| [1]陈红霞,杨志敬,潘锐焕,等.中西医结合康复方案对脑卒中后偏瘫患者运动功能、日常生活活动能力和生活质量的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2016,36(4):395-398.[2]中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组.中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J].中华神经科杂志,2018, 51(9):666-682.[3]柏晓玲,王天兰,石国凤,等. 临床护理路径在脑梗死患者健康教育中应用效果的Meta分析[J].中华医院管理杂志,2016, 32(2): 158-160.[4]张永明,姚奕,王金标,等.骨髓间充质干细胞动脉移植对缺血性脑损伤小鼠行为学的影响[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2016,25(9): 791-796.[5]郑臻,母得志.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗缺氧缺血性脑损伤的研究现状[J].中华妇幼临床医学杂志(电子版),2017,13(4):373-377.[6]Donega V, van Velthoven CT, Nijboer CH, et al. Intranasal mesenchymal stem cell treatment for neonatal brain damage: long-term cognitive and sensorimotor improvement. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e51253.[7]van Velthoven CT, Kavelaars A, van Bel F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell treatment after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury improves behavioral outcome and induces neuronal and oligodendrocyte regeneration. Brain Behav Immun. 2010;24(3): 387-393.[8]Jellema RK, Wolfs TG, Lima Passos V, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce T-cell tolerance and protect the preterm brain after global hypoxia-ischemia. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e73031.[9]Donega V, Nijboer CH, van Tilborg G, et al. Intranasally administered mesenchymal stem cells promote a regenerative niche for repair of neonatal ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2014;261:53-64.[10]van Velthoven CT, Kavelaars A, van Bel F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation changes the gene expression profile of the neonatal ischemic brain. Brain Behav Immun. 2011;25(7): 1342-1348.[11]Hu ZL, Li N, Wei X, et al. Neuroprotective effects of BDNF and GDNF in intravitreally transplanted mesenchymal stem cells after optic nerve crush in mice. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017;10(1):35-42.[12]Liu X, Wang X, Li A, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rats with Tourette syndrome. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(4):1211-1216.[13]Wang Q, Sun G, Gao C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate 2,5-hexanedione-induced neuronal apoptosis through a NGF/AKT-dependent pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34715.[14]Sohni A, Verfaillie CM. Mesenchymal stem cells migration homing and tracking. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:130763.