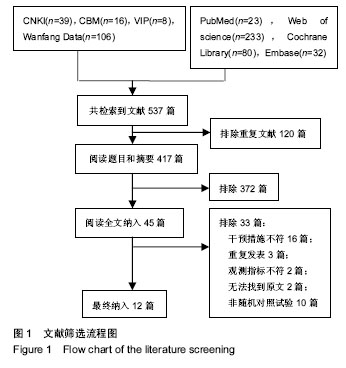
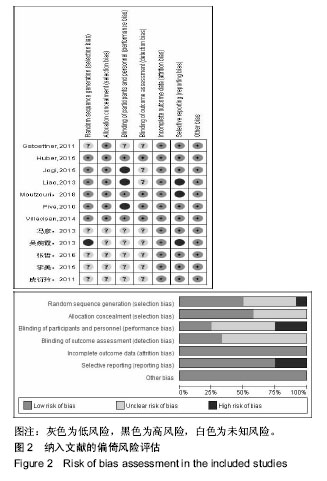
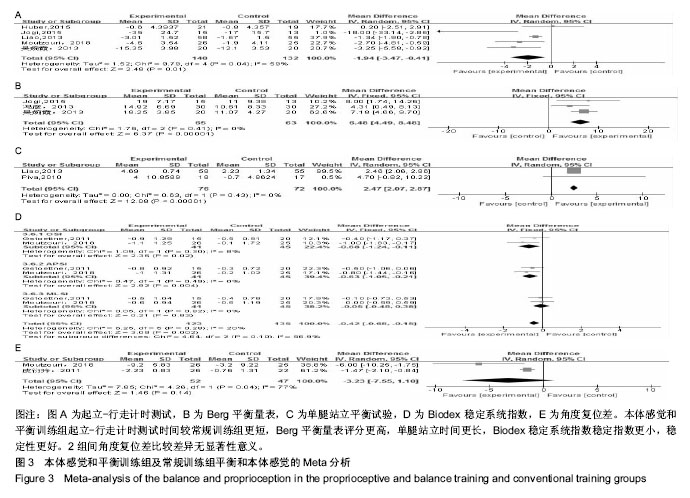
| [1] Wang J, Yang L, Li Q, et al. Construction of an adherence rating scale for exercise therapy for patients with knee osteoarthritis. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2018;19(1): 263.[2] Komang-Agung IS, Sindrawati O, William PS. Do age and co-morbidy, among other factors, affect length of hospital stay following total knee arthroplasty. Malays Orthop J. 2018; 12(2): 25-30.[3] Chan A, Jehu DA, Pang M. Falls after total knee arthroplasty: frequency, circumstances, and associated factors-a prospective cohort study. Phys Ther. 2018;98(9): 767-778.[4] Zemková E, Hamar D. Sport-Specific Assessment of the effectiveness of neuromuscular training in young athletes. Front Phys. 2018; 9:264.[5] Blasco J, Igualcamacho C, Roigcasasús S. In-home versus hospital preoperative balance and proprioceptive training in patients undergoing TKR; rationale, design, and method of a randomized controlled trial. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2017;18(1):518. [6] Bennell K, Dobson F, Hinman R. Measures of physical performance assessments: self-paced walk test (spwt), stair climb test (sct), six-minute walk test (6mwt), chair stand test (cst), timed up & go (tug), sock test, lift and carry test (lct), and car task. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63(S11):S350-S370.[7] Muir SW, Berg K, Chesworth B, et al. Use of the berg balance scale for predicting multiple falls in community-dwelling elderly people: a prospective study. Phys Ther. 2008;88(4): 449-459.[8] Vellas BJ, Wayne SJ, Romero L, et al. One-leg balance is an important predictor of injurious falls in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997;45(6):735-738.[9] Higgins JPT, Green S(editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.1.0[updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.[10] Huber EO, Roos EM, Meichtry A, et al. Effect of preoperative neuromuscular training (NEMEX-TJR) on functional outcome after total knee replacement: an assessor-blinded randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013; 16(1):101.[11] Moutzouri M, Gleeson N, Coutts F, et al. Early self-managed focal sensorimotor rehabilitative training enhances functional mobility and sensorimotor function in patients following total knee replacement: a controlled clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(7):888-898.[12] Liao CD, Liou TH, Huang YY, et al. Effects of balance training on functional outcome after total knee replacement in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2013;27(8):697-709.[13] Jogi P, Overend TJ, Spaulding SJ, et al. Effectiveness of balance exercises in the acute post-operative phase following total hip and knee arthroplasty: A randomized clinical trial. SAGE Open Med. 2015;3: 2102642769.[14] Piva SR, Gil AB, Almeida GJ, et al. A balance exercise program appears to improve function for patients with total knee arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Phys Ther. 2010;90(6): 880-894.[15] Gstoettner M, Raschner C, Dirnberger E, et al. Preoperative proprioceptive training in patients with total knee arthroplasty. Knee.2011; 18(4):265-270.[16] Villadsen A, Overgaard S, Holsgaard-Larsen A, et al. Postoperative effects of neuromuscular exercise prior to hip or knee arthroplasty: a randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1130-1137. [17] 李美,马磊,宋鑫,等. 本体感觉强化训练对全膝关节置换术后膝关节功能的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(3):275-278.[18] 冯彦,唐建华,陈亚丽. 平衡训练对初次全膝关节置换术后患者平衡功能的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2013, 28(11): 1060-1062.[19] 张哲,马辉,康一凡,等. 本体感觉训练在全膝关节置换术后康复中的应用价值[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016, 10(4): 17-20.[20] 皮衍玲,王雪强,杨树芬,等. 全膝关节置换术前本体感觉训练对术后的影响[J]. 中国康复,2011,26(5):350-352.[21] 吴婉霞,徐武华,刘文权,等. 早期本体感觉训练对全膝关节置换术后患者步行能力的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(15): 1508-1512.[22] Lanting BA, Lieberman JR, Callaghan JJ, et al. Ensuring a winner: the abcs of primary total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2015;64:369-379.[23] Westby MD, Brittain A, Backman CL. Expert consensus on best practices for post-acute rehabilitation after total hip and knee arthroplasty: a canada and united states delphi study. Arthritis Care Res. 2014;66(3):411-423.[24] Rakel BA, Zimmerman MB, Geasland K, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for the control of pain during rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: A randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Pain. 2014; 155(12): 2599-2611.[25] Saleh KJ, Lee LW, Gandhi R, et al. Quadriceps strength in relation to total knee arthroplasty outcomes. Instr Course Lect. 2010;59:119.[26] Xu J, Zhang J, Wang XQ, et al. Effect of joint mobilization techniques for primary total knee arthroplasty: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Medicine. 2017;96(49): e8827.[27] Soison A, Riratanapong S, Chouwajaroen N, et al. Prevalence of fall in patients with total knee arthroplasty living in the community. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97(12):1338-1343.[28] Wodowski AJ, Swigler CW, Liu H, et al. Proprioception and knee arthroplasty: a literature review. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016; 47(2):301-309.[29] Pohl T, Brauner T, Wearing S, et al. Effects of sensorimotor training volume on recovery of sensorimotor function in patients following lower limb arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1):1-9.[30] Nam D, Nunley RM, Barrack RL. Patient dissatisfaction following total knee replacement: a growing concern? Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(11-Supple-A):96-100. |
.jpg)


.jpg)