中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (33): 5399-5407.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0647
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
脂肪干细胞治疗复杂性肛瘘:作用与机制
刘艳妮1,倪 敏2,张 睿1,黄小波1,周春根1,江 滨2
- 1南京中医药大学,江苏省南京市 210000;2南京市中医院,江苏省南京市 210000
-
修回日期:2018-07-22出版日期:2018-11-28发布日期:2018-11-28 -
通讯作者:江滨,博士,主任医师,南京市中医院,江苏省南京市 210000 -
作者简介:刘艳妮,女,1992年生,陕西省凤翔县人,汉族,在读硕士,主要从事干细胞的基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:南京市卫生局重点资助项目(ZKX17034,ZKX15040)
Treatment of complex anal fistula with adipose-derived stem cells: roles and mechanisms
Liu Yan-ni1, Ni Min2, Zhang Rui1, Huang Xiao-bo1, Zhou Chun-gen1, Jiang Bin2
- 1Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Nanjing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2018-07-22Online:2018-11-28Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Jiang Bin, MD, Chief physician, Nanjing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Liu Yan-ni, Master candidate, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Major Funded Projects of Nanjing Health Department, No. ZKX17034, ZKX15040
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 复杂性肛瘘:是指侵犯外括约肌超过30%的肛瘘。外科手术是治疗复杂性肛瘘的主要方式,但由于复杂性肛瘘(包括克罗恩肛瘘)侵犯括约肌范围广,易出现肛门失禁。传统手术不同程度损伤肛门括约肌,失禁发生率高,微创术式又无法解决已有感染造成的损伤修复困难问题。感染和多次手术导致大量有修复能力的干细胞死亡,内口和创面愈合困难,复发率高。 脂肪干细胞治疗复杂性肛瘘的优势:是从脂肪组织中分离得到的一种具有自我更新及多向分化潜能的间充质干细胞,属于成体干细胞。由于取材容易,体内储备量大,并且具有强大的组织再生、修复、抑制炎症反应等功能,逐渐成为近年来的研究热点之一。国外脂肪干细胞治疗肛瘘临床研究结果显示:无论是自体脂肪干细胞还是异体脂肪干细胞治疗肛瘘,均具有创伤小、无括约肌损伤、疼痛轻、修复快、复发率低、住院时间短等特殊优势,安全性与有效性得到了初步认证。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘艳妮,倪 敏,张 睿,黄小波,周春根,江 滨. 脂肪干细胞治疗复杂性肛瘘:作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(33): 5399-5407.
Liu Yan-ni, Ni Min, Zhang Rui, Huang Xiao-bo, Zhou Chun-gen, Jiang Bin. Treatment of complex anal fistula with adipose-derived stem cells: roles and mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5399-5407.
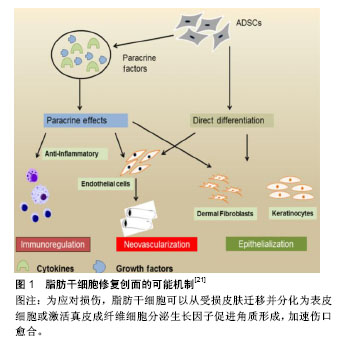
2.2 ASCs移植促进创面愈合的作用及机制 皮肤或组织创面愈合是涉及炎症、上皮形成、新生血管生成、增殖和胶原基质形成的复杂过程[20-21]。ASCs可通过多种机制来发挥这些作用,如诱导分化、调节炎症免疫、促进血管新生、激活成纤维细胞等作用,在创面愈合的各个环节中发挥重要的作用(图1)。Rodriguez等[22]在裸鼠皮肤伤口皮下注射ASCs,通过愈合后的皮肤免疫组织化学和血液灌注分析发现,与自发愈合组相比,ASCs治疗组创面愈合速度更快。Lee等[23]进行的一项初步研究中,采用肌肉内多次注射ASCs治疗严重肢体缺血患者,随访6个月发现 66.7%的患者临床症状、疼痛评分量表和跛行距离较治疗前均显着改善。总结文献发现, ASCs在创面愈合中的作用机制主要有以下几个方面。
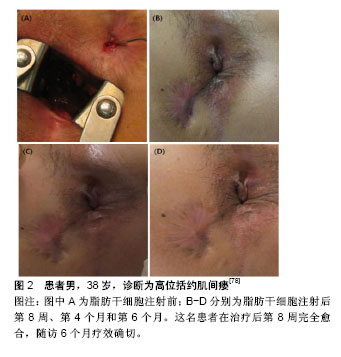
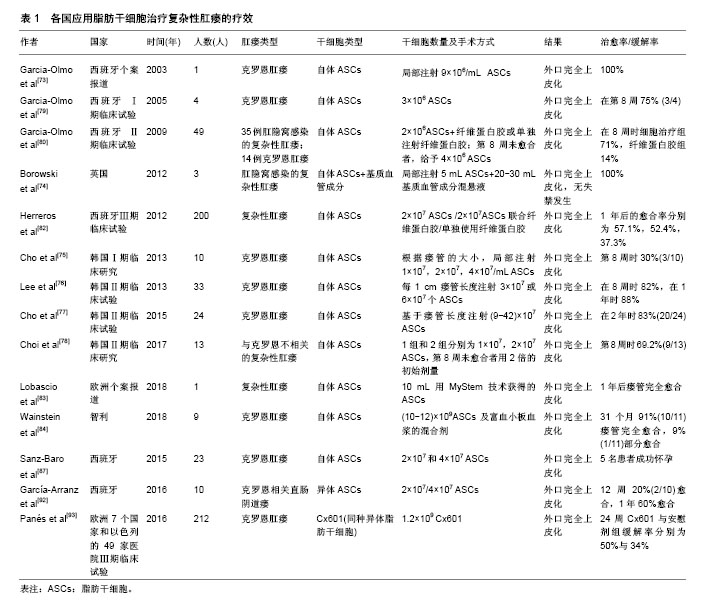
(1)选择ASCs的剂量:由于各实验室对ASCs的培养、扩增技术不同,有1×107,2×107,3×107,4×107,9×106等不同剂量,也有ASCs结合纤维蛋白胶混悬液、ASCs结合基质血管成分混悬液等不同形式。2003年Garcia-Olmo等[73]学者报道了临床上首例使用ASCs治疗炎症性肠病相关的克罗恩肛瘘,该33岁女性患者,患有克罗恩病11年,因肛周脓肿术后形成直肠阴道瘘;使用肿瘤坏死因子α单抗和挂线引流术后症状没有改善,局部注射9×106自体ASCs治疗1周后,手术伤口完全闭合,仅留有轻微的炎症症状,无大便失禁或阴道出血,3个月内疾病未复发。2012年英国克利夫兰的北帝斯医院结直肠外科报道了3例自体ASCs治疗复杂性肛瘘患者,研究人员清理3例患者的瘘管,封闭内口后,将5 mL ASCs和20-30 mL脂肪组织中基质血管成分混悬液采用十字交叉格状注射到瘘管及周围组织内,达到最大的组织密度并填满相邻组织间隙,然后堵塞外口。经过两三年的随访,3例患者都能维持较好的治疗效果[74]。2013年,韩国报道了一项ASCs剂量递增Ⅰ期临床研究[75],10例克罗恩肛瘘患者分为3组,注射前彻底搔刮瘘管,用2-0 vicryl线缝合关闭内口,注射细胞体积与瘘道的大小成正比,将每组所需的ASCs均匀注入瘘管壁和瘘管内口周围黏膜组织中,再将凝血酶和纤维蛋白原的混合溶液灌注到瘘道中。前3例患者(组1)给予1×107/mL ASCs的第一次剂量注射,4周后,该剂量被认为是安全时,另外4例患者(组2)给予2×107/mL ASCs,其中1例患者中途退出。再过4周后,第2次剂量认为是安全的,第3次给最后一组的3例患者给予4×107/mL ASCs。注射8周后随访,第2组中2例患者显示完全愈合,第3组中1例患者显示完全愈合,其他患者均部分愈合,引流量较术前减少。