[15]Wei ZZ, Gu X, Ferdinand A, et al. Intranasal delivery of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improved neurovascular regeneration and rescued neuropsychiatric deficits after neonatal stroke in rats. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(3):391-402.[16]Cui C, Cui Y, Gao J, et al. Intraparenchymal treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium exerts neuroprotection following intracerebral hemorrhage. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):2374-2382.[17]Hasan A, Deeb G, Rahal R, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Neurol. 2017;8:28.[18]马志波. CTA与DSA在脑血管疾病诊断中的价值研究[J].中国医学创新,2013,10(5):110-111.[19]周平,谢伟杰,孙桂波,等.缺血性脑卒中发病机制及药物干预研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(34):53-54,61.[20]孟文婷,李东翔,佟玲.缺血性脑卒中的治疗研究进展[J].中国新药杂志,2016,25(10):1114-1120.[21]付睿,戴威,席春江,等.不同剂量阿托伐他汀对缺血性脑卒中介入诊疗术后对比剂肾损害的预防作用研究[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(7): 812-816.[22]王伊龙.短暂性脑缺血发作的中国专家共识[J].中国实用乡村医生杂志,2013,20(2):883-885.[23]Compston A. Brain repair: an overview. J Neurol. 1994;242 (1 Suppl 1):S1-4.[24]易娟,李贵南.神经干细胞移植治疗新生儿脑损伤的前景展望[J].中国新生儿科杂志, 2017, 32(5):398-400.[25]Song M, Kim YJ, Kim YH, et al. Long-term effects of magnetically targeted ferumoxide-labeled human neural stem cells in focal cerebral ischemia. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(2): 183-190.[26]Chen L, Qiu R, Li L, et al. The role of exogenous neural stem cells transplantation in cerebral ischemic stroke. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(11):3219-3230.[27]Wang J, Xia J, Zhang F, et al. Galectin-1-secreting neural stem cells elicit long-term neuroprotection against ischemic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9621.[28]Tavares I. Human neural stem cell transplantation in spinal cord injury models: how far from clinical application. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(3):61.[29]林小娟,唐毅,陈建豪,等.脂肪干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血后微血管生成及MT1-MMP表达的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2018, 21(14):1514-1520.[30]Yao Y, Zheng XR, Zhang SS, et al. Transplantation of vascular endothelial growth factor-modified neural stem/progenitor cells promotes the recovery of neurological function following hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Neural Regen Res. 2016; 11(9):1456-1463.[31]Komatsu K, Honmou O, Suzuki J, et al. Therapeutic time window of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1334:84-92.[32]吴中华.脑外源性神经因子基因修饰神经干细胞对脑卒中的神经保护机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(45):7331-7336.