中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2614-2624.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1219
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇
颈后路微型钛板及侧块螺钉内固定治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的Meta分析
汪 伟1,马均峰1,崔子健2,张黎龙2,江泽华2,陆 芸3
- 1天津医科大学,天津市 300070;2天津市人民医院,天津市 300121;3天津医院,天津市 300210
Meta-analysis of posterior cervical laminectomy titanium mini-plate versus lateral mass screw fixation for treating multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Wang Wei1, Ma Junfeng1, Cui Zijian2, Zhang Lilong2, Jiang Zehua2, Lu Yun3
- 1Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Tianjin People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300121, China; 3Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300210, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义:单开门钛板内固定椎管扩大成形:在脊髓型颈椎病椎板相应部位设计并作出两侧的槽沟痕;用咬骨钳制成槽沟,设计开门的一侧咬透全层椎板,掀开切透侧椎板减压;并用微型钛板固定保持椎板的“开门”位,掀开侧硬脊膜外用人工硬脊膜和明胶海绵片覆盖。
全椎板减压侧块螺钉内固定:是通过病变节段椎板全部切断及扩大椎板矢状径,从而达到减压目的,并用侧块螺钉将病变节段固定,融合到一起,防止术后因椎板的切除而造成后凸畸形的发生。
摘要
背景:目前治疗多节段脊髓压迫性脊髓病的主要术式为颈后路单开门微型钛板内固定椎管扩大成形及颈后路全椎板减压侧块螺钉内固定,然而,这2种术式在临床中的优越性仍有很大争议,关于两者比较的相关文献较多,但大多因为样本量的局限未予以客观的评价。
目的:通过Meta分析来比较接受以上2种颈后路术式治疗多节段脊髓压迫性脊髓病的临床结果、安全性及术后并发症情况,进一步评价2种术式的优缺点。
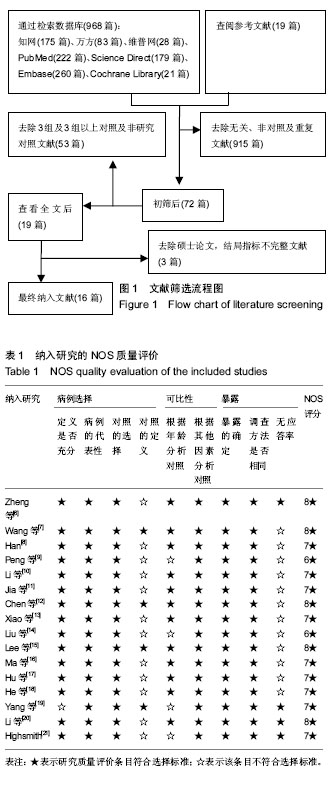
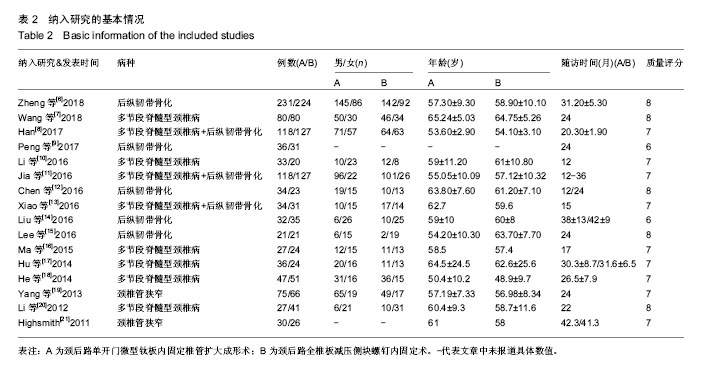
方法:在CNKI、WANGFANG、VIP、PubMed、Embase、Cochrane图书馆和Science Direct数据库中检索关于颈后路单开门微型钛板内固定椎管扩大成形和颈后路全椎板减压侧块螺钉内固定比较的随机或非随机对照试验文献,同时手动检索纳入文献的参考文献。从纳入文献中提取以下结果指标:手术时间,术中出血量、日本骨科协会评分、目测类比评分、颈椎曲度指数、颈椎功能障碍指数、C5神经根麻痹、轴性症状、后凸畸形及其他并发症数据。使用STATA 15.1进行数据分析。
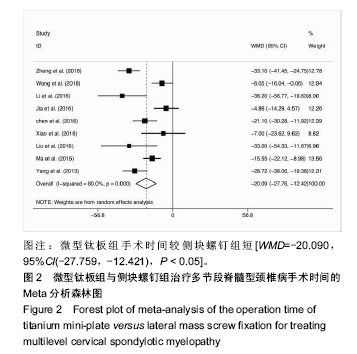
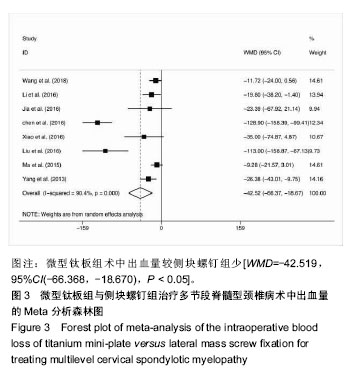
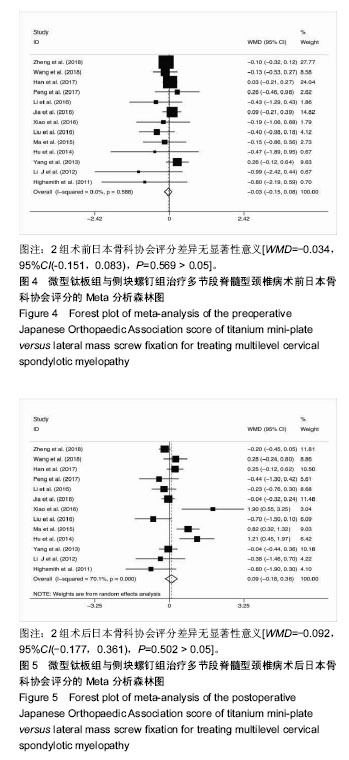
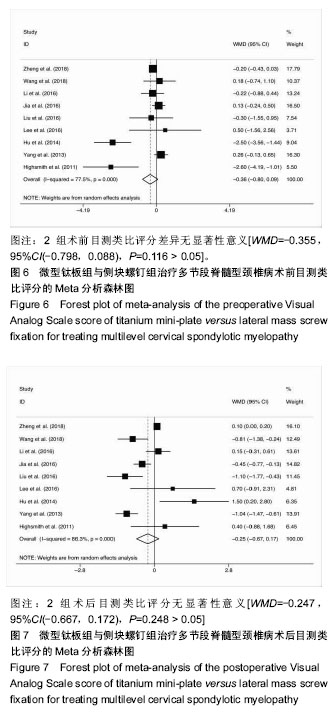
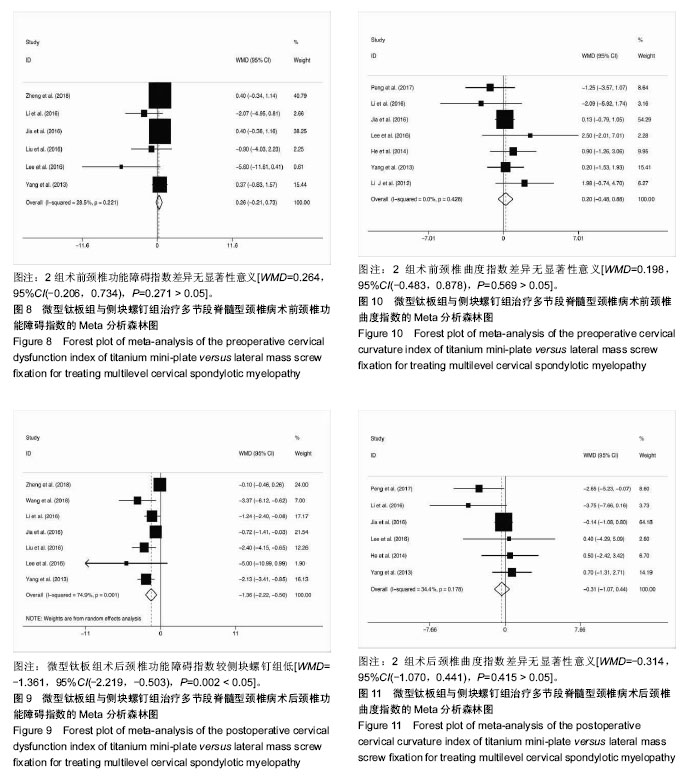
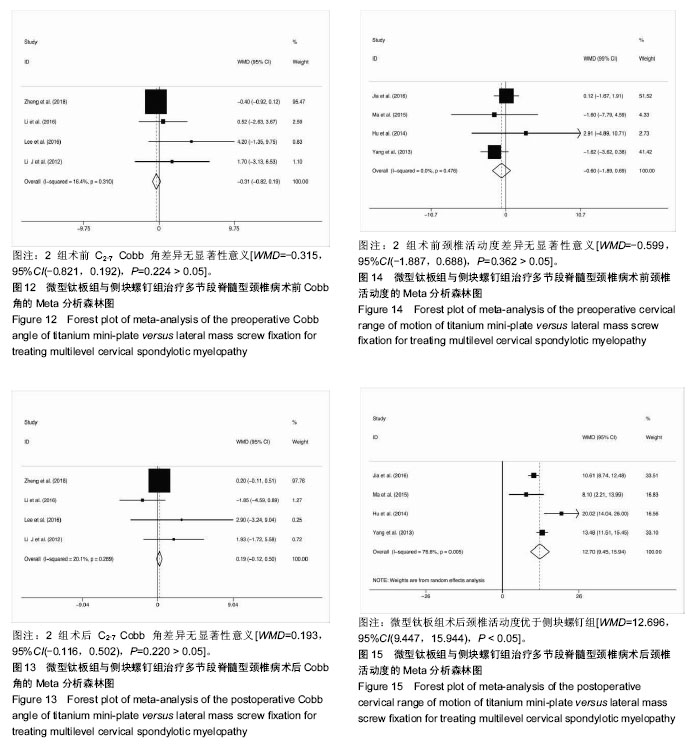
