| [1]Rigo M, Jela?i? M. Brace technology thematic series: the 3D Rigo Chêneau-type brace. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12:10. [2]Çolak TK, Akgül T, Çolak I, et al. Health related quality of life and perception of deformity in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2017;30(3):597-602. [3]Han J, Xu Q, Yang Y, et al. Evaluation of quality of life and risk factors affecting quality of life in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2015;4(1):12-16.[4]Schwieger T, Campo S, Weinstein SL, et al. Body image and quality-of-life in untreated versus brace-treated females with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2015;41(4):311-319.[5]Xu L, Li Y, Sheng F, et al. The efficacy of brace treatment for thoracolumbar kyphosis in patients with achondroplasia. Spine. 2018; 43(16):1133-1138.[6]Chalmers E, Lou E, Hill D, et al. An advanced compliance monitor for patients undergoing brace treatment for idiopathic scoliosis. Med Eng Phys. 2015; 37(2):203-209.[7]Karol L A, Virostek D, Felton K, et al. Effect of compliance counseling on brace use and success in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016; 98(1):9-14.[8]Poscia A, Aulisa AG, Marzetti E, et al. Correlation between compliance and brace treatment in juvenile and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: SOSORT 2014 award winner. Scoliosis. 2014;9(1):1-9.[9]Lou EHM, Hill DL, Raso JV, et al. How quantity and quality of brace wear affect the brace treatment outcomes for AIS. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(2):495-499.[10]Weiss HR, Nan XF, Moramarco M, et al. Bracing Scoliosis - State of the Art (Mini-Review). Curr Pediatr Rev. 2016;12(1):36-42.[11]Herget GW, Patermann S, Strohm PC, et al. Spinal Orthoses: The Crucial Role of Comfort on Compliance of Wearing - Monocentric Prospective Pilot Study of Randomized Cross-Over Design. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2017;2:91-96.[12]黄亚翔,赵自平,王治国,等.夜用型脊柱侧弯矫形支具的数字化设计[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(27):4327-4331.[13]Weiss HR, Tournavitis N, Nan X, et al. Workflow of CAD/CAM scoliosis brace adjustment in preparation using 3d printing. Open Med Inform J. 2017;11(1):44-51.[14]Jr CF. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, bracing, and the Hueter- Volkmann principle. Spine J. 2003; 3(3):180-185.[15]钟环,欧阳汉斌,魏波,等.桡骨远端骨折锁定钢板的拓扑优化及有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(23):2189-2194.[16]Tack P, Victor J, Gemmel P, et al. 3D-printing techniques in a medical setting: a systematic literature review. Biomed Eng Online. 2016;15(1): 115.[17]张爱平,刘羲,刘志峰,等. 基于3D打印的定制脊柱侧弯矫形器设计制造与舒适度评价[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2017,43(4):518-525.[18]Du HG, Liao SH, Jiang Z, et al. Biomechanical analysis of press-extension technique on degenerative lumbar with diodeling of brace treatment of scoliosis: effects of gravitational loads. Medical & biological engineerisc herniation and staggered facet joint. Saudi Pharmaceutical J. 2016; 24(3):305-311.