| [1]Shim B , Kim DW , Kim BH , et al. Mechanical and heat sensitization of cutaneous nociceptors in rats with experimental peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience. 2005; 132(1):193-201. [2]Devor M. Ectopic discharge in Abeta afferents as a source of neuropathic pain.Exp Brain Res. 2009; 196(1):115-128.[3]Ying M , Liu H , Zhang T , et al. Effect of artemisinin on neuropathic pain mediated by P2X4 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Neurochem Int. 2017;108:27-33.[4]Hanani M. Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: from form to function. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.2005;48(3):457-476.[5]Souza GR, Talbot J, Lotufo CM, et al. Fractalkine mediates inflammatory pain through activation of satellite glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(27):11193-11198.[6]Hanani M. Role of satellite glial cells in gastrointestinal pain. Frontiers in Cellular.Neuroscience. 2015;9(7):412.[7]Hanani M. Intercellular communication in sensory ganglia by purinergic receptors and gap junctions: Implications for chronic pain. Brain Res.2012;1487(17):183-191.[8]Pannese E. The structure of the perineuronal sheath of satellite glial cells (SGCs) in sensory ganglia. Neuron Glia Biol.2010;6(1):3-10.[9]Pannese E. Perikaryal surface specializations of neurons in sensory ganglia. Int Rev Cytol. 2002;220:1-34.[10]Schiønning JD, Danscher G.Autometallographic mercury correlates with degenerative changes in dorsal root ganglia of rats intoxicated with organic mercury. APMIS. 1999;107(3): 303-310.[11]Procacci P , Magnaghi V , Pannese E. Perineuronal satellite cells in mouse spinal ganglia express the gap junction protein connexin43 throughout life with decline in old age. Brain Res Bull.2008;75(5):0-569.[12]Ohara PT, Vit JP, Bhargava A, et al. Evidence for a Role of Connexin 43 in Trigeminal Pain Using RNA Interference In Vivo. J Neurophysiol.2008;100(6):3064-3073.[13]Chen J, He L, Dinger B , et al. Chronic hypoxia upregulates connexin43 expression, in rat carotid body and petrosal ganglion. J Appl Physiol. 2002;92(4):1480-1486.[14]Penuela S, Gehi R, Laird DW.The biochemistry and function of pannexin channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1828(1): 15-22.[15]Zhang Y, Laumet G , Chen S R , et al. Pannexin-1 Upregulation in the Dorsal Root Ganglion Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Development.J Biol Chem.2015;290(23):14647.[16]Montero TD, Orellana JA . Hemichannels: new pathways for gliotransmitter release.Neuroscience.2015; 286:45-59.[17]Retamal MA , Alcayaga J , Verdugo CA , et al. Opening of pannexin- and connexin-based channels increases the excitability of nodose ganglion sensory neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:158.[18]Kaji K, Shinoda M , Honda K , et al. Connexin 43 contributes to ectopic orofacial pain following inferior alveolar nerve injury. Mol Pain.2016;12:12/0/1744806916633704.[19]Retamal MA, Riquelme MA, Jimmy S, et al. Connexin43 Hemichannels in Satellite Glial Cells, Can They Influence Sensory Neuron Activity?. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:374.[20]Chen G, Park CK , Xie RG , et al. Connexin-43 induces chemokine release from spinal cord astrocytes to maintain late-phase neuropathic pain in mice.Brain. 2014;137(Pt 8): 2193-2209.[21]Retamal MA, Reyes EP, Garc?-A IE,et al.Diseases associated with leaky hemichannels.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:267.