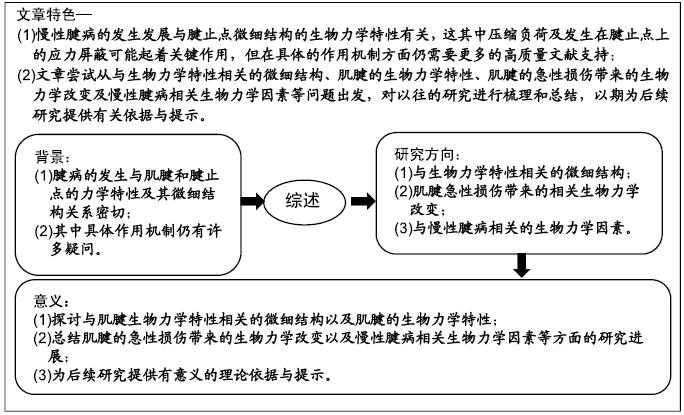
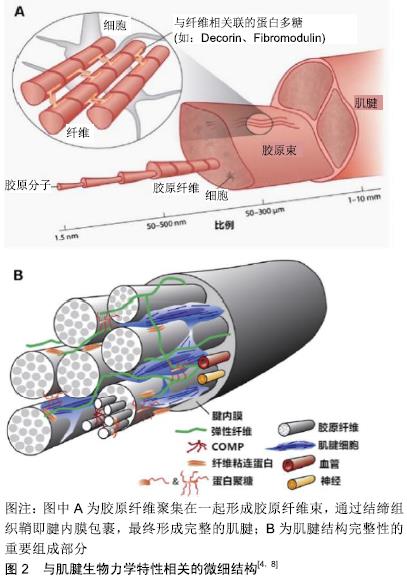
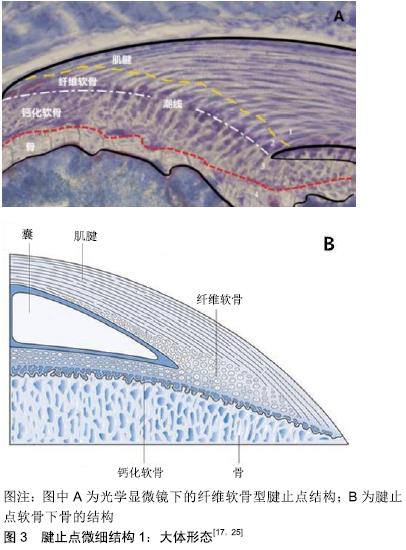
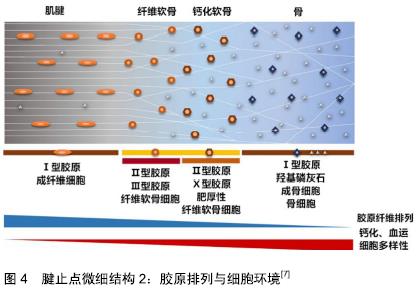
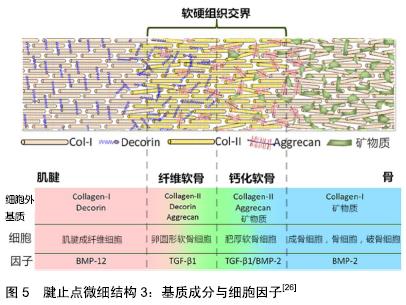
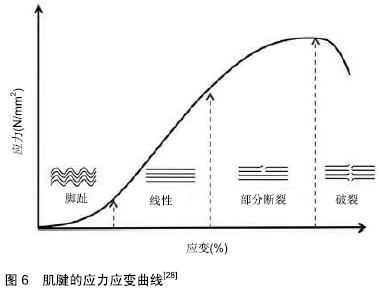
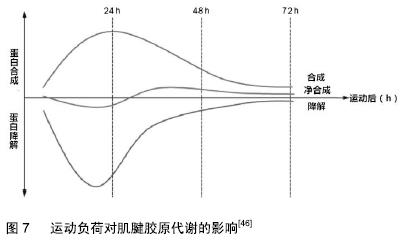
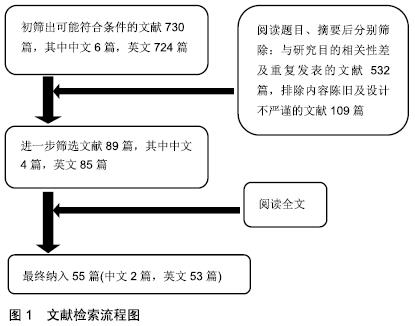
[1] 刘春雨,韩小燕,王琳.末端病与细胞外基质:骨腱结合部重要蛋白及酶类的关系尚需深入研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(15): 2265-2272.
[2] KANNUS P.Structure of the tendon connective tissue.Scand J Med Sci Sports.2000;10(6): 312-320.