对第8周显示完全愈合的3例患者又追踪随访6个月,以监测ASCs治疗的持续有效性和安全性。所有患者对治疗都表现出良好的耐受性,没有发生3级或4级严重不良事件,且没有发生与研究药物有关的不良事件。在跟踪治疗8个月后,仍保持疗效并无复发现象。因此,该研究显示了ASCs治疗克罗恩肛瘘的耐受性、安全性和潜在疗效,并为进一步的临床研究提供了基础支持。Lee等[76]进行了一项评估ASCs与纤维蛋白胶结合使用的Ⅱ期临床试验。首先打开瘘管,用2-0 vicryl缝合瘘管内口,ASCs注射在内口处黏膜下层及瘘管周围。瘘管用ASCs和纤维蛋白胶混合剂灌注。注射前用探针测量瘘管的直径和长度来确定瘘管的大小。当瘘管直径大约不超过1 cm时,每厘米瘘管长度注射3×107/mL ASCs,当瘘管直径在1.0-2.0 cm之间时,重复注射2次ASCs。注射8周后瘘管未愈合者,进行第2次注射。第2次注射ASCs的剂量为第1次注射所用细胞数量的1.5倍。注射第4,6,8周后拍摄病变部位,并与注射后第1天照片进行比较。根据修改后的方案分析,82%(27/33)的患者在第8周时表现出完全愈合,而在意向治疗分析中为64.3% (27/42)。在27例完全愈合患者中,26例完成1年随访,其中23例(88%)完全闭合。另一项研究对其长期结果进行了分析,在24个月时,经过修改后的方案分析中80.6% (21/26)患者完全愈合,在改进的意向性治疗分析中为75%(27/36)[77]。没有与ASCs治疗相关的不良事件发生。Choi等[78]比较1×107/mL ASCs与2×107/mL ASCs 2种不同剂量ASCs治疗与克罗恩不相关的复杂性肛瘘的临床安全性与有效性,将患者分为两组,组1使用1×107/mL ASCs,组2使用2×107/mL ASCs。注射后第8周评估疗效,第8周瘘管完全闭合者再随访6个月。未愈合者接受2倍的初始注射剂量。患者在第8周,第4个月和第6个月时分别拍照片记录肛周局部变化(图2)。注射ASCs的15例患者中13例完成了这项研究。在第8周时69.2%(9/13)患者瘘管完全闭合。第1组中5例患者中有3例,第2组中8例患者中有6例瘘管完全闭合,发现两组之间无明显差异。瘘管完全闭合的9例患者中有6例参与了随访,其中5例患者(83.3%)在第6个月时仍维持疗效。未观察到3级或4级不良事件。因此,对于传统手术无法治愈的复杂性肛瘘,ASCs移植可能是一个很好的选择方式。ASCs治疗肛瘘具有良好耐受性和安全性,但各实验室使用剂量不统一,需要大样本的临床试验寻找适合患者疾病特点的细胞剂量。
(3)ASCs的细胞来源:ASCs根据来源不同可分为自体、异体及同种异体。例如,2015年,西班牙进行了一项ASCs治疗克罗恩肛瘘相关的妇女妊娠临床回顾性观察研究[87]。23名肛瘘妇女每间隔三四个月依次接受2×107和4×107 2种剂量的自体ASCs局部灌注治疗。6名妇女在干细胞治疗缓解期成功怀孕,并且5名妇女足月妊娠,1名发生2次妊娠早期流产,流产率符合一般人群发生率(20%)[88],且明显低于文献报道与克罗恩疾病相关的流产率(40%)[89-91]。因此,ASCs治疗似乎并没有增加流产率,其认为接受ASCs治疗可以帮助克罗恩肛瘘患者跨越妊娠的心理障碍,减轻肠道炎症反应,增加怀孕成功率。最近一项Ⅰ-Ⅱ期临床试验研究异体ASCs治疗克罗恩相关直肠阴道瘘的安全性和可行性[92]。异体ASCs治疗10例直肠阴道瘘患者,如果外科医生认为有必要,则增加阴道或直肠推移皮瓣。治疗方案包括在阴道壁的黏膜下层和瘘道内注射2×107 ASCs。治疗12周后评估愈合情况,愈合定义为阴道和直肠两侧的再上皮化以及阴道没有引流物。治疗12周时2例患者愈合,8例患者接受4×107 ASCs注射。血液中细胞因子谱和免疫毒性检测,没有发现严重不良事件。随访1年,60%的患者达到完全愈合。这表明ASCs可作为不同类型的克罗恩病变的替代疗法之一。2016年,武田制药和TiGenix公司联合在欧洲7个国家和以色列的49家医院进行的一项随机、双盲、平行、安慰剂对照的Ⅲ期临床试验[93],总共212例克罗恩肛瘘患者纳入该试验。随机分为2组,治疗组107例采用1.2×109Cx601(同种异体脂肪干细胞),安慰剂组105例采用24 mL生理盐水。治疗24周后,Cx601治疗组与安慰剂组疾病缓解率分别为50%与34%(P=0.024);治疗相关的不良事件发生率分别为17%与29%;出现肛周脓肿分别为6例与9例,出现肛门痛分别为5例与9例。52周后,Cx601治疗组与安慰剂组缓解率分别为56.3%与38.6%(P=0.010),复发率分别为55.9%与75%(P=0.052)。在1年后随访发现CX601组与安慰剂组相比更加安全和有效。这一结果表明对传统治疗或生物治疗无效的克罗恩病肛瘘,同种异体脂肪干细胞移植是一种安全有效的治疗方法。由上可见,不同国家,不同临床中心采用了不同的细胞来源、剂量及手术方式(表1)。
应用ASCs治疗复杂性肛瘘,是一项具有巨大发展潜力的医疗技术,可为一系列难治性结直肠外科疾病提供新的治疗方向,引起了各国临床医生、科研工作者的关注。国外文献研究也证实了ASCs治疗复杂性肛瘘疾病的安全性和有效性。但目前此研究仍处于初级阶段,可能存在一些问题需要进一步改进:①虽然ASCs来源丰富、取材简便,但干细胞不同于普通药物治疗,不同研究单位其培养方法、移植剂量和质量检测都有差异,因此确定ASCs最佳来源,建立ASCs标准化的培养体系,治疗流程非常重要;②临床研究大多是单中心、小样本回顾性病例报告,观察时间较短,样本量较少,缺乏有力的对照数据,未来需要开展多中心、大样本、前瞻性的临床随机对照研究;③目前虽然没有报道临床干细胞治疗增加致瘤风险,但建议在临床治疗前,需对ASCs进行体内外的致瘤分析。开展自体、异体及同种异体ASCs之间的实验研究及临床对照研究,明确各自的优缺点及适应证;④各临床中心的治疗评估体系不尽相同,可以采用统一的临床瘘管愈合评估标准以及实验室、影像学评估标准,增强结果的可信度;⑤自体ASCs移植需要进行2次手术,一次用于提取脂肪组织,另一次用于注射ASCs,总的治疗费用也高于一般手术,也给患者造成了一定经济压力。因此,加强对干细胞技术和人员的培养,降低干细胞提取过程的中间投资,减少治疗成本,从而更好的应用于临床。
