中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (28): 4481-4486.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0367
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
脑死亡模型兔炎症因子表达和肺损伤性变化
李 玲1,徐 千1,魏婉慧1,赵慧佳1,时玉颖1,刘 璐1,王彦峰1,叶啟发1,2
- 1武汉大学中南医院,武汉大学肝胆疾病研究院,武汉大学移植医学中心,移植医学技术湖北省重点实验室,湖北省武汉市 430071;2中南大学湘雅三医院,卫生部移植医学工程技术研究中心,湖南省长沙市 410013
Lung injury and inflammatory responses in a rabbit model of brain death
Li Ling1, Xu Qian1, Wei Wan-hui1, Zhao Hui-jia1, Shi Yu-ying1, Liu Lu1, Wang Yan-feng1, Ye Qi-fa1, 2
- 1Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Institute for Hepatobiliary Diseases of Wuhan University, Transplant Center of Wuhan University, Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Technology on Transplantation, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China; 2the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Research Center of National Health Ministry on Transplantation Medicine Engineering and Technology, Changsha 410013, Hunan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
脑死亡状态:大脑整体功能不可逆性丧失的病理状态,其判定标准为:①明确为颅内加压引起的深昏迷;②瞳孔对光反射、角膜反射消失;③自主呼吸停止;④脑电图呈扁平波。
缓慢间断颅内加压法:通过动物颅骨开孔,颅内放置球囊导管,缓慢间断输注生理盐水,逐渐升高颅内压,使脑灌注压下降,脑血流量随之急剧减少,从而建立脑死亡模型。
文题释义:
脑死亡状态:大脑整体功能不可逆性丧失的病理状态,其判定标准为:①明确为颅内加压引起的深昏迷;②瞳孔对光反射、角膜反射消失;③自主呼吸停止;④脑电图呈扁平波。
缓慢间断颅内加压法:通过动物颅骨开孔,颅内放置球囊导管,缓慢间断输注生理盐水,逐渐升高颅内压,使脑灌注压下降,脑血流量随之急剧减少,从而建立脑死亡模型。
.jpg) 文题释义:
脑死亡状态:大脑整体功能不可逆性丧失的病理状态,其判定标准为:①明确为颅内加压引起的深昏迷;②瞳孔对光反射、角膜反射消失;③自主呼吸停止;④脑电图呈扁平波。