[33]Li M, Zhou ZP, Sun M, et al. Reduced Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate, a Pentose Phosphate Pathway Product, Might Be a Novel Drug Candidate for Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2016;47(1):187-195.[34]Gudkov AV, Komarova EA. Pathologies associated with the p53 response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2(7):a001180.[35]Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND, Ji K, et al. p53 opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to trigger necrosis. Cell. 2012;149(7):1536-1548.[36]Yan YP, Lang BT, Vemuganti R, et al. Osteopontin is a mediator of the lateral migration of neuroblasts from the subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia.Neurochem Int.2009;55(8):826-832.[37]Ellison JA, Velier JJ, Spera P, et al. Osteopontin and its integrin receptor alpha(v)beta3 are upregulated during formation of the glial scar after focal stroke. Stroke.1998;29(8):1698-1706.[38]李欣遥,张良荣,张硕,等.急性脑梗死患者血清骨桥蛋白水平的改变及其对预后的影响[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2016, 33(3): 211-214.[39]张文婷,侯华娟,赵昊,等. P2Y1和ITGB3基因多态性与中国汉族大动脉粥样硬化性卒中患者阿司匹林抵抗的相关性[J].国际脑血管病杂志, 2017,25(11):1018-1022.[40]Furie B, Furie BC. Thrombus formation in vivo. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115(12):3355-3362.[41]陈乔,朱金华,李征峰,等.红景天苷对新生大鼠缺氧缺血脑组织MMP-9、TIMP-1含量的影响[J].亚太传统医药,2017,13(13):6-8.[42]Montaner J, Alvarez-Sabín J, Molina C, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase expression after human cardioembolic stroke: temporal profile and relation to neurological impairment. Stroke. 2001;32(8):1759-1766.[43]Romanic AM, White RF, Arleth AJ, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase expression increases after cerebral focal ischemia in rats: inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 reduces infarct size. Stroke. 1998;29(5):1020-1030.[44]Bendeck MP, Hou G, Chen J, et al. Matrix, Matrix Metalloproteinases and Smooth Muscle Cell Function in Atherosclerosis. International Congress.2004;1262(2): 486-489.[45]张毕奎. CD40/CD40L系统在脑梗塞疾病发生发展中的作用及机制研究[D].长沙:中南大学, 2013.[46]陈建昌,孙其中,郝跃伟.阿司匹林抵抗的动脉粥样硬化缺血性脑卒中患者COX-2基因启动子区-765G/C多态性观察[J].山东医药,2016, 56(35):91-93.[47]陈忠云,卫景沛,张洁,等.环氧化酶-2基因-765G/C位点多态性与缺血性脑卒中相关性的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2016,16(1): 48-53.[48]丁利静,李菲,石京山,等.淫羊藿苷对大脑中动脉阻塞诱导的缺血性脑卒中模型大鼠的保护作用[J].遵义医学院学报, 2015,38(2): 137-145.[49]李孝明.异补骨脂素通过雌激素α受体对脊髓的神经保护作用机制研究[D].上海:第二军医大学, 2017.[50]杨青梅,白松,雷又鸣,等. EZH2的功能及在肿瘤中的表达[J].中国老年保健医学, 2014,12(6):72-75. |
.jpg)
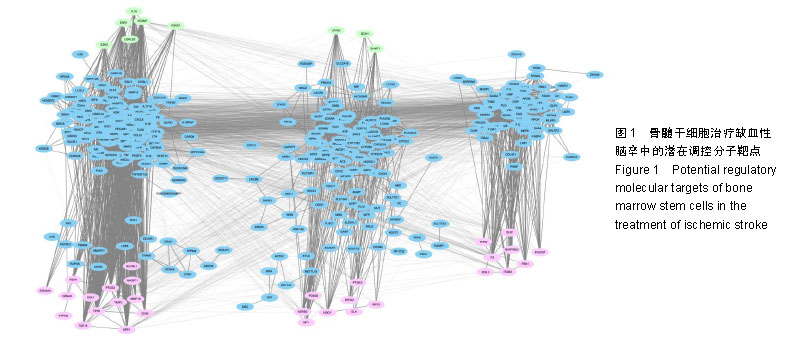
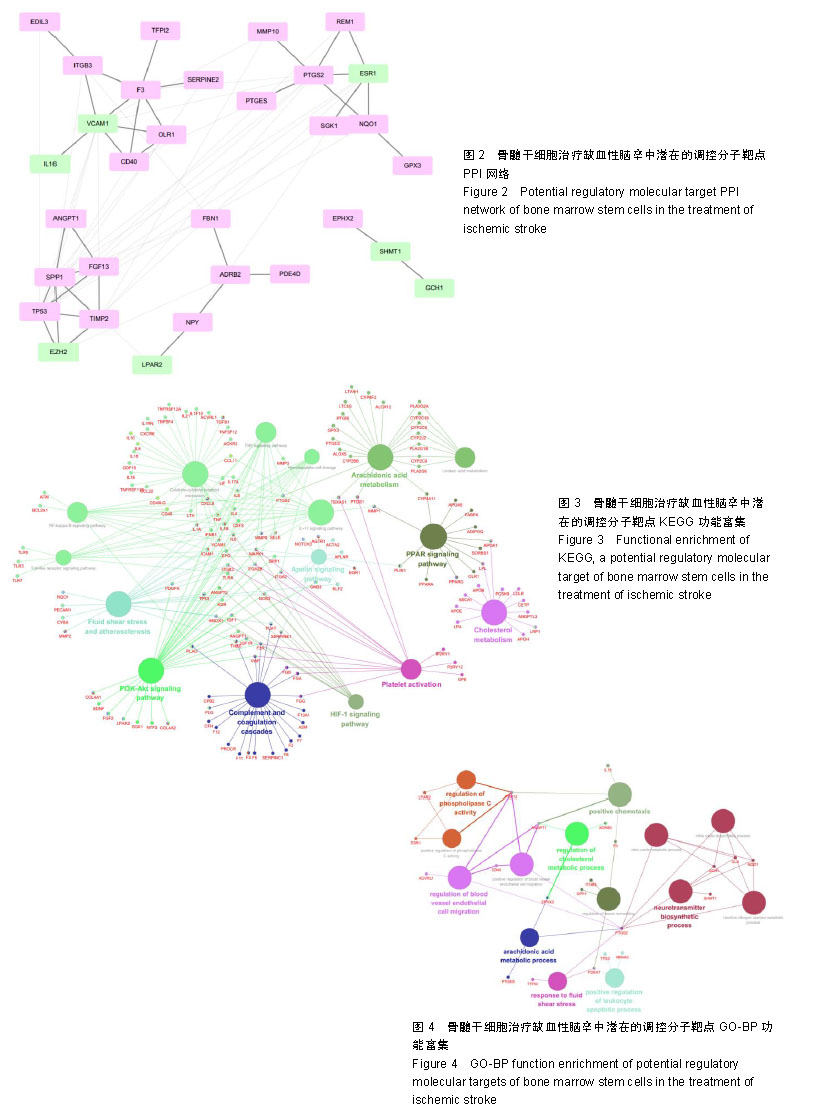
.jpg)
.jpg)