中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (7): 1013-1017.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1119
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
针灸并构音训练脑卒中后构音障碍:文献计量分析及临床治疗结果验证
韩 建
- (沈阳市第一人民医院康复科,辽宁省沈阳市 110041)
Post-stroke dysarthria treated by acupuncture combined with speech-language training: bibliometric analysis and verification of clinical efficacy
Han Jian
- (Department of Rehabilitation, the First People’s Hospital of Shenyang, Shenyang 110041, Liaoning Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
卒中后构音障碍:构音障碍是脑卒中后延髓麻痹导致的主要症状之一,是因神经-肌肉系统器质性损害导致说话动作控制失常而产生的语言障碍,其主要表现为言语模糊不清、说话字句较简单且音调缓慢拖长,临床常伴有吞咽困难、饮水呛咳、痰涎增多、强哭强笑等症状。
卒中后构音障碍的康复治疗:构音障碍目前在治疗上尚缺乏能明显奏效的药物,目前常用的康复治疗方法主要有言语功能训练、呼吸训练、功能电刺激、口面与发音器官的训练、中国传统康复及针灸治疗等。
文题释义:
卒中后构音障碍:构音障碍是脑卒中后延髓麻痹导致的主要症状之一,是因神经-肌肉系统器质性损害导致说话动作控制失常而产生的语言障碍,其主要表现为言语模糊不清、说话字句较简单且音调缓慢拖长,临床常伴有吞咽困难、饮水呛咳、痰涎增多、强哭强笑等症状。
卒中后构音障碍的康复治疗:构音障碍目前在治疗上尚缺乏能明显奏效的药物,目前常用的康复治疗方法主要有言语功能训练、呼吸训练、功能电刺激、口面与发音器官的训练、中国传统康复及针灸治疗等。
.jpg) 文题释义:
卒中后构音障碍:构音障碍是脑卒中后延髓麻痹导致的主要症状之一,是因神经-肌肉系统器质性损害导致说话动作控制失常而产生的语言障碍,其主要表现为言语模糊不清、说话字句较简单且音调缓慢拖长,临床常伴有吞咽困难、饮水呛咳、痰涎增多、强哭强笑等症状。
卒中后构音障碍的康复治疗:构音障碍目前在治疗上尚缺乏能明显奏效的药物,目前常用的康复治疗方法主要有言语功能训练、呼吸训练、功能电刺激、口面与发音器官的训练、中国传统康复及针灸治疗等。
文题释义:
卒中后构音障碍:构音障碍是脑卒中后延髓麻痹导致的主要症状之一,是因神经-肌肉系统器质性损害导致说话动作控制失常而产生的语言障碍,其主要表现为言语模糊不清、说话字句较简单且音调缓慢拖长,临床常伴有吞咽困难、饮水呛咳、痰涎增多、强哭强笑等症状。
卒中后构音障碍的康复治疗:构音障碍目前在治疗上尚缺乏能明显奏效的药物,目前常用的康复治疗方法主要有言语功能训练、呼吸训练、功能电刺激、口面与发音器官的训练、中国传统康复及针灸治疗等。摘要
背景:卒中后构音障碍目前在治疗上尚缺乏能明显奏效的药物,单纯的康复训练效果不是很显著,传统中医针灸治疗在临床上取得了不错的效果。
目的:应用文献计量学方法分析卒中后构音障碍的研究重点及趋势;并观察针灸合并构音训练治疗卒中后构音障碍的效果。
