| [1]Causa F,Netti PA,Ambrosio L.A multi-functional scaffold for tissue regeneration: the need to engineer a tissue analogue. Biomaterials.2007;28(34):5093-5099.[2]Frenkel SR,Di Cesare PE.Scaffolds for articular cartilage repair.Ann Biomed Eng.2004;32(1):26-34.[3]Xia W,Liu W,Cui L,et al.Tissue engineering of cartilage with the use of chitosan-gelation complex scaffolds.Biomed MaterRes B Appl Biomater.2004;71(2):373-380.[4]Wang W,Li B,Yang J,et al.The restoration of full-thickness cartilage defects with BMSCs and TGF-beta 1 loaded PLGA/fibrin gel constructs.Biomaterials.2010;31:8964-8973.[5]Fan H,Hu Y,Zhang C,et al.Cartilage regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and a PLGA-gelatin/ chondroitin/hyaluronate hybrid scaffold. Biomaterials. 2006;27(26):4573-4580.[6]Dai W,Kawazoe N,Lin X,et al.The influence of structural design of PLGA/collagen hybrid scaffolds in cartilage tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2010;31(8):2141-2152.[7]Zhou H,Lawrence JG,Bhaduri SB.Fabrication aspects of PLA-CaP/PLGA-CaP composites for orthopedic applications: a review.Acta Biomater.2012;8(6):1999-2016.[8]Li WJ,Tuan RS. Polymeric scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering[C].Macromolecular Symposia, 2005;227:65.[9]Tanaka Y,Yamaoka H,Nishizawa S,et al.The optimization of porous polymeric scaffolds for chondrocyte/atelocollagen based tissue-engineered cartilage.Biomaterials. 2010;31(16): 4506-4516.[10]Hollister SJ.Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering.Nat Mater.2005;4:518-524.[11]McMahon LA,O'Brien FJ,Prendergast PJ.Biomechanics and mechanobiology in osteochondral tissues. Regen Med. 2008; 3:743-759.[12]Schek RM,Taboas JM,Segvich SJ,et al.Engineered osteochondral grafts using biphasic composite solid free-form fabricated scaffolds.Tissue Eng.2004;10(9-10):1376-1385.[13]Chen GP,Sato T,Tanaka J,et al.Preparation of a biphasic scaffold for osteochondral tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C.2006;26(1):118-123.[14]Ho STB,Hons BE,Hutmacher DW,et al.The evaluation of a biphasic osteochondra implant coupled with an electrospun membrane in a large animal model.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010; 16(4):1123-1141.[15]Nava MM,Draghi L,Giordano C,et al.The effect of scaffold pore size in cartilage tissue engineering. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater.2016;14(3):e223-229. [16]Murphy CM,Haugh MG,O'Brien FJ.The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation and migration in collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2010;31(3):461-466.[17]Dai Y,Li X,Wu R,et al.Macrophages of Different Phenotypes Influence the Migration of BMSCs in PLGA Scaffolds with Different Pore Size.Biotechnol J.2017.doi: 10.1002/biot.201700297.[Epub ahead of print][18]Murphy CM,Duffy GP,Schindeler A,et al.Effect of collagen- glycosaminoglycan scaffold pore size on matrix mineralization and cellular behavior in different cell types.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(1):291-304.