| [1] Minteer DM, Marra KG, Rubin JP. Adipose stem cells: biology, safety, regulation, and regenerative potential. Clin Plast Surg. 2015;42(2): 169-179.[2] Bajek A, Gurtowska N, Olkowska J, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool in Cell-Based Therapies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64(6):443-454.[3] Ratajczak MZ. Stem cells and mechanisms regulating their trafficking - a new and challenging area of investigation in modern psychiatry. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018;80(Pt A):1-2.[4] Bourin P, Bunnell BA, Casteilla L, et al. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy. 2013; 15(6):641-648.[5] Münch DP. Breast augmentation with autologous fat - experience of 96 procedures with the BEAULI-technique. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2013;45(2):80-92.[6] Strioga M, Viswanathan S, Darinskas A, et al. Same or not the same? Comparison of adipose tissue-derived versus bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem and stromal cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(14): 2724-2752.[7] Gir P, Oni G, Brown SA, et al. Human adipose stem cells: current clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(6):1277-1290.[8] Cadeddu F, Salis F, Lisi G, et al. Complex anal fistula remains a challenge for colorectal surgeon. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015;30(5): 595-603.[9] Limura E, Giordano P. Modern management of anal fistula. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(1):12-20.[10] Rasmussen JG, Frøbert O, Holst-Hansen C, et al. Comparison of human adipose-derived stem cells and bone marrow-derived stem cells in a myocardial infarction model. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(2): 195-206.[11] Mimeault M, Hauke R, Batra SK. Stem cells: a revolution in therapeutics-recent advances in stem cell biology and their therapeutic applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(3):252-264.[12] Zhou Z, Chen Y, Zhang H, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal stromal cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(4):434-448.[13] Yoshimura K, Sato K, Aoi N, et al. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for cosmetic breast augmentation: supportive use of adipose-derived stem/stromal cells. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2008;32(1):48-55.[14] Bhattacharya I, Ghayor C, Weber FE. The Use of Adipose Tissue-Derived Progenitors in Bone Tissue Engineering - a Review. Transfus Med Hemother. 2016;43(5):336-343.[15] Jo CH, Lee YG, Shin WH, et al. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells. 2014;32(5): 1254-1266.[16] Bura A, Planat-Benard V, Bourin P, et al. Phase I trial: the use of autologous cultured adipose-derived stroma/stem cells to treat patients with non-revascularizable critical limb ischemia. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(2):245-257.[17] Rajashekhar G, Ramadan A, Abburi C, et al. Regenerative therapeutic potential of adipose stromal cells in early stage diabetic retinopathy. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e84671.[18] Bielefeld KA, Amini-Nik S, Alman BA. Cutaneous wound healing: recruiting developmental pathways for regeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(12):2059-2081.[19] Gould L, Abadir P, Brem H, et al. Chronic wound repair and healing in older adults: current status and future research. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(3):427-438.[20] Juniantito V, Izawa T, Yamamoto E, et al. Heterogeneity of macrophage populations and expression of galectin-3 in cutaneous wound healing in rats. J Comp Pathol. 