缓慢间断颅内加压法:通过动物颅骨开孔,颅内放置球囊导管,缓慢间断输注生理盐水,逐渐升高颅内压,使脑灌注压下降,脑血流量随之急剧减少,从而建立脑死亡模型。
文题释义:
脑死亡状态:大脑整体功能不可逆性丧失的病理状态,其判定标准为:①明确为颅内加压引起的深昏迷;②瞳孔对光反射、角膜反射消失;③自主呼吸停止;④脑电图呈扁平波。
缓慢间断颅内加压法:通过动物颅骨开孔,颅内放置球囊导管,缓慢间断输注生理盐水,逐渐升高颅内压,使脑灌注压下降,脑血流量随之急剧减少,从而建立脑死亡模型。摘要
背景:脑死亡供体器官质量是影响移植成功率的关键。对脑死亡诱发器官损伤的机制和保护方面的研究,将为临床上供体器官的合理利用提供实验依据。
目的:观察兔脑死亡后不同时间点肺脏形态学和炎症因子的变化,探究脑死亡状态致肺损伤过程中的作用机制。
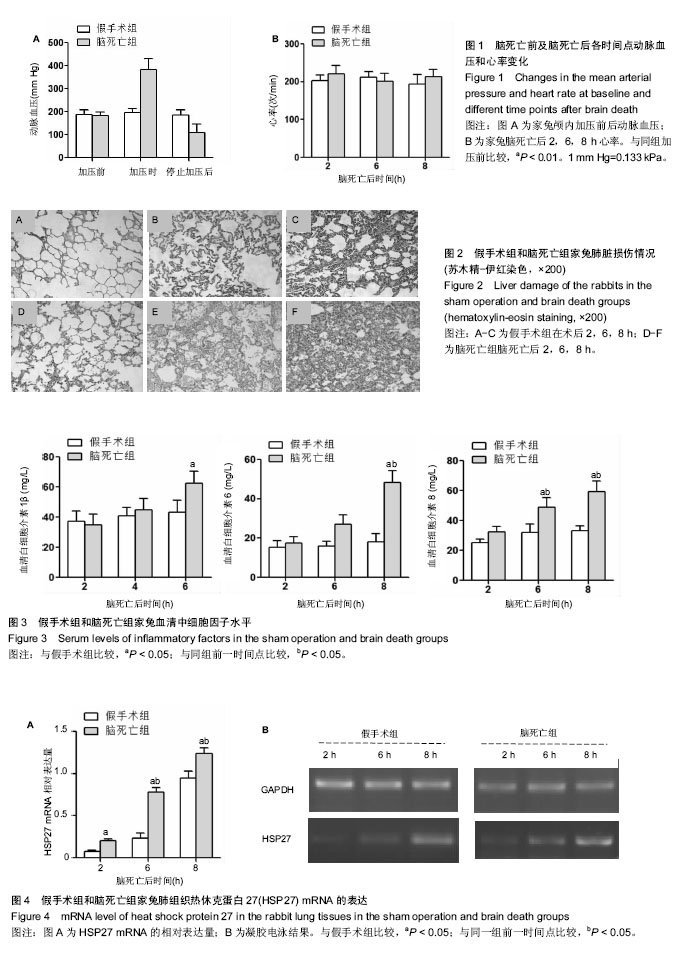
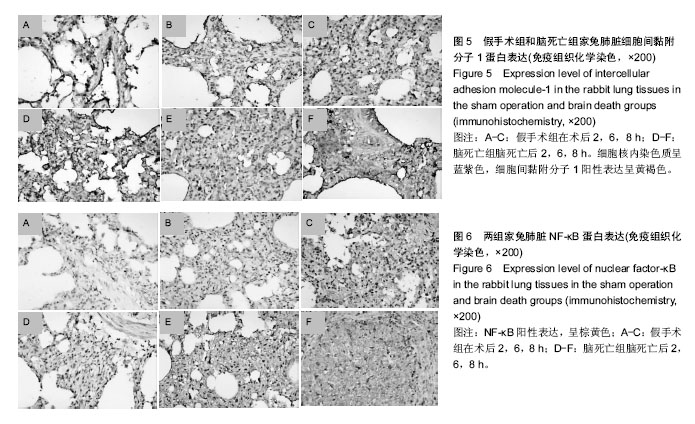
方法:40只健康家兔,随机分成2组,假手术组(n=20):行气管、股动脉插管及颅骨钻孔术;脑死亡组(n=20):建立兔缓慢间断颅内加压脑死亡模型。各组在术后2,6及8 h记录动脉血压和心率变化,苏木精-伊红染色观察肺组织病理改变,RT-PCR检测各组肺脏热休克蛋白27的mRNA表达,免疫组织化学法检测肺组织核因子κB和细胞间黏附分子1的表达,并用ELISA法检测白细胞介素1β及白细胞介素6,8的水平。
结果与结论:①脑死亡后2,6,8 h家兔动脉血压、心率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②血清中白细胞介素1β及白细胞介素6、8的水平随着脑死亡时间延长有上升趋势(P < 0.05);③脑死亡组各时间点热休克蛋白27 mRNA水平较假手术组明显升高(P < 0.05);④光镜下可见脑死亡后2 h肺泡腔完整,6 h时肺泡间隔增宽并有水肿,炎症细胞浸润增多,8 h损伤最为严重,炎症细胞几乎浸润整个肺脏组织,该形态学变化与脑死亡组炎症相关因子细胞间黏附分子1和核因子κB表达逐渐升高的趋势一致;⑤结果表明,脑死亡状态下肺脏出现损伤性变化且呈进行性加重,该表现与炎症因子的释放有关;脑死亡状态维持8 h以上,肺脏的形态和功能将发生明显改变。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-0396-0579(李玲)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
脑死亡状态:大脑整体功能不可逆性丧失的病理状态,其判定标准为:①明确为颅内加压引起的深昏迷;②瞳孔对光反射、角膜反射消失;③自主呼吸停止;④脑电图呈扁平波。
缓慢间断颅内加压法:通过动物颅骨开孔,颅内放置球囊导管,缓慢间断输注生理盐水,逐渐升高颅内压,使脑灌注压下降,脑血流量随之急剧减少,从而建立脑死亡模型。
文题释义:
脑死亡状态:大脑整体功能不可逆性丧失的病理状态,其判定标准为:①明确为颅内加压引起的深昏迷;②瞳孔对光反射、角膜反射消失;③自主呼吸停止;④脑电图呈扁平波。
缓慢间断颅内加压法:通过动物颅骨开孔,颅内放置球囊导管,缓慢间断输注生理盐水,逐渐升高颅内压,使脑灌注压下降,脑血流量随之急剧减少,从而建立脑死亡模型。