[22]Ohara PT, Vit JP , Bhargava A, et al. Evidence for a Role of Connexin 43 in Trigeminal Pain Using RNA Interference In Vivo. J Neurophysiol. 2008;100(6):3064-3073.[23]Jasmin L, Vit J P, Bhargava A , et al. Can satellite glial cells be therapeutic targets for pain control?. Neuron Glia Biol.2010; 6(1):63-71.[24]Xu Q , Cheong YK , Yang F , et al. Intrathecal carbenoxolone inhibits neuropathic pain and spinal wide-dynamic range neuronal activity in rats after an L5 spinal nerve injury. Neurosci Lett. 2014;563:45-50.[25]Bele T , Fabbretti E. The scaffold protein calcium/calmodulin‐dependent serine protein kinase controls ATP release in sensory ganglia upon P2X3 receptor activation and is part of an ATP keeper complex. J Neurochem. 2016;138(4):11.[26]Huang LYM, Gu Y, Chen Y. Communication between neuronal somata and satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia. Glia. 2013; 61(10):1571-1581.[27]Nakatsuka T, Gu JG. P2X purinoceptors and sensory transmission. Pslug Arch Eur J Ph. 2006;452(5):598-607.[28]Chen Y, Li G, Huang LY.P2X7 receptors in satellite glial cells mediate high functional expression of P2X3 receptors in immature dorsal root ganglion neurons. Mol Pain. 2012;8:9.[29]Franke H, Verkhratsky A, Burnstock G, et al. Pathophysiology of astroglial purinergic signalling. Purinerg Signal. 2012;8(3): 629-657.[30]Wu B, Ma Y, Yi Z . Resveratrol-decreased hyperalgesia mediated by the P2X7 receptor in gp120-treated rats.Mol Pain. 2017;13:1744806917707667.[31]Liu J, Li G, Peng H , et al. Sensory–sympathetic coupling in superior cervical ganglia after myocardial ischemic injury facilitates sympathoexcitatory action via P2X7receptor. Purinerg Signal.2013;9(3):463-479.[32]Chessell IP, Hatcher JP, Bountra C , et al. Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain.2005;114(3):386-396.[33]Song J, Ying Y, Wang W, et al. The role of P2X7R/ERK signaling in dorsal root ganglia satellite glial cells in the development of chronic postsurgical pain induced by skin/muscle incision and retraction (SMIR). Brain Behav Immun. 2017.[34]Xie J , Liu S , Wu B , et al. The protective effect of resveratrol in the transmission of neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X7 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia. Neurochem Int. 2017;103: 24-35.[35]Molliver DC, Malin SA. Gi- and Gq-coupled ADP (P2Y) receptors act in opposition to modulate nociceptive signaling and inflammatory pain behavior. Mol Pain.2010;6(1):1-12.[36]Magni G, Ceruti S. P2Y purinergic receptors: New targets for analgesic and antimigraine drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85(4):466-477.[37]Yousuf A, Klinger F, Schicker K, et al. Nucleotides control the excitability of sensory neurons via two P2Y receptors and a bifurcated signaling cascade.Pain.2011;152(8): 1899-1908.[38]Chen Y, Zhang X, Wang C, et al. Activation of P2X7 receptors in glial satellite cells reduces pain through downregulation of P2X3 receptors in nociceptive neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(43):16773-16778. [39]Gerevich Z, Christoph Müller, Illes P . Metabotropic P2Y1 receptors inhibit P2X3 receptor-channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Eur J Pharmacol.2005;521(1-3):34-38.[40]Gerevich Z, Borvendeg SJ, Schröder, Wolfgang, et al. Inhibition of N-type voltage-activated calcium channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons by P2Y receptors is a possible mechanism of ADP-induced analgesia.J Neurosci. 2004;24(4): 797-807.