):142-147.
[22] FOERSTER CG, LANGENBUCHER A, CURSIEFEN C, et al. Delayed epithelial healing after keratoplasty for lattice corneal dystrophy.Cornea.2007;26(10):1182-1183.
[23] 钟兴武,龚向明,廖武.角膜缘干细胞缺乏对角膜上皮损伤修复的影响[J].临床眼科杂志,1999,7(4):246-248.
[24] SCHERMER A, GALVIN S, SUN TT.Differentiation-related expression of a major 64K corneal keratin in vivo and in culture suggests limbal location of corneal epithelial stem cells.J Cell Biol.1986;103(1):49-62.
[25] 孙秀丽,史伟云,王婷,等.板层角膜移植术后植片上皮延缓愈合的相关因素分析[J].临床眼科杂志,2013, 21(2):97-100.
[26] PARK JH, JEOUNG JW, WEE WR, et al.Clinical efficacy of amniotic membrane transplantation in the treatment of various ocular surface diseases.Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2008;31(2):73-80.
[27] YILDIZ EH, NUROZLER AB, OZKAN AN, et al.Amniotic membrane transplantation: indications and results.Eur J Ophthalmol.2008;18(5):685-690.
[28] 史伟云,谢立信,刘艳霞,等.羊膜移植在难治性角膜溃疡中的应用[J].眼科新进展,2001,21(4):252-254.
[29] 黄宝玲,郎平,梅立新,等.新鲜羊膜移植治疗难治性眼表疾病的临床观察[J].临床眼科杂志,2006,14(1):31-33.
[30] 王智崇,徐锦堂.显微板层角膜移植术后神经再生的观察[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2000,18(9):527-529.
[31] 张萍.深板层角膜移植治疗角膜病的临床观察[J].中国卫生标准管理,2015,6(8):130-131.
[32] LI J, YU L, DENG Z, et al.Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty using acellular corneal tissue for prevention of allograft rejection in high-risk corneas.Am J Ophthalmol. 2011;152(5):762-770.
[33] COOMBES AG, KIRWAN JF, ROSTRON CK.Deep lamellar keratoplasty with lyophilised tissue in the management of keratoconus.Br J Ophthalmol.001;85(7):788-791.
[34] WATSON SL, RAMSAY A, DART JK, et al.Comparison of deep lamellar keratoplasty and penetrating keratoplasty in patients with keratoconus.Ophthalmology.2004;111(9): 1676-1682.
[35] PANG K, DU L, WU X.A rabbit anterior cornea replacement derived from acellular porcine cornea matrix, epithelial cells and keratocytes.Biomaterials.2010;31(28):7257-7265.
[36] LI N, WANG X, WAN P, et al.Tectonic lamellar keratoplasty with acellular corneal stroma in high-risk corneal transplantation. Mol Vis.2011;17(17):1909-1917.
[37] SHAO Y, YU Y, PEI CG, et al.Evaluation of novel decellularizing corneal stroma for cornea tissue engineering applications.Int J Ophthalmol.2012;5(4):415-418.
[38] 史伟云,谢立信.高危角膜移植[J].中国实用眼科杂志,1998, 16(12):712-714.
[39] PHILIPP W, SPEICHER L, HUMPEL C.Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in inflamed and vascularized human corneas.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41(9):2514-2522.
[40] SHAHARUDDIN B, AHMAD S, MEESON A, et al.Concise Review: Immunological Properties of Ocular Surface and Importance of Limbal Stem Cells for Transplantation.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(8):614-624.
[41] CHANG HY, CHODOSH J.Diagnostic and therapeutic considerations in fungal keratitis.Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2011; 51(4):33.
[42] 杨红,薛劲松,蒋沁.角膜新生血管治疗的研究进展[J].国际眼科杂志,2016,16(4):665-669.
|