[19]Wang L, Zhang B, Chen S, et al. A validated finite element analysis of facet joint stress in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. World Neurosurg. 2016; 95:126-133.[20]Périé D, Aubin CE, Petit Y, et al. Personalized biomechanical simulations of orthotic treatment in idiopathic scoliosis . Clin Biomech. 2004;19(2):190.[21]Aubin CE, Dansereau J, De Guise JA, et al. A study of biomechanical coupling between spine and rib cage in the treatment by orthosis of scoliosis. Ann Chir. 1996;50(8):641.[22]Cheung JPY, Yiu KKL, Vidyadhara S, et al. Predictability of supine radiographs for determining in-brace correction for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2017;43(14):971-974.[23]Ekici G, Unal E, Akbayrak T, et al. Effects of active/passive interventions on pain, anxiety and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: randomized controlled pilot trial. Women Health. 2016; 57(1):88-107.[24]Lin H, Shi L, Wang D. A rapid and intelligent designing technique for patient-specific and 3D-printed orthopedic cast. 3d Printing Med. 2016; 2(1):7-17.[25]Wong MS. Computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacture (CAD/CAM) system for construction of spinal orthosis for patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Physiother Theory Pract. 2011;27(1): 74-79.[26]Sattout A, Clin J, Cobetto N, et al. Biomechanical assessment of providence nighttime brace for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2016;4(4):253-260.[27]Cobetto N, Aubin, CE, Parent S, et al. 3D correction of AIS in braces designed using CAD/CAM and FEM: a randomized controlled trial. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12:24.[28]杨新宇,詹成,李明,等.3D打印技术在医学中的应用进展[J].复旦学报(医学版),2016,43(4):490-494.[29]Berman B. 3-D printing: The new industrial revolution. Business Horizons. 2012;55(2): 162.[30]Khajavi SH, Holmström J, Partanen J. Additive manufacturing in the spare parts supply chain. Comput Industry. 2013;65(1):50-63.[31]陈拥,王增辉,朴成哲. 3D打印个性化截骨导板辅助行全膝关节置换的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(8):1155-1160.[32]Santos S, Soares B, Leite M, et al. Design and development of a customised knee positioning orthosis using low cost 3D printers. Virt Phys Protot. 2017:1-11.[33]Khodaei B, Saeedi H, Jalali M, et al. Comparison of plantar pressure distribution in CAD-CAM and prefabricated foot orthoses in patients with flexible flatfeet. Foot. 2017;33:76-80.[34]Geoffroy M, Gardan J, Goodnough J, et al. Cranial remodeling orthosis for infantile plagiocephaly created through a 3d scan, topological optimization, and 3d printing process. J Prosthet Orthot. 2018;1(1): 201-209.陆亮亮,史廷春,于云,等.3D打印指骨骨折支具的研究[J].航天医学与医学工程, 2017,30(4):30-37. |
.jpg)
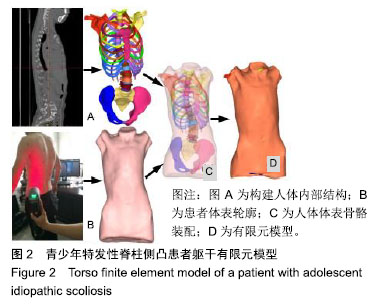
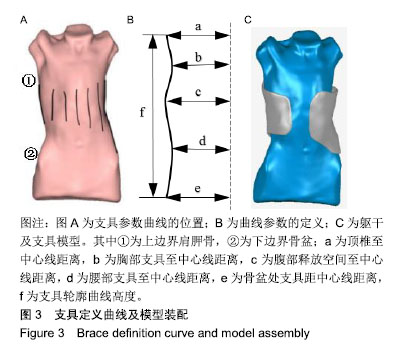
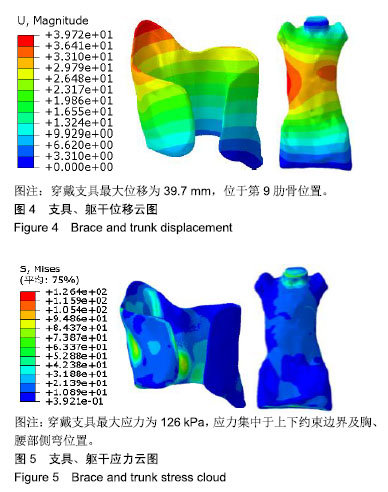
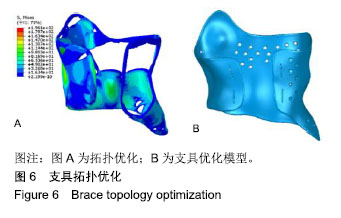

.jpg)
.jpg)