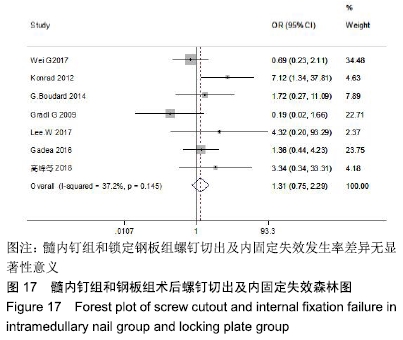
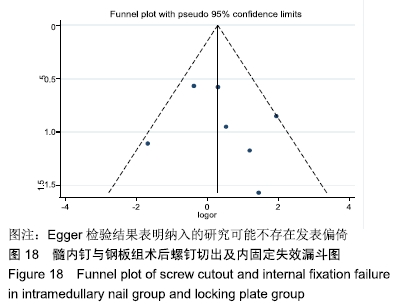
[1] HAK DJ, STAHEL PF, HAK DJ, et al. Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: current diagnostic and treatment strategies. Orthopedics. 2015; 38(4):247-251.
[2] NEER CS. Displaced proximal humeral fractures. I. Classification and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1970;52(6):1077.
[3] 江涛,江林,史俊德,等. 正骨手法治疗肱骨近端骨折合并肩关节脱位[J]. 中国骨伤,2018,31(2):175-179.
[4] LAUX CJ, GRUBHOFER F, WERNER CML, et al. Current concepts in locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017; 12(1):137.
[5] SOBEL AD, SHAH KN, PAXTON ES. Fixation of a proximal humerus fracture with an intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31 Suppl 3:S47.
[6] BRANKO KOPJAR,王簕,杨云峰. 肱骨近端骨折反置式人工全肩关节置换术与人工肱骨头置换术的比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012,14(1):61-67.
[7] WEI G, QI S, GEN L, et al. Efficacy comparison of intramedullary nails, locking plates and conservative treatment for displaced proximal humeral fractures in the elderly. Clin Int Aging. 2017;12:2047-2054.
[8] KONRAD G, AUDIGÉ L, LAMBERT S, et al. Similar Outcomes for Nail versus Plate Fixation of Three-part Proximal Humeral Fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(2):602-609.
[9] BOUDARD G, POMARES G, MILIN L, et al. Locking plate fixation versus antegrade nailing of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures in patients without osteoporosis. Comparative retrospective study of 63 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(8):917-924.
[10] GRADL G, DIETZE A, KÄÄB M, et al. Is locking nailing of humeral head fractures superior to locking plate fixation? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467(11):2986-2993.
[11] LEE W, PARK JY, CHUN YM. Operative treatment of 2-part surgical neck fracture of the humerus: intramedullary nail versus locking compression plate with technical consideration.J Orthop Trauma. 2017; 31(9):e270-e274.
[12] GADEA F, FAVARD L, BOILEAU P, et al. Fixation of 4-part fractures of the proximal humerus: Can we identify radiological criteria that support locking plates or IM nailing? Comparative, retrospective study of 107 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016:S1877056816301608.
[13] ZHU Y, LU Y, SHEN J, et al. Locking intramedullary nails and locking plates in the treatment of two-part proximal humeral surgical neck fractures: a prospective randomized trial with a minimum of three years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(2):159-168.
[14] 高峰,王秀会,夏胜利,等. 锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗肱骨近端骨折的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2018,26(12):1068-1073.
[15] 黄安全,邹天明.成人肱骨近端骨折治疗进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2016,18(7): 442-446.
[16] BRUNNER F, SOMMER C, BAHRS C, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using a proximal humeral locked plate: a prospective multicenter analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(3):163-172.
[17] BRORSON S, RASMUSSEN JV, FRICH LH, et al. Benefits and harms of locking plate osteosynthesis in intraarticular (OTA Type C) fractures of the proximal humerus:A systematic review. Injury.2012;43(7): 999-1005.
[18] CLAVERT P, HATZIDAKIS A, BOILEAU P. Anatomical and biomechanical evaluation of an intramedullary nail for fractures of proximal humerus fractures based on tuberosity fixation. Clin Biomech. 2015:S0268003315003290.
[19] KANCHERLA VK, SINGH A, ANAKWENZE OA. Management of acute proximal humeral fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(1):42-52.
[20] 陈薇,方赛男,陈可冀,等. 国际循证医学证据分级体系的发展与现状[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2017,37(12):1413-1419.
[21] GRACITELLI MEC, MALAVOLTA EA, ASSUNÇÃO JH, et al. Locking intramedullary nails versus locking plates for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2017;14(9):733-739.
[22] WANG GQ, MAO Z, ZHANG LH, et al. Meta-analysis of locking plate versus intramedullary nail for treatment of proximal humeral fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10(1):122.
[23] GADEA F, FAVARD L, BOILEAU P, et al. Fixation of 4-part fractures of the proximal humerus: Can we identify radiological criteria that support locking plates or IM nailing? Comparative, retrospective study of 107 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016:S1877056816301608.
[24] ALLENDE C, AGUSTÍN PAZ, ALTUBE G, et al. Revision with plates of humeral nonunions secondary to failed intramedullary nailing. Int Orthop. 2014;38(4):899-903.
[25] LIN J, HOU SM. Locked-nail treatment of humeral surgical neck nonunions. J Trauma. 2003;54(3):530-535.
[26] 吴其鹏,刘国辉,夏天,等. Multiloc髓内钉治疗肱骨近端二、三部分骨折[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2017,20(2):251.
[27] LIN J. Effectiveness of locked nailing for displaced three-part proximal humeral fractures. J Trauma. 2006;61(2):363-374.
[28] KAZAKOS K , LYRAS DN, GALANIS V , et al. Internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the Polarus intramedullary nail. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(7):503-508.
[29] CLAVERT P, HATZIDAKIS A, BOILEAU P. Anatomical and biomechanical evaluation of an intramedullary nail for fractures of proximal humerus fractures based on tuberosity fixation. Clin Biomech. 2015:S0268003315003290.
[30] BHANDARI M, DEVEREAUX PJ, MCKEE MD, et al. Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures—a meta-analysis. Acta Orthopaedica. 2006;77(2):279-284.
[31] 吴晓明,吴剑宏,王秋根. 肱骨近端骨折髓内钉治疗的老概念与新方法——第三代肱骨近端髓内钉的设计理念和临床实践[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015, 17(10):915-920.
|