2011;145(4):378-389.[21] Hassan WU, Greiser U, Wang W. Role of adipose-derived stem cells in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(3):313-325.[22] Rodriguez J, Boucher F, Lequeux C, et al. Intradermal injection of human adipose-derived stem cells accelerates skin wound healing in nude mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:241.[23] Lee HC, An SG, Lee HW, et al. Safety and effect of adipose tissue-derived stem cell implantation in patients with critical limb ischemia: a pilot study. Circ J. 2012;76(7):1750-1760.[24] Desai VD, Hsia HC, Schwarzbauer JE. Reversible modulation of myofibroblast differentiation in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e86865.[25] 黄宏,朱方强,孙宏振,等.脂肪来源干细胞体外成骨诱导和成脂诱导分化[J].第三军医大学学报,2008,30(13):1219-1222.[26] Park A, Hogan MV, Kesturu GS, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells treated with growth differentiation factor-5 express tendon-specific markers. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(9):2941-2951.[27] Dimarino AM, Caplan AI, Bonfield TL. Mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair. Front Immunol. 2013;4:201.[28] Fischer LJ, McIlhenny S, Tulenko T, et al. Endothelial differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells: effects of endothelial cell growth supplement and shear force. J Surg Res. 2009;152(1):157-166.[29] Steinberg JP, Hong SJ, Geringer MR, et al. Equivalent effects of topically-delivered adipose-derived stem cells and dermal fibroblasts in the ischemic rabbit ear model for chronic wounds. Aesthet Surg J. 2012;32(4):504-519.[30] García-Gómez I, Elvira G, Zapata AG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: biological properties and clinical applications. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(10):1453-1468.[31] Raffaghello L, Bianchi G, Bertolotto M, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neutrophil apoptosis: a model for neutrophil preservation in the bone marrow niche. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1): 151-162.[32] Yoo KH, Jang IK, Lee MW, et al. Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult human tissues. Cell Immunol. 2009;259(2):150-156.[33] 卫传元,顾建英.脂肪来源干细胞在慢性创面愈合中作用的研究进展[J].中国临床医学,2017,24(4):650-655.[34] Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Camussi G. The secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells: Role of extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation. Immunol Lett. 2015;168(2):154-158.[35] Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729.[36] Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(2):141-150.[37] Prigione I, Benvenuto F, Bocca P, et al. Reciprocal interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and gammadelta T cells or invariant natural killer T cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(3):693-702.[38] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372. [39] Groh ME, Maitra B, Szekely E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells require monocyte-mediated activation to suppress alloreactive T cells. Exp Hematol. 