[19]Pan Z,Duan P,Liu X,et al.Effect of porosities of bilayered porous scaffolds on spontaneous osteochondral repair in cartilage tissue engineering.Regen Biomater. 2015;2(1): 9-19.[20]Jing D,Wu L,Ding J.Solvent-assisted room-temperature compression molding approach to fabricate porous scaffolds for tissue engineering.Macromol Biosci. 2006;6:747-757.[21]Wu LB,Jing DY,Ding JD.A “room-temperature” injection molding/ particulate leaching approach for fabrication of biodegradable three-dimensional porous scaffolds. Biomaterials.2006;27(2):185-191. [22]Pan Z,Ding J.Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) porous scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Interface Focus.2012;2(3):366-377. [23]Shao XX,Goh J,Hutmacher DW,et al.Repair of large articular osteochondral defects using hybrid scaffolds and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model. Tissue Eng.2006;12(6): 1539-1551.[24]Xue DT,Zheng Q,Zong C,et al.Osteochondral repair using porous poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/nano-hydroxyapatite hybrid scaffolds with undifferentiated mesen- chymal stem cells in a rat model.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(1): 259-270.[25]段平国,董健.双层支架构建组织工程骨软骨修复关节软骨缺损[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,18(2):189-191.[26]Conoscenti G,Schneider T,Stoelzel K,et al.PLLA scaffolds produced by thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) allow human chondrocyte growth and extracellular matrix formation dependent on pore size.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;80:449-459.[27]Nuernberger S,Cyran N,Albrecht C,et al.The influence of scaffold architecture on chondrocyte distribution and behavior in matrix-associated chondrocyte transplantation grafts. Biomaterials.2011;32(4):1032-1040.[28]Zeltinger J,Sherwood JK,Graham DA,et al.Effect of pore size and void fraction on cellular adhesion, proliferation, and matrix deposition.Tissue Eng.2001;7(5):557-572.[29]Uematsu K,Hattori K,Ishimoto Y,et al.Cartilage regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and a three-dimensional poly-lactic- glycolic acid (PLGA) scaffold. Biomaterials. 2005;26(20):4273-4279.[30]Koga H,Muneta T,Ju YJ,et al.Synovial stem cells are regionally specified according to local microenvironments after implantation for cartilage regeneration.Stem Cells. 2007;25(3):689-696.[31]Qu D,Li J,Li Y,et al.Ectopic osteochondral formation of biomimetic porous PVA-n-HA/PA6 bilayered scaffold and BMSCs construct in rabbit.J Biomed Mater Res Part B. 2011;96(1):9-15.[32]周勇,贾兆锋,刘威,等.聚乙烯醇/壳聚糖多孔水凝胶复合骨髓间充质干细胞修复膝关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(18):2881-2889. [33]Di Luca A,Szlazak K,Lorenzo-Moldero I,et al.Influencing chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells in scaffolds displaying a structural gradient in pore size. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:210-219. |
.jpg)
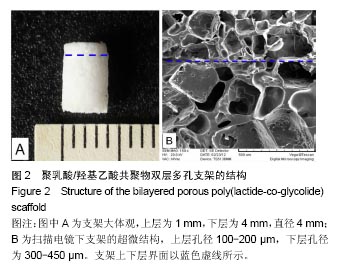
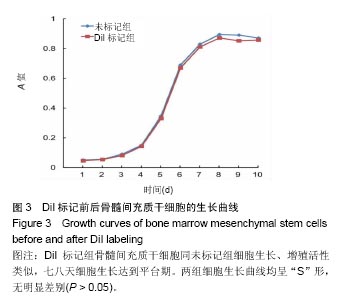
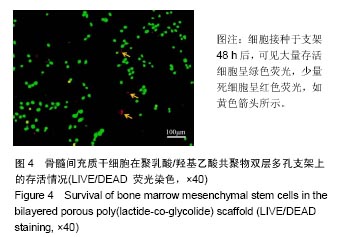
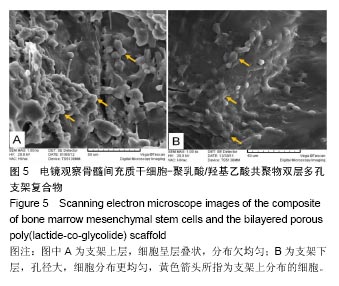
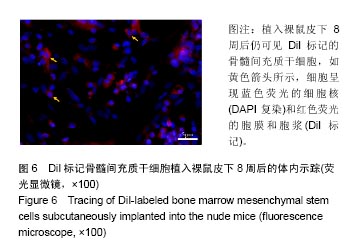
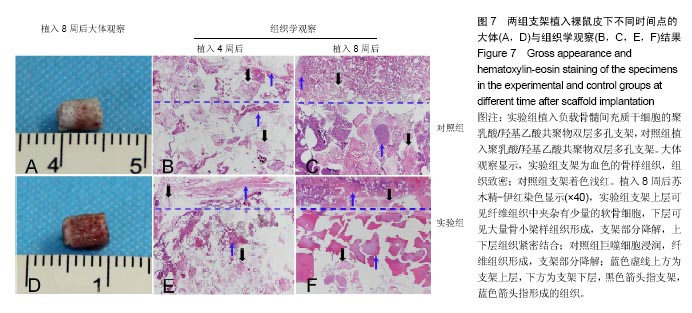
.jpg)
.jpg)