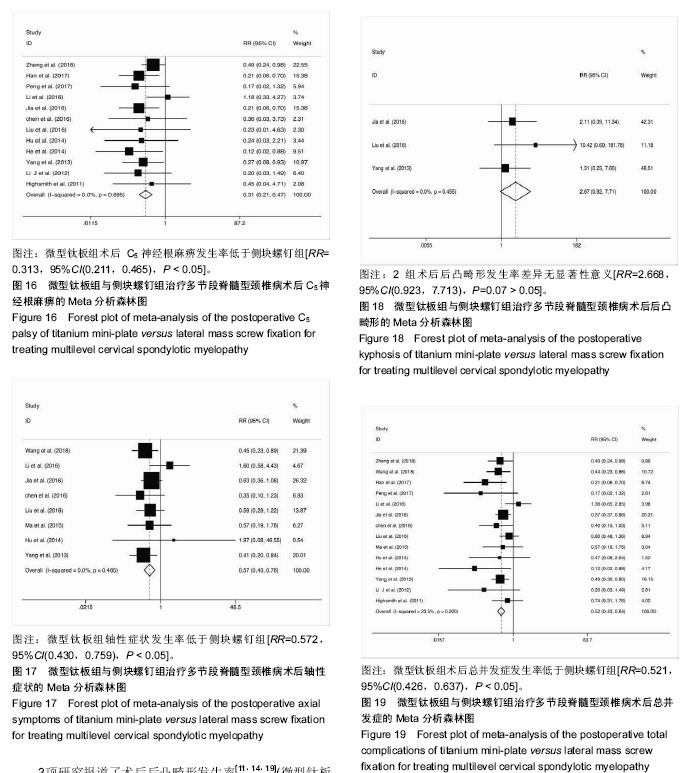
结果与结论:①共纳入16项回顾性队列研究,共1 666例患者;②Meta分析结果显示,微型钛板组在手术时间[WMD=-20.090,95%CI(-27.759,-12.421),P < 0.000 01]及术中出血量[WMD=-42.519,95%CI(-66.368,-18.670),P < 0.000 01]上均优于侧块螺钉组;③2组术式在术后日本骨科协会评分[WMD=0.092,95%CI(-0.177,0.361),P=0.502 > 0.05]、术后目测类比评分[WMD=-0.247,95%CI(-0.667,0.172),P=0.248 > 0.05]、术后颈椎曲度指数[WMD=-0.314,95%CI(-1.070,0.441),P=0.415 > 0.05]、术后Cobb角[WMD=0.193,95%CI(-0.116,0.502),P=0.220 > 0.05]上差异无显著性意义;④微型钛板组术后颈椎功能障碍指数[WMD=-1.361,95%CI(-2.219,-0.503),P =0.002 < 0.05]及轴性症状[RR=0.572,95%CI(0.43,0.759),P < 0.000 01]、C5神经根麻痹[RR=0.313,95%CI(0.211,0.465),P < 0.000 01]、总并发症发生率[RR=0.521,95%CI(0.426,0.637),P < 0.000 01]均低于侧块螺钉组;⑤提示临床上治疗多节段脊髓压迫性脊髓病时,使用微型钛板固定与侧块螺钉固定早期均能取得较好的临床效果,远期效果因随访时间的局限性有待进一步研究;但与侧块螺钉组相比,微型钛板组术后C5神经根麻痹、轴性症状、总并发症发生率更低,手术时间较短,术中失血较少。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2168-2165(汪伟)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: