中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 274-280.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0018
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
基于FLUENT3D生物打印喷头内部流场的数值模拟分析
刘东方1,2,周骥平1,史宏灿3,许晓东2,姜亚妮2,张 琦1
- 1扬州大学机械工程学院,江苏省扬州市 225127;2扬州大学动物科学与技术学院,江苏省扬州市 225009;3扬州大学医学院,江苏省扬州市 225001
Numerical simulation analysis of the internal flow field of a 3D biological printhead based on FLUENT
Liu Dong-fang1, 2, Zhou Ji-ping1, Shi Hong-can3, Xu Xiao-dong2, Jiang Ya-ni2, Zhang Qi1
- 1College of Mechanical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225127, Jiangsu Province, China; 2College of Animal Science and Technology, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Medical College of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225001, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
流场:研究材料在挤出过程中的速度随压强和材料黏度的不同而发生的变化。
模拟:其主要是利用Fluent软件对于在不同的压强和黏度条件下,对于3D打印材料流动过程中的速度变化的数值模拟。
背景:随着3D打印技术的发展,人工构建组织和器官的一种方法是通过构建有利于细胞生长的三维支架来进行器官和组织的培养。
目的:为解决支架在进行3D打印过程中的过堆积问题。
方法:利用美国ANSYS公司开发的有限元分析软件Fluent,对打印喷头的挤出过程进行分析,得到适合纤维素凝胶复合物3D打印的材料黏度和挤出压强,进行实验并运用对比观察的方法。
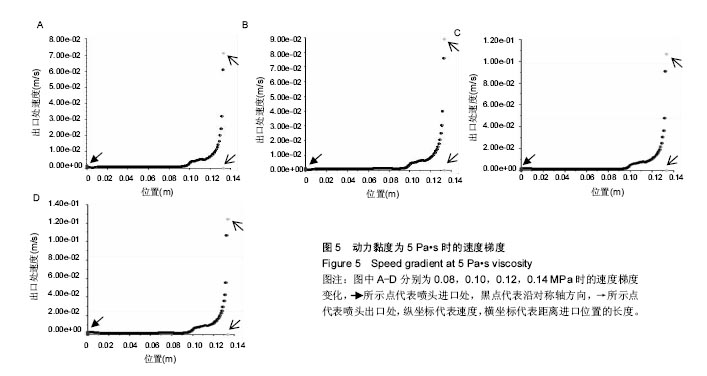
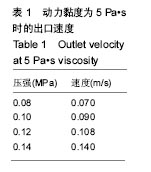
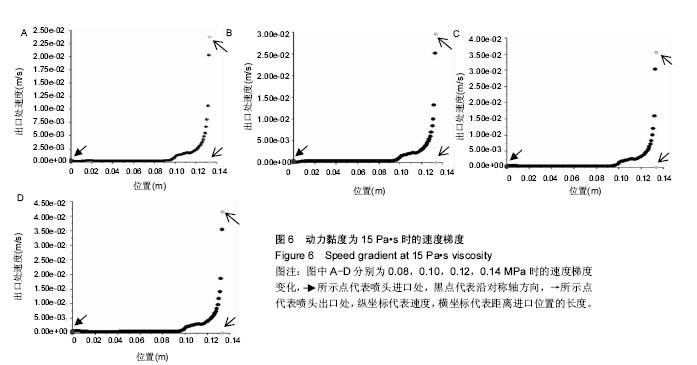
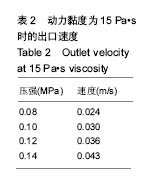
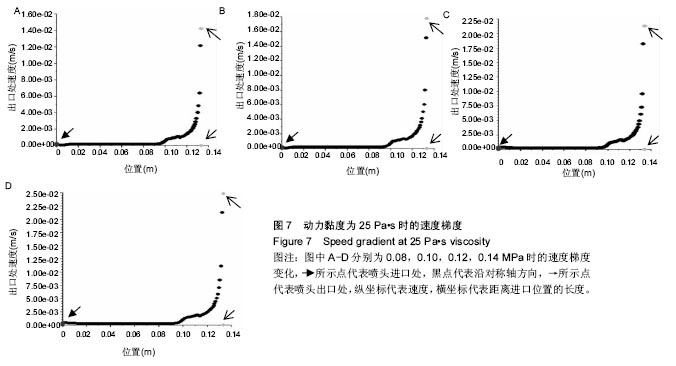
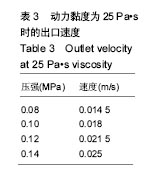
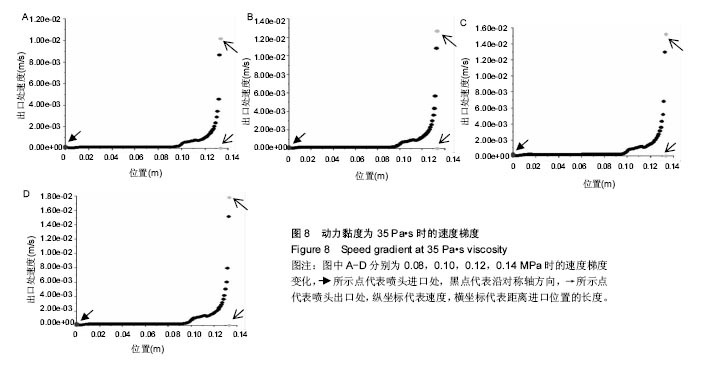
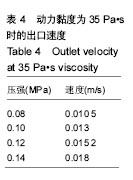
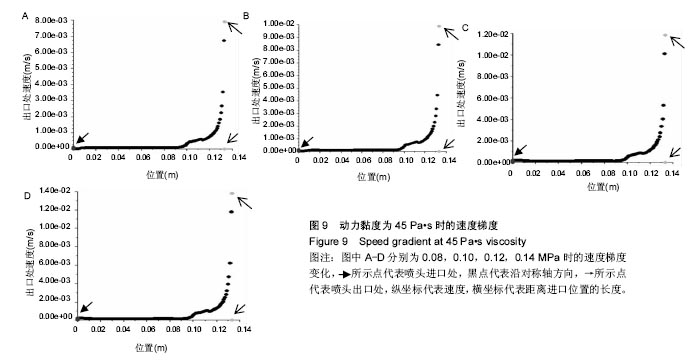
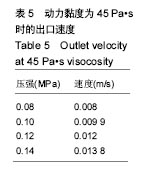
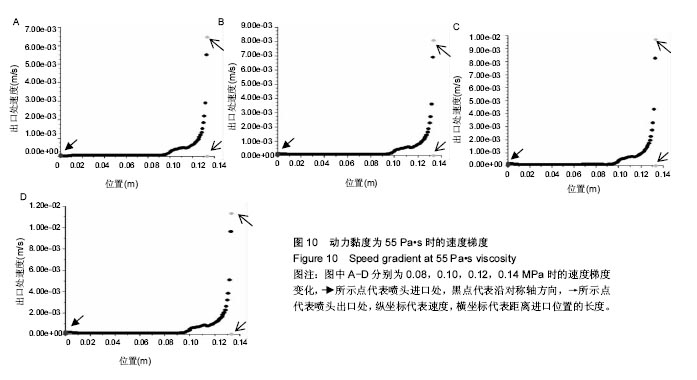
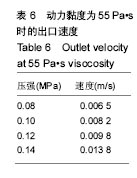
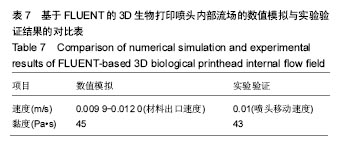
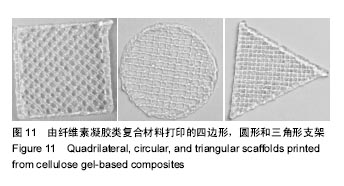
结果和结论:模拟结果和实验结果的误差小于5%。模拟数值在动力黏度为45和压强为0.10-0.12 MPa,解决了纤维素凝胶类复合材料在进行3D打印过程中的过堆积现象得到了解决,保证了3D生物打印支架有良好的空隙。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)