[41]Mo G , Peleshok J C , Cao C Q , et al. Control of P2X3 channel function by metabotropic P2Y2 utp receptors in primary sensory neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 2013;83(3): 640-647.[42]Castillo C , Norcini M , Hernandez L A M , et al. Satellite glia cells in dorsal root ganglia express functional NMDA receptors. Neuroscience.2013;240(9):135-146.[43]Gu Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, et al. Neuronal soma–satellite glial cell interactions in sensory ganglia and the participation of purinergic receptors. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010;6(01):10.[44]Ferrari LF , Lotufo CM , Dionéia Araldi, et al. Inflammatory sensitization of nociceptors depends on activation of NMDA receptors in DRG satellite cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(51):18363-18368.[45]Carozzi V A , Canta A , Oggioni N, et al. Expression and distribution of ‘high affinity’ glutamate transporters GLT1, GLAST, EAAC1 and of GCPII in the rat peripheral nervous system. J Anat.2008;213(5):8.[46]Ohara P, Vit J P , Bhargava A , et al. Gliopathic Pain: When Satellite Glial Cells Go Bad. Neuroscientist. 2009;15(5): 450-63.[47]Sung B , Lim G , Mao J . Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci.2003;23(7):2899.[48]Tang X , Schmidt TM , Perezleighton CE , et al. Inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir4.1 is responsible for the native inward potassium conductance of satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia. Neuroscience. 2010;166(2):397-407.[49]Zhang H , Mei X , Zhang P , et al. Altered Functional Properties of Satellite Glial Cells in Compressed Spinal Ganglia. Glia.2009;57(15):1588-1599.[50]Silva JR, Lopes AH, Talbot J, et al. Neuro-immune-glia interactions in the sensory ganglia account for the development of acute herpetic neuralgia. J Neurosci. 2017; 37(27):6408-6422.[51]Takeda M , Takahashi M , Nasu M , et al. Peripheral inflammation suppresses inward rectifying potassium currents of satellite glial cells in the trigeminal ganglia.Pain.2011;152(9): 2147-2156.[52]Vit J P , Ohara PT , Bhargava A, et al. Silencing the Kir4.1 Potassium Channel Subunit in Satellite Glial Cells of the Rat Trigeminal Ganglion Results in Pain-Like Behavior in the Absence of Nerve Injury.J Neurosci.2008;28(16):4161-4171.[53]Murata Y, Yasaka T, Takano M , et al. Neuronal and glial expression of inward rectifier potassium channel subunits Kir2.x in rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 2016;617:59-65.[54]Pagadala P, Park CK , Bang S, et al. Loss of NR1 Subunit of NMDARs in Primary Sensory Neurons Leads to Hyperexcitability and Pain Hypersensitivity: Involvement of Ca2+-Activated Small Conductance Potassium Channels. J Neurosci.2013;33(33):13425-13430.[55]Thompson JM, Ji G, Neugebauer V. Small-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium (SK) Channels in the Amygdala Mediate Pain-Inhibiting Effects of Clinically Available Riluzole in a Rat Model of Arthritis Pain. Mol Pain. 2015;11(1): s12990-015-0055.[56]Tsantoulas C , Mcmahon SB . Opening paths to novel analgesics: the role of potassium channels in chronic pain. Trends Neurosci 2014;37(3):146-158.[57]Lu R, Flauaus C, Kennel L, et al. K Ca 3.1 channels modulate the processing of noxious chemical stimuli in mice. Neuropharmacology.2017;125:386-395.[58]Pomonis JD, Rogers SD, Peters CM , et al. Expression and Localization of Endothelin Receptors: Implications for the Involvement of Peripheral Glia in Nociception. J Neurosci. 2001;21(3):999-1006.