中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5413-5417.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.001
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 下一篇
多孔钛合金支撑棒在踝关节损伤中的应用及生物力学性能
李大成,付 莹,陈望军,冯 跨
- 承德市中心医院(承德医学院第二临床学院)骨一科,河北省承德市 067000
Application and biomechanical study of porous titanium alloy support rod in ankle joint injuries
Li Da-cheng, Fu Ying, Chen Wang-jun, Feng Kua
- Department of Orthopedics, Chengde Central Hospital (Second Clinical School of Chengde Medical University), Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
钛合金:是以钛元素为基础加入其他元素组成的合金。钛有两种同质异晶体:钛是同素异构体,熔点为1 668 ℃,在低于882 ℃时呈密排六方晶格结构,称为α-钛;在882 ℃以上呈体心立方品格结构,称为β-钛。利用钛的上述两种结构的不同特点,添加适当的合金元素,使其相变温度及组分含量逐渐改变而得到不同组织的钛合金。
生物力学:生物力学是应用力学原理和方法对生物体中的力学问题定量研究的生物物理学分支。生物力学的基础是能量守恒、动量定律、质量守恒三定律并加上描写物性的本构方程。生物力学研究的重点是与生理学、医学有关的力学问题。依研究对象的不同可分为生物流体力学、生物固体力学和运动生物力学等。
背景:研究表明钛合金材料具有良好的生物相容性,便于加工合成为合适孔径的多孔结构,将其用于踝关节损伤中效果理想,但其生物力学性能尚不明确。
目的:探讨多孔钛合金支撑棒在踝关节损伤中的应用效果及生物力学性能。
方法:取健康Beagle犬30只,利用止血钳挑起并暴力拉断外侧副韧带,建立踝关节损伤模型。实验分为2组:对照组(n=15)和实验组(n=15)。利用CAD设计多孔钛合金棒三维模型,并将其输入到EBM S12系统中,将Ti6A14V粉末放入机器中并进行逐层熔融,最终制备成直径为4 mm、长度为12 mm的多孔圆柱状棒体。对照组采用常规方法修复,多孔钛合金支撑棒组将多孔钛合金支撑棒植入损伤处,比较2组犬踝关节肿胀程度、修复优良率、电生理学指标及生物力学性能。
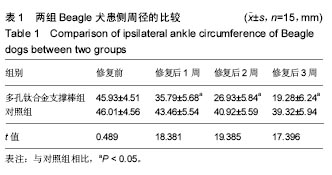
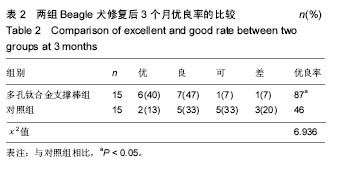
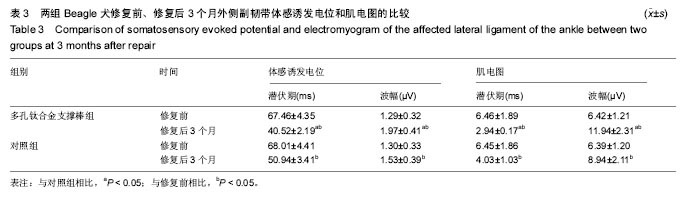
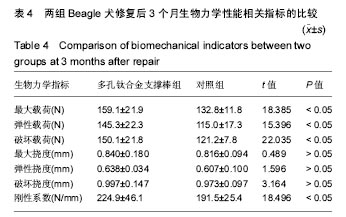
结果与结论:①2组修复前患侧踝关节周径无明显差异(P > 0.05);多孔钛合金支撑棒组修复后1、2及3周,患侧踝关节周径均显著低于对照组(P < 0.05);②多孔钛合金支撑棒组修复后3个月的优良率显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);③2组Beagle犬修复前患侧外侧副韧带体感诱发电位和肌电图潜伏期、波幅比较无明显差异(P > 0.05);多孔钛合金支撑棒组修复后3个月,患侧外侧副韧带体感诱发电位和肌电图的潜伏期显著短于对照组(P < 0.05);而体感诱发电位和肌电图的波幅显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);④与对照组相比,多孔钛合金支撑棒组的最大桡度、弹性桡度、破坏桡度无明显差异(P > 0.05);而最大载荷、弹性载荷、破坏载荷及刚性系数显著提高(P < 0.05);⑤结果提示,将多孔钛合金支撑棒应用于踝关节损伤的治疗,具有较好的修复效果,且有助于改善踝关节生物力学性能。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)