中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (24): 3805-3811.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1178
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
三种植入物治疗老年脑梗死偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折的比较
张擎柱1,樊 琪2,尹雪莲1,王鹏程3,侯 敬1,冯 震1,石利涛1,张忠岩1,李爱华1,万 乾1
- 1承德医学院附属医院创伤骨科,河北省承德市 067000;2承德医学院,河北省承德市 067000;3河北医科大学第三医院,河北省石家庄市 050000
Comparison of three implants for treating intertrochanteric fractures of cerebral infarction hemiplegia side in older adults
Zhang Qingzhu1, Fan Qi2, Yin Xuelian1, Wang Pengcheng3, Hou Jing1, Feng Zhen1, Shi Litao1, Zhang Zhongyan1, Li Aihua1, Wan Qian1
- 1Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China; 2Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China; 3the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
骨水泥型人工股骨头置换:骨水泥型人工股骨头置换治疗股骨转子间骨折不涉及骨折愈合问题,可尽快恢复髋关节功能,适用于预期寿命较短的患者。
股骨近端防旋髓内钉:是目前临床应用较多的股骨转子间骨折髓内固定物,手术创伤小,固定强度大,且有效防旋,亦可使骨折患者做到早期下地活动,减少卧床并发症,故受到众多学者推崇。
股骨近端锁定加压钢板:具有骨折断端复位佳及锁定钉孔设计固定稳定的优势,临床治疗老年转子间骨折应用广泛。
摘要
背景:股骨近端防旋髓内钉与锁定加压钢板均为临床治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的常用方法,同时也有部分学者认为骨水泥型人工股骨头置换治疗老年转子间骨折亦可取得较好疗效,但针对老年脑梗死偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折患者的手术治疗方案,目前仍存在较多争议。
目的:比较骨水泥型人工股骨头置换、股骨近端防旋髓内钉和锁定加压钢板植入治疗老年脑梗偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折的临床疗效。
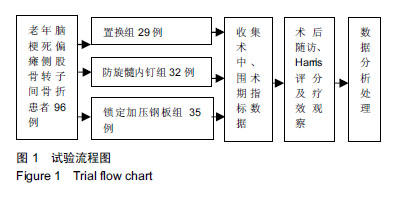
方法:纳入2010年6月至2017年1月承德医学院附属医院和河北医科大学第三医院收治的96例老年脑梗死偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折患者,男38例,女58例,年龄≥65岁,其中29例选择骨水泥型人工股骨头置换治疗(置换组),32例选择股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗(防旋髓内钉组),35例选择股骨近端锁定加压钢板内固定治疗(锁定加压钢板组)。对比3组手术时间、术中出血量、手术前后血红蛋白差值、术后卧床时间、术后并发症发生率及术后半年、1年的髋关节Harris评分。
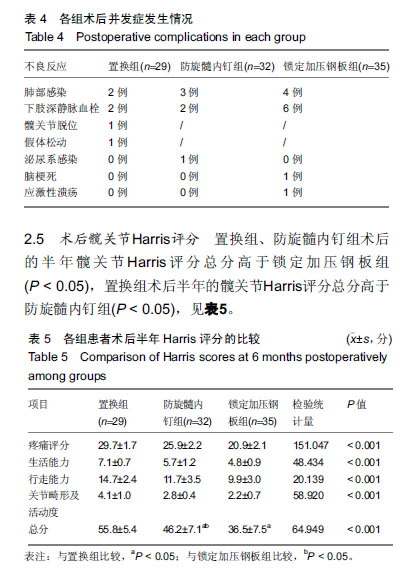
结果与结论:①防旋髓内钉组手术时间短于置换组、锁定加压钢板组(P < 0.05);置换组术中出血量多于防旋髓内钉组、锁定加压钢板组(P < 0.05);锁定加压钢板组术后卧床时间长于置换组、锁定加压钢板组(P < 0.05),手术前后血红蛋白差值低于置换组、锁定加压钢板组(P < 0.05);②3组术后并发症发生率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③置换组术后半年的Harris评分高于防旋髓内钉组、锁定加压钢板组(P < 0.05),置换组、防旋髓内钉组术后1年的Harris评分高于锁定加压钢板组(P < 0.05);④结果说明,与锁定加压钢板相比,骨水泥型人工股骨头置换和股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年脑梗偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折的术后卧床时间短、术后髋关节功能恢复更好,均可做为优先选择;但关节置换因术中出血多,手术风险相对增大,所以临床工作中需对每例患者进行个体化评估和治疗。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-3148-2324(万乾)
中图分类号:
R459.9



.jpg)
.jpg)