2005;33(8):928-934.[40] Batten P, Sarathchandra P, Antoniw JW, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells induce T cell anergy and downregulate T cell allo-responses via the TH2 pathway: relevance to tissue engineering human heart valves. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(8):2263-2273.[41] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815-1822.[42] Sato K, Ozaki K, Oh I, et al. Nitric oxide plays a critical role in suppression of T-cell proliferation by mesenchymal stem cells. Blood. 2007;109(1):228-234.[43] Li GY, Zhou F, Gong YQ, et al. Activation of VEGF and ERK1/2 and improvement of urethral function by adipose-derived stem cells in a rat stress urinary incontinence model. Urology. 2012;80(4):953.e1-8.[44] Cai A, Qiu R, Li L, et al. Atorvastatin treatment of rats with ischemia-reperfusion injury improves adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell migration and survival via the SDF-1α/CXCR-4 axis. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e79100.[45] Marino G, Moraci M, Armenia E, et al. Therapy with autologous adipose-derived regenerative cells for the care of chronic ulcer of lower limbs in patients with peripheral arterial disease. J Surg Res. 2013;185(1):36-44.[46] Kim EK, Li G, Lee TJ, et al. The effect of human adipose-derived stem cells on healing of ischemic wounds in a diabetic nude mouse model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128(2):387-394.[47] 汪建平.中华结直肠肛门外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2014: 776.[48] Parks AG. Pathogenesis and treatment of fistuila-in-ano. Br Med J. 1961;1(5224):463-469.[49] 王猛,王贵玉.2016年版美国结直肠外科医师学会《肛周脓肿、肛瘘和直肠阴道瘘治疗指南》解读[J].中国实用外科杂志, 2017,37(2):162-165.[50] Vogel JD, Johnson EK, Morris AM, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Anorectal Abscess, Fistula-in-Ano, and Rectovaginal Fistula. Dis Colon Rectum. 2016;59(12):1117-1133.[51] Bubbers EJ, Cologne KG. Management of Complex Anal Fistulas. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2016;29(1):43-49.[52] 蒋晓雪,郭修田.高位复杂性肛瘘手术治疗进展[J].甘肃中医药大学学报, 2017,34(3):90-93.[53] Marzo M, Felice C, Pugliese D, et al. Management of perianal fistulas in Crohn's disease: an up-to-date review[C]//APS Meeting. APS Meeting Abstracts, 2015:147-150. [54] 竺平,谷云飞,杨柏霖.复杂性肛瘘手术治疗的现存问题及对策[J].中西医结合学报,2009,7(12):1101-1103.[55] 吕长遥,伍静,何洪波.肛瘘微创手术治疗进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2018,27(1):106-111.[56] Dudukgian H, Abcarian H. Why do we have so much trouble treating anal fistula. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(28):3292-3296.[57] Göttgens KW, Janssen PT, Heemskerk J, et al. Long-term outcome of low perianal fistulas treated by fistulotomy: a multicenter study. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015;30(2):213-219.[58] Ritchie RD, Sackier JM, Hodde JP. Incontinence rates after cutting seton treatment for anal fistula. Colorectal Dis. 2009;11(6):564-571.[59] Adamina M, Hoch JS, Burnstein MJ. To plug or not to plug: a cost-effectiveness analysis for complex anal fistula. Surgery. 2010; 147(1):72-78.