| [1] Termine JD,Posner AS.Amorphous/crystalline interrelationships in bone mineral.Calcif Tissue Res. 1967;1(1):8-23.[2] Termine JD,Posner AS.Infrared absorption of carbonate apatite.Science.1967;155(3762): 607-608.[3] Vieira AEM,Danelon M,Camara DMD,et al.In vitro effect of amorphous calcium phosphate paste applied for extended periods of time on enamel remineralization.J Appl Oral Sci. 2017;25(6): 596-603. [4] Liu S,Weng W,Li Z,et al.Effect of PEG amount in amorphous calcium phosphate on its crystallized products.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2009;20(1):359-363.[5] Jin W,Jiang S,Pan H,et al.Amorphous Phase Mediated Crystallization: Fundamentals of Biomineralization. Crystals. 2018; 8(1):48.[6] Jiang S,Pan H,Chen Y,et al.Amorphous calcium phosphate phase-mediated crystal nucleation kinetics and pathway. Faraday Discuss.2015;179:451-461.[7] Li Y,Weng W.In vitro synthesis and characterization of amorphous calcium phosphates with various Ca/P atomic ratios.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2007;18(12):2303-2308.[8] Tadic D,Peters F,Epple M.Continuous synthesis of amorphous carbonated apatites. Biomaterials. 2002;23(12):2553-2559.[9] Nagano M,Nakamura T,Kokubo T,et al.Differences of bone bonding ability and degradation behaviour in vivo between amorphous calcium phosphate and highly crystalline hydroxyapatite coating.Biomaterials.1996;17(18):1771-1777.[10] Combes C,Rey C.Amorphous calcium phosphates: synthesis, properties and uses in biomaterials.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(9): 3362-3378.[11] Ma N,Ma C,Li C,et al.Influence of nanoparticle shape, size, and surface functionalization on cellular uptake.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013;13(10):6485-6498.[12] Singh SS,Roy A,Lee B,et al. Study of hMSC proliferation and differentiation on Mg and Mg-Sr containing biphasic β-tricalcium phosphate and amorphous calcium phosphate ceramics.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;64:219-228.[13] Par M,Šanti? A,Gamulin O,et al.Impedance changes during setting of amorphous calcium phosphate composites.Dent Mater. 2016;32(11):1312-1321.[14] Oyane A,Araki H,Nakamura M,et al.Controlled superficial assembly of DNA-amorphous calcium phosphate nanocomposite spheres for surface-mediated gene delivery.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;141:519-527.[15] Heravi F,Bagheri H,Rangrazi A,et al.Incorporation of CPP-ACP into Luting and Lining GIC: Influence on Wear Rate (in the Presence of Artificial Saliva) and Compressive Strength. Acs Biomater Sci Eng.2016;2(11):1867-1871.[16] Li Y,Wiliana T,Tam KC.Synthesis of amorphous calcium phosphate using various types of cyclodextrins.Mater Res Bull. 2007;42(5):820-827.[17] LuoJ,Qiu S,Zhou X,et al.In situ grafting polyethylene glycol chains onto amorphous calcium phosphate nanoparticles to improve the storage stability and organic solvent redispersibility. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2014;444(Supplement C): 81-88.[18] Delgado-López JM,Bertolotti F,Lyngsø J,et al.The synergic role of collagen and citrate in stabilizing amorphous calcium phosphate precursors with platy morphology. Acta Biomater.2017; 49: 555-562.[19] Li Y,Weng W,Cheng K,et al.Preparation of amorphous calcium phosphate in the presence of poly(ethylene glycol).J Mater Sci Lett.2003;22(14):1015-1016.[20] Chen Z,Cao S,Wang H,et al.Biomimetic remineralization of demineralized dentine using scaffold of CMC/ACP nanocomplexes in an in vitro tooth model of deep caries.PLoS One.2015; 10(1):e0116553.[21] Yang W,Fu J,Wang D,et al.Study on chitosan/polycaprolactone blending vascular scaffolds by electrospinning.J Biomed Nanotechnol.2010;6(3):254-259.[22] Wang T,Ji X,Jin L,et al.Fabrication and characterization of heparin-grafted poly-L-lactic acid-chitosan core-shell nanofibers scaffold for vascular gasket.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013; 5(9):3757-3763.[23] Fonseca-Santos B, Chorilli M.An overview of carboxymethyl derivatives of chitosan: Their use as biomaterials and drug delivery systems.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77: 1349-1362.[24] Zhu Y,Chen F.pH-responsive drug-delivery systems.Chem Asian J.2015;10(2):284-305.