[59]Piovezan AP, D'Orléans-Juste P, Souza GE, et al. Endothelin-1-induced ET A, receptor-mediated nociception, hyperalgesia and oedema in the mouse hind-paw: modulation by simultaneous ET B, receptor activation.Br J Pharmacol. 2010;129(5):961-968.[60]Vellani V, Prandini M , Giacomoni C , et al. Functional endothelin receptors are selectively expressed in isolectin B4-negative sensory neurons and are upregulated in isolectin B4-positive neurons by neurturin and glia-derived neurotropic factor. Brain Res.2011;1381(none):31-37.[61]Feldman-Goriachnik R, Hanani M. Functional study of endothelin B receptors in satellite glial cells in trigeminal ganglia. NeuroReport.2011;22(10):465-469.[62]Feldman-Goriachnik R, Hanani M. The effects of endothelin-1 on satellite glial cells in peripheral ganglia. Neuropeptides. 2017;63:37-42.[63]Huang TY , Belzer V , Hanani M . Gap junctions in dorsal root ganglia: Possible contribution to visceral pain. Eur J Pain. 2010;4(1):490-2147483647.[64]Hanani M , Huang TY , Cherkas PS , et al. Glial cell plasticity in sensory ganglia induced by nerve damage. Neuroscience. 2002;114(2):279-283.[65]Dublin P, Hanani M . Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: Their possible contribution to inflammatory pain. Brain Behav Immun. 2007;21(5):592-598.[66]Liu W , Glueckert R , Linthicum F H , et al. Possible role of gap junction intercellular channels and connexin 43 in satellite glial cells (SGCs) for preservation of human spiral ganglion neurons. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;355(2):267-278.[67]Suadicani SO, Cherkas PS, Zuckerman J, et al. Bidirectional calcium signaling between satellite glial cells and neurons in cultured mouse trigeminal ganglia. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010; 6(1):43-51.[68]Warwick RA, Hanani M. Involvement of aberrant calcium signalling in herpetic neuralgia. Exp Neurol.2016; 277:10-18.[69]Chen X , Pang RP , Shen KF , et al. TNF-α enhances the currents of voltage gated sodium channels in uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons following motor nerve injury. Exp Neurol.2011;227(2):279-286.[70]Zhang X, Liu C, Nestor KE , et al. The effect of glypican-1 glycosaminoglycan chains on turkey myogenic satellite cell proliferation, differentiation, and fibroblast growth factor 2 responsiveness.Poult Sci.2007; 86(9):2020-2028.[71]Vicente R, Escalada A, Soler C, et al. Pattern of Kv beta subunit expression in macrophages depends upon proliferation and the mode of activation. J Immunol. 2005; 174(8):4736.[72]Pang RP, Xie MX, Yang J , et al. Downregulation of ClC-3 in dorsal root ganglia neurons contributes to mechanical hypersensitivity following peripheral nerve injury. Neuropharmacology.2016;110:181-189.[73]Song DD , Li Y , Tang D , et al. Neuron-glial communication mediated by TNF-? and glial activation in dorsal root ganglia in visceral inflammatory hypersensitivity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014;306(9):G788-795.[74]Qiao LN, Tan LH, Yang JJ, et al. Effects of Electroacupuncture on Activities of Satellite Glial Cells of Dorsal Root Ganglia in Rats with Neck Incision Pain.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2017;42(4):283-289.[75]李瑞午,李翠红,汪智民. 足三里穴区不同层次感觉和运动神经元的节段性分布研究[J].中国针灸, 2000,20(3):161-163.[76]边冠鹤,李泽山.猫大肠各部的初级传入神经来源及节段性分布—HRP法研究[J]. 锦州医科大学学报,1993(2):1-6.[77]Tang Y, Yin HY, Liu J,et al. P2X receptors and acupuncture analgesia.Brain Res Bull. 2018;17:1-28. |
.jpg)
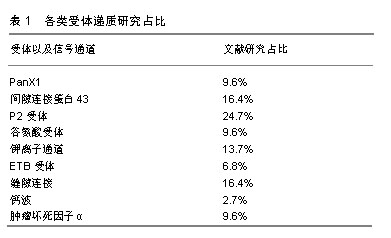
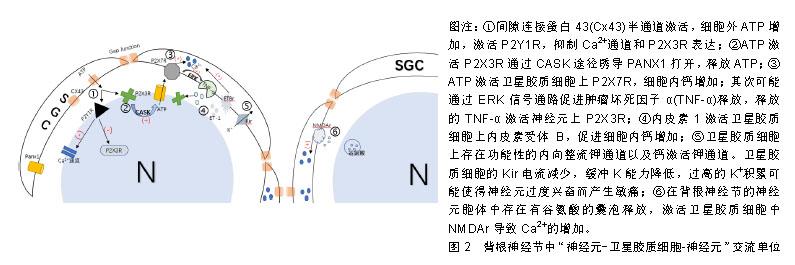
.jpg)
.jpg)