[60] El-Gazzaz G, Zutshi M, Hull T. A retrospective review of chronic anal fistulae treated by anal fistulae plug. Colorectal Dis. 2010;12(5): 442-447.[61] Kleif J, Hagen K, Wille-Jørgensen P. Acceptable results using plug for the treatment of complex anal fistulas. Dan Med Bull. 2011;58(3): A4254.[62] Safar B, Jobanputra S, Sands D, et al. Anal fistula plug: initial experience and outcomes. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52(2):248-252.[63] Stamos MJ, Snyder M, Robb BW, et al. Prospective multicenter study of a synthetic bioabsorbable anal fistula plug to treat cryptoglandular transsphincteric anal fistulas. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015;58(3):344-351.[64] Lindsey I, Smilgin-Humphreys MM, Cunningham C, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of fibrin glue vs. conventional treatment for anal fistula. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002;45(12):1608-1615.[65] Altomare DF, Greco VJ, Tricomi N, et al. Seton or glue for trans-sphincteric anal fistulae: a prospective randomized crossover clinical trial. Colorectal Dis. 2011;13(1):82-86.[66] Mitalas LE, Dwarkasing RS, Verhaaren R, et al. Is the outcome of transanal advancement flap repair affected by the complexity of high transsphincteric fistulas. Dis Colon Rectum. 2011;54(7):857-862.[67] Madbouly KM, El Shazly W, Abbas KS, et al. Ligation of intersphincteric fistula tract versus mucosal advancement flap in patients with high transsphincteric fistula-in-ano: a prospective randomized trial. Dis Colon Rectum. 2014;57(10):1202-1208.[68] Soltani A, Kaiser AM. Endorectal advancement flap for cryptoglandular or Crohn's fistula-in-ano. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010;53(4):486-495.[69] Goos M, Manegold P, Grüneberger M, et al. Long-term results after endoanal advancement flap repair for fistulas-in-ano. How important is the aetiology. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015;30(3):413-419.[70] Schwandner O. Obesity is a negative predictor of success after surgery for complex anal fistula. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011;11:61.[71] Uribe N, Balciscueta Z, Mínguez M, et al. "Core out" or "curettage" in rectal advancement flap for cryptoglandular anal fistula. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015;30(5):613-619.[72] Malakorn S, Sammour T, Khomvilai S, et al. Ligation of Intersphincteric Fistula Tract for Fistula in Ano: Lessons Learned From a Decade of Experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 2017;60(10):1065-1070.[73] García-Olmo D, García-Arranz M, García LG, et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for treatment of rectovaginal fistula in perianal Crohn's disease: a new cell-based therapy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2003; 18(5):451-454. [74] Borowski DW, Gill TS, Agarwal AK, et al. Autologous adipose-tissue derived regenerative cells for the treatment of complex cryptoglandular fistula-in-ano: a report of three cases. BMJ Case Rep. 2012;2012.[75] Cho YB, Lee WY, Park KJ, et al. Autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells for the treatment of Crohn's fistula: a phase I clinical study. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(2):279-285.[76] Lee WY, Park KJ, Cho YB, et al. Autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells treatment demonstrated favorable and sustainable therapeutic effect for Crohn's fistula. Stem Cells. 2013;31(11): 2575-2581.[77] Cho YB, Park KJ, Yoon SN, et al. Long-term results of adipose-derived stem cell therapy for the treatment of Crohn's fistula. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(5):532-537.[78] Choi S, Ryoo SB, Park KJ, et al. Autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells for the treatment of complex perianal fistulas not associated with Crohn's disease: a phase II clinical trial for safety and efficacy. Tech Coloproctol. 2017;21(5):345-353.[79] García-Olmo D, García-Arranz M, Herreros D, et al. A phase I clinical trial of the treatment of Crohn's fistula by adipose mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005;48(7):1416-1423.[80] Garcia-Olmo D, Herreros D, Pascual I, et al. Expanded adipose-derived stem cells for the treatment of complex perianal fistula: a phase II clinical trial. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52(1):79-86.[81] Christman KL, Vardanian AJ, Fang Q, et al. Injectable fibrin scaffold improves cell transplant survival, reduces infarct expansion, and induces neovasculature formation in ischemic myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(3):654-660.[82] Herreros MD, Garcia-Arranz M, Guadalajara H, et al. Autologous expanded adipose-derived stem cells for the treatment of complex cryptoglandular perianal fistulas: a phase III randomized clinical trial (FATT 1: fistula Advanced Therapy Trial 1) and long-term evaluation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2012;55(7):762-772.[83] Lobascio P, Balducci G, Minafra M, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells (MYSTEM® EVO Technology) as a treatment for complex transsphincteric anal fistula. Tech Coloproctol. 2018;22(5):373-377.[84] Wainstein C, Quera R, Fluxá D, et al. Stem Cell Therapy in Refractory Perineal Crohn's Disease: Long-term Follow-up. Colorectal Dis. 2018 Jan 6. [Epub ahead of print][85] Solomon MJ, McLeod RS, O’Connor BI, et al. Combination of ciprofloxacin and metronidazole in severe perianal Crohn’s disease. Can J Gastroenterol. 1993;7:571-573.[86] Mizrahi N, Wexner SD, Zmora O, et al. Endorectal advancement flap: are there predictors of failure. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002;45(12): 1616-1621.[87] Sanz-Baro R, García-Arranz M, Guadalajara H, et al. First-in-Human Case Study: Pregnancy in Women With Crohn's Perianal Fistula Treated With Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A Safety Study. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(6):598-602.[88] Mountifield R, Bampton P, Prosser R, et al. Fear and fertility in inflammatory bowel disease: a mismatch of perception and reality affects family planning decisions. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15(5): 720-725.[89] Mañosa M, Navarro-Llavat M, Marín L, et al. Fecundity, pregnancy outcomes, and breastfeeding in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a large cohort survey. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013;48(4): 427-432.[90] Hatch Q, Champagne BJ, Maykel JA, et al. Crohn's disease and pregnancy: the impact of perianal disease on delivery methods and complications. Dis Colon Rectum. 2014;57(2):174-178.[91] Cheng AG, Oxford EC, Sauk J, et al. Impact of mode of delivery on outcomes in patients with perianal Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20(8):1391-1398.[92] García-Arranz M, Herreros MD, González-Gómez C, et al. Treatment of Crohn's-Related Rectovaginal Fistula With Allogeneic Expanded-Adipose Derived Stem Cells: A Phase I-IIa Clinical Trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(11):1441-1446.[93] Panés J, García-Olmo D, Van Assche G, et al. Expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in Crohn's disease: a phase 3 randomised, double-blind controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10051):1281-1290.[94] 李森娟,沈桂鑫,邱敏,等.干细胞移植治疗复杂性肛瘘疗效的Meta分析[J].浙江医学,2018,40(3): 262-265.[95] Lightner AL, Wang Z, Zubair AC, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injections for the Treatment of Perianal Crohn's Disease: Progress Made and Future Directions. Dis Colon Rectum. 2018;61(5):629-640. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | 史洋洋, 秦英飞, 吴福玲, 何 潇, 张雪静. 胎盘间充质干细胞预处理预防小鼠毛细支气管炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | 梁学奇, 郭黎姣, 陈贺捷, 武 杰, 孙雅琪, 邢稚坤, 邹海亮, 陈雪玲, 吴向未. 泡状棘球绦虫原头蚴抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向成纤维细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | 樊全宝, 罗惠娜, 王丙云, 陈胜锋, 崔连旭, 江文康, 赵明明, 王静静, 罗冬章, 陈志胜, 白银山, 刘璨颖, 张 晖. 低氧培养犬脂肪间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | 耿 瑶, 尹志良, 李兴平, 肖东琴, 侯伟光. hsa-miRNA-223-3p调控人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | 伦志刚, 金 晶, 王添艳, 李爱民. 过氧化物还原酶6干预骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及体外向神经谱系诱导分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | 朱雪芬, 黄 成, 丁 健, 戴永平, 刘元兵, 乐礼祥, 王亮亮, 杨建东. 胶质细胞神经营养因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向功能性神经元分化的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | 段丽芸, 曹晓沧. 人胎盘间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡调节肠炎小鼠肠黏膜胶原的沉积[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | 裴丽丽, 孙贵才, 王 弟. 丹酚酸B抑制骨髓间充质干细胞氧化损伤及促进分化为心肌样细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | 邹 刚, 徐 志, 刘子铭, 李豫皖, 杨继滨, 金 瑛, 张 骏, 葛 振, 刘 毅. 人脱细胞羊膜支架促进Scleraxis修饰人羊膜间充质干细胞体外成韧带分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1037-1044. |
| [14] | 管 倩, 栾 佐, 叶 豆, 杨印祥, 汪兆艳, 王 倩, 姚瑞芹. 人少突胶质前体细胞传代过程中形态学的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | 王正东, 黄 娜, 陈婧娴, 郑作兵, 胡鑫宇, 李 梅, 苏 晓, 苏学森, 颜 南. 丁酸钠抑制氟中毒可诱导小胶质细胞活化及炎症因子表达增多[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
.jpg)
随着干细胞移植和组织工程技术的发展,脂肪干细胞移植疗法由最初的整形重建领域已经逐步应用于临床实践中的各个方向。复杂性肛瘘由于侵犯括约肌范围广,易出现肛门失禁。目前各种肛瘘术式均未达到理想的治疗效果。国外脂肪干细胞治疗肛瘘临床研究结果显示:无论是自体脂肪干细胞还是异体脂肪干细胞治疗肛瘘,均具有创伤小、无括约肌损伤、疼痛轻、修复快、复发率低、住院时间短等特殊优势,安全性与有效性得到了初步认证,其优势是目前括约肌切开术和保留括约肌手术等治疗方法所不具备的。目前国内尚无脂肪干细胞治疗复杂性肛瘘的相关研究报道。对国外文献中脂肪干细胞在复杂性肛瘘治疗中的临床应用现状进行归纳分析,有利于国内外同行学习,推动干细胞在组织工程中的发展。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||