[3] KILLIAN ML, AVINATTO L, GALATZ LM, et al.The role of mechanobiology in tendon healing.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(2):228-237.
[4] YOON JH, HALPER J.Tendon proteoglycans: biochemistry and function.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2005;5(1): 22-34.
[5] THORPE CT, SCREEN HR.Tendon Structure and Composition. Adv Exp Med Biol.2016;920:3-10.
[6] HAMMOUDI TM, TEMENOFF JS.Biomaterials for Regeneration of Tendons and Ligaments. Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications.Springer Vienna, 2011: 307-341.
[7] NOURISSAT G, BERENBAUM F, DUPREZ D.Tendon injury: from biology to tendon repair.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(4): 223-233.
[8] THORPE CT, BIRCH HL, LEGG PD, et al.The role of the non-collagenous matrix in tendon function. Int J Exp Pathol. 2013;94(4):248-259.
[9] DERWIN KA, SOSLOWSKY LJ, KIMURA JH, et al. Proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycan fine structure in the mouse tail tendon fascicle.J Orthop Res. 2001;19(2):269-277.
[10] YANAGISHITA M.Function of proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix.Acta Pathol Jpn.1993;43(6):283-293.
[11] ARNOCZKYS P, LAVAGNINO M, EGERBACHER M, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors prevent a decrease in the mechanical properties of stress-deprived tendons: an in vitro experimental study.Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(5):763-769.
[12] BENJAMIN M, MORIGGL B, BRENNER E, et al.The "enthesis organ" concept: why enthesopathies may not present as focal insertional disorders.Arthritis Rheum.2004; 50(10):3306-3313.
[13] SCHETT G, ORIES RJ, D'AGOSTINO MA, et al.Enthesitis: from pathophysiology to treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017; 13(12):731-741.
[14] ROSSETTI L, KUNTZ LA, UNOLD E, et al.The microstructure and micromechanics of the tendon-bone insertion.Nat Mater. 2017;16(6):664-670.
[15] RIGOZZI S, MULLER R, STEMMER A, et al.Tendon glycosaminoglycan proteoglycan sidechains promote collagen fibril sliding-AFM observations at the nanoscale.J Biomech.2013;46(4):813-818.
[16] ANDLEY C, PARKINSON J, SAMIRIC T, et al.Overuse tendinopathy is characterised by changes in the metabolism of proteoglycans present in the extracellular matrix of tendons.J Sci Med Sport.2010;13(supp-S1):e21-22.
[17] Apostolakos J, Durant TJ, Dwyer CR, et al.The enthesis: a review of the tendon-to-bone insertion.Muscles Ligaments Tendons J.2014;4(3):333-342.
[18] BENJAMIN M, KUMAI T, MILZ S, et al.The skeletal attachment of tendons—tendon ‘entheses’. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol.2002;133(4):931-945.
[19] LYONS TJ, STODDART RW, MCCLURE SF, et al.The tidemark of the chondro-osseous junction of the normal human knee joint.J Mol Histol.2005;36(3):207-215.
[20] THOMOPOULOS S, GENIN GM, GALATZ LM.The development and morphogenesis of the tendon-to-bone insertion - what development can teach us about healing. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.2010; 10(1):35-45.
[21] HEMS T, TILLMANN B.Tendon entheses of the human masticatory muscles.Anat Embryol (Berl). 2000;202(3): 201-208.
[22] BENJAMIN M, TOUMI H, SUZUKI D, et al.Microdamage and altered vascularity at the enthesis-bone interface provides an anatomic explanation for bone involvement in the HLA-B27- associated spondylarthritides and allied disorders. Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(1):224-233.
[23] MILZ S, RUFAI A, UETTNER A, et al.Three-dimensional reconstructions of the Achilles tendon insertion in man.J Anat. 2002;200(Pt 2):145-152.
[24] THOMOPOULOS S, ILLIAMS GR, GIMBEL JA, et al.Variation of biomechanical, structural, and compositional properties along the tendon to bone insertion site.J Orthop Res. 2003; 21(3): 413-419.
[25] KOLT G, SNYDER-MACKLER L(Eds.).Physical Therapies in Sport and Exercise.2nd Edition.Churchill Livingstone, 2007: 30.
[26] WOPENKA B, KENT A, PASTERIS JD, et al.The tendon-to-bone transition of the rotator cuff: a preliminary Raman spectroscopic study documenting the gradual mineralization across the insertion in rat tissue samples.Appl Spectrosc.2008;62(12):1285-1294.
[27] CONNIZZO BK, YANNASCOLI SM, SOSLOWSKY LJ. Structure-function relationships of postnatal tendon development: a parallel to healing.Matrix Biol. 2013;32(2): 106-116.
[28] LAKE SP, MILLER KS, ELLIOTT DM, et al.Tensile properties and fiber alignment of human supraspinatus tendon in the transverse direction demonstrate inhomogeneity, nonlinearity, and regional isotropy.J Biomech.2010;43(4):727-732.