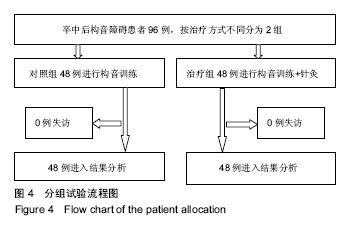
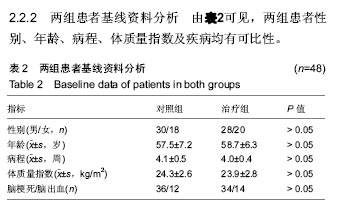
方法:①应用计算机检索中国知网CNKI数据库2004年1月至2018年12月收录的与卒中后构音障碍相关文献,利用知网的分组分层次浏览功能及可视化工具分析文献的发表年度趋势,作者、机构及基金分布情况等;阅读文题和摘要,排除综述文章及护理影像类文献,筛选针灸相关的文章,总结分析针灸治疗卒中后构音障碍的方法;②纳入2013年6月至2015年8月在沈阳市第一人民医院治疗的卒中后构音障碍患者96例,按治疗方式不同分为2组,对照组48例进行构音训练,治疗组48例进行构音训练+针灸(舌针、项针)治疗,每个患者接受2个疗程共40 d治疗,应用改良Frenchay构音障碍评价法评估临床疗效,并记录不良反应。
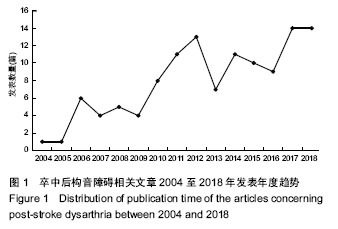
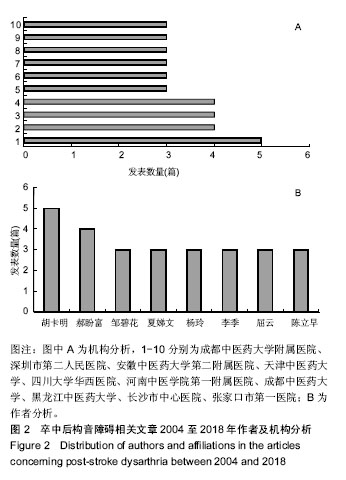
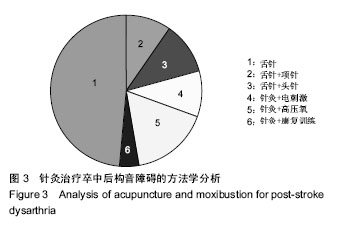
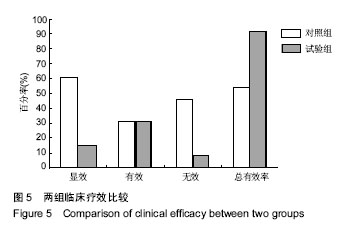
结果与结论:①共检索到卒中后构音障碍相关的中文文献121篇,从2004年发表1篇至2018年14篇,整体呈上升趋势;发表卒中后构音障碍相关文章最多的是成都中医药大学附属医院(5篇),均为胡卡明团队发表,发表文章最多前10个单位及前8位作者中有60%来自中医药大学或中医药大学附属医院;121篇中有72篇包含针灸治疗,其中单纯舌针治疗的7篇,舌针+项针治疗的8篇,舌针+头针治疗的7篇,针灸+电刺激治疗的12篇,针灸+高压氧治疗的3篇,针灸+康复训练的35篇;②在沈阳市第一人民医院治疗的卒中后构音障碍患者96例的临床治疗结果显示:治疗组总有效率92%,明显高于对照组总有效率54%,组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。提示:在中国,目前研究卒中后构音障碍治疗最多的是中医药大学及相应的附属医院,中医方法尤其针灸是治疗卒中后构音障碍的重要手段,最常用的是舌针及项针。临床治疗结果显示,项针、舌针联合构音训练治疗脑卒中后构音障碍疗效满意。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5488-8074(韩建)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
卒中后构音障碍:构音障碍是脑卒中后延髓麻痹导致的主要症状之一,是因神经-肌肉系统器质性损害导致说话动作控制失常而产生的语言障碍,其主要表现为言语模糊不清、说话字句较简单且音调缓慢拖长,临床常伴有吞咽困难、饮水呛咳、痰涎增多、强哭强笑等症状。
卒中后构音障碍的康复治疗:构音障碍目前在治疗上尚缺乏能明显奏效的药物,目前常用的康复治疗方法主要有言语功能训练、呼吸训练、功能电刺激、口面与发音器官的训练、中国传统康复及针灸治疗等。
文题释义:
卒中后构音障碍:构音障碍是脑卒中后延髓麻痹导致的主要症状之一,是因神经-肌肉系统器质性损害导致说话动作控制失常而产生的语言障碍,其主要表现为言语模糊不清、说话字句较简单且音调缓慢拖长,临床常伴有吞咽困难、饮水呛咳、痰涎增多、强哭强笑等症状。
卒中后构音障碍的康复治疗:构音障碍目前在治疗上尚缺乏能明显奏效的药物,目前常用的康复治疗方法主要有言语功能训练、呼吸训练、功能电刺激、口面与发音器官的训练、中国传统康复及针灸治疗等。