[25] Yin Y,Dang Q,Liu C,et al.Itaconic acid grafted carboxymethyl chitosan and its nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and evaluation.Int J Biol Macromol.2017;102:10-18.[26] Lin YS,Renbutsu E,Morimoto M,et al.Preparation of stable chitosan-carboxymethyl dextran nanoparticles.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2009;9(4):2558-2565.[27] Wang J,Zhang D,Liu F,et al.Structure and properties of chitosan derivatives modified calcium polyphosphate scaffolds.Polym Degrad Stab.2010;95(7):1205-1210.[28] Budiraharjo R,Neoh KG,Kang ET.Hydroxyapatite-coated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for promoting osteoblast and stem cell differentiation.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;366(1): 224-232.[29] Ikawa N,Kimura T,Oumi Y,et al.Amino acid containing amorphous calcium phosphates and the rapid transformation into apatite.J Mater Chem.2009;19(28):4906-4913.[30] Niu X,Liu Z,Tian F,et al.Sustained delivery of calcium and orthophosphate ions from amorphous calcium phosphate and poly(L-lactic acid)-based electrospinning nanofibrous scaffold.Sci Rep. 2017;7:45655.[31] Bar-Yoaef O,Govrin-Lippman R,Garti N,et al.The Influence of Polyelectrolytes on the Formation and Phase Transformation of Amorphous Calcium Phosphate.Crystal Growth Design. 2004; 4(1):177-183.[32] Jin L,Zeng X,Liu M,et al.Current progress in gene delivery technology based on chemical methods and nano-carriers. Theranostics.2014;4(3):240-255[2014]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/pmc/articles/PMC3915088/pdf/thnov04p0240.pdf.[33] Gupta RR,Kim H, Chan YK,et al.Axial strain enhances osteotomy repair with a concomitant increase in connexin43 expression. Bone Res.2015;3:15007[2015]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/pmc/ articles/PMC4411567/pdf/boneres20157.pdf.[34] Liu J,Schmidlin PR,Philipp A,et al.Novel bone substitute material in alveolar bone healing following tooth extraction: an experimental study in sheep.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27(7): 762-770.[35] Azarpazhooh A,Limeback H.Clinical efficacy of casein derivatives: a systematic review of the literature.J Am Dent Assoc. 2008; 139(7):915-924;quiz 994-915.[36] Taranath A,Pai D,Pentapati K.The role of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate products in remineralization of incipient enamel lesions and its substantivity.J Exp Integr Med.2014;4(1):67-70.[37] Huang LY,Liu TY,Liu KH,et al.Electrospinning of amphipathic chitosan nanofibers for surgical implants application.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2012;12(6):5066-5070.[38] Sahariah P,Masson M.Antimicrobial Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives: A Review of the Structure-Activity Relationship. Biomacromolecules.2017;18(11):3846-3868.[39] ChengBX,Pei BY,Wang ZK,et al.Advances in chitosan-based superabsorbent hydrogels. Rsc Adv.2017;7(67):42036-42046.[40] Asmatulu R,Patrick S,Ceylan M,et al.Antibacterial Polycaprolactone/Natural Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite Fibers for Bone Scaffoldings.J Bionanosci.2016;9(2):1-7.[41] Huang GQ,Cheng LY,Xiao JX,et al.Preparation and characterization of O-carboxymethyl chitosan-sodium alginate polyelectrolyte complexes. Colloid Polym Sci. 2015;293(2):401-407.[42] Onuma K,Ito A.Cluster Growth Model for Hydroxyapatite. City, 1998.[43] Eanes E.Amorphous calcium phosphate.Monogr Oral Sci. 2001; 18:130-147.[44] Zhao J,Liu Y,Sun WB,et al.First detection, characterization, and application of amorphous calcium phosphate in dentistry.J Dent Sci.2012;7(4):316-323.[45] Zhao D,Huang J,Hu S,et al.Biochemical activities of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan from squid cartilage.Carbohydr Polym.2011;85(4):832-837.[46] Wahid F,Wang HS,Zhong C,et al.Facile fabrication of moldable antibacterial carboxymethyl chitosan supramolecular hydrogels cross-linked by metal ions complexation.Carbohydr Polym. 2017;165:455-461.[47] Pan H,Liu XY,Tang R,et al.Mystery of the transformation from amorphous calcium phosphate to hydroxyapatite.Chemical communications(Cambridge, England). 2010;46(39):7415-7417. |
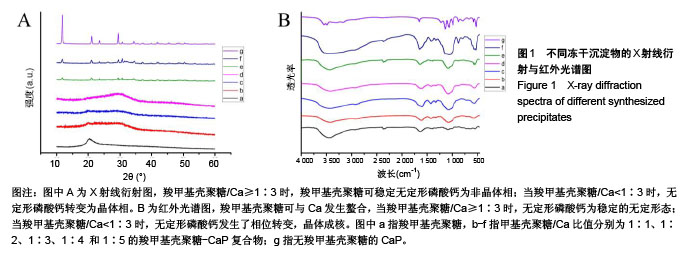
.jpg)


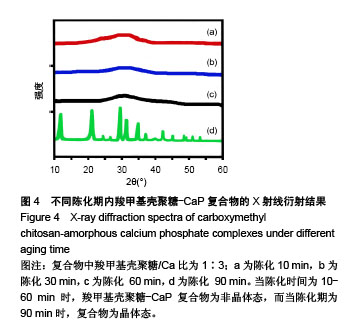
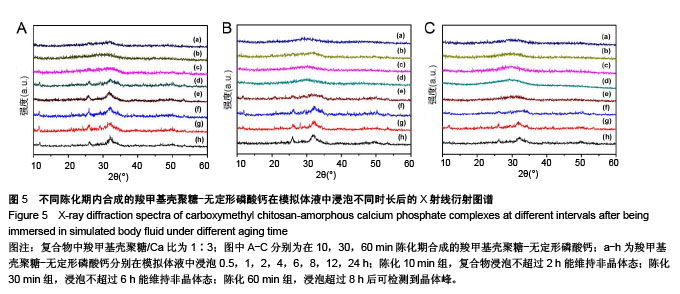
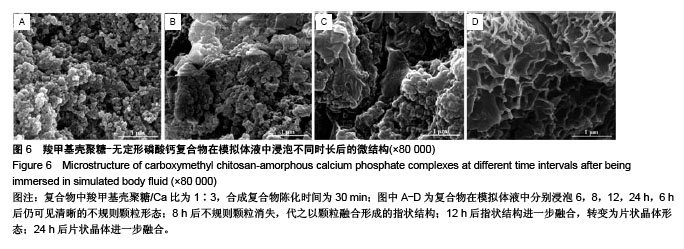
.jpg)