[29] SHARMA P, MAFFULLI N.Biology of tendon injury: healing, modeling and remodeling.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2006;6(2):181-190.
[30] VERES SP, LEE JM.Designed to fail: a novel mode of collagen fibril disruption and its relevance to tissue toughness.Biophys J.2012;102(12):2876-2884.
[31] GAUTIERI A, VESENTINIS, REDAELLI A, et al.Hierarchical structure and nanomechanics of collagen microfibrils from the atomistic scale up.Nano Lett.2011;11(2):757-766.
[32] VAN DER RIJT JA, VAN DER WERF KO, BENNINK ML, et al. Micromechanical testing of individual collagen fibrils. Macromol Biosci.2006;6(9):697-702.
[33] GAUTIERI A, VESENTINI S, REDAELLI A, et al.Viscoelastic properties of model segments of collagen molecules.Matrix Biol.2012;31(2):141-149.
[34] WOO SL, DEBSKI RE, ZEMINSKI J, et al.Injury and repair of ligaments and tendons.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2000;2: 83-118.
[35] FRANCHI M, FINI M, QUARANTA M, et al.Crimp morphology in relaxed and stretched rat Achilles tendon.J Anat. 2007; 210(1):1-7.
[36] LUJAN TJ, UNDERWOOD CJ, JACOBS NT, et al. Contribution of glycosaminoglycans to viscoelastic tensile behavior of human ligament.J Appl Physiol(1985).2009; 106(2):423-431.
[37] FESSEL G, GERBER C, SNEDEKER JG.Potential of collagen cross-linking therapies to mediate tendon mechanical properties.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2012;21(2):209-217.
[38] ELLIOTT DM, ROBINSON PS, GIMBEL JA, et al. Effect of altered matrix proteins on quasilinear viscoelastic properties in transgenic mouse tail tendons.Ann Biomed Eng. 2003; 31(5):599-605.
[39] UZEL SG, BUEHLER MJ.Molecular structure, mechanical behavior and failure mechanism of the C-terminal cross-link domain in type I collagen.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011; 4(2):153-161.
[40] JAMES R, KESTURU G, BALIAN G, et al.Tendon: biology, biomechanics, repair, growth factors, and evolving treatment options.J Hand Surg Am.2008;33(1):102-112.
[41] VOLETI PB, BUCKLEY MR, SOSLOWSKY LJ.Tendon healing: repair and regeneration.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;14:47-71.
[42] ANSORGE HL, ADAMS S, BIRK DE, et al.Mechanical, compositional, and structural properties of the post-natal mouse Achilles tendon.Ann Biomed Eng. 2011;39(7): 1904-1913.
[43] NAKAMURA N, HART DA, OORMAN RS, et al.Decorin antisense gene therapy improves functional healing of early rabbit ligament scar with enhanced collagen fibrillogenesis in vivo.J Orthop Res.2000;18(4):517-523.
[44] GAROFALO R, CESARI E, VINCI E, et al.Role of metalloproteinases in rotator cuff tear. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev.2011;19(3):207-212.
[45] SHARMA P, MAFFULLI N.Tendon injury and tendinopathy: healing and repair.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2005;87(1):187-202.
[46] MAGNUSSON SP, LANGBERG H, KJAER M.The pathogenesis of tendinopathy: balancing the response to loading.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2010;6(5):262-268.
[47] LYMAN J, WEINHOLD PS, ALMEKINDERS LC.Strain behavior of the distal achilles tendon: implications for insertional achilles tendinopathy.Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32(2):457-461.
[48] ALMEKINDERS LC, BAYNES AJ, BRACEY LW.An in vitro investigation into the effects of repetitive motion and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication on human tendon fibroblasts. Am J Sports Med.1995;23(1):119-123.
[49] COOK JL, PURDAM C.Is compressive load a factor in the development of tendinopathy?Br J Sports Med. 2012;46(3): 163-168.
[50] SOSLOWSKY LJ, THOMOPOULOS S, ESMAIL A, et al. Rotator cuff tendinosis in an animal model: role of extrinsic and overuse factors.Ann Biomed Eng.2002;30(8):1057-1063.
[51] ALMEKINDERS LC, VELLEMA JH, WEINHOLD PS.Strain patterns in the patellar tendon and the implications for patellar tendinopathy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002; 10(1):2-5.
[52] BENJAMIN M, RALPHS JR.Biology of fibrocartilage cells.Int Rev Cytol.2004;233:1-45.
[53] 刘振东.骨折愈合原理[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2012:116.
[54] MAGANARIS CN, ARICI MV, ALMEKINDERS LC, et al. Biomechanics and pathophysiology of overuse tendon injuries: ideas on insertional tendinopathy.Sports Med. 2004; 34(14):1005-1017.
[55] BENJAMIN M, RALPHS JR.Fibrocartilage in tendons and ligaments-an adaptation to compressive load.J Anat. 1998; 193(Pt 4):481-494.
|