中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5499-5505.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.015
• 生物材料模型构建 biomaterial modeling • 上一篇 下一篇
角膜修复材料有效性评价动物模型的建立和验证
韩倩倩1,李 青2,王宝全2,杨昭鹏1,王春仁1
- 1中国食品药品检定研究院,北京市 102629;2青岛中皓生物工程有限公司,山东省青岛市 266000
Establishment and validation of an animal model for evaluating the effectiveness of corneal repair materials
Han Qian-qian1, Li Qing2, Wang Bao-quan2, Yang Zhao-peng1, Wang Chun-ren1
- 1National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 102629, China; 2Zhonghao Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
板层角膜移植:是以角膜部分组织为操作对象进行的手术,只切除有病变的角膜浅层组织,深层比较完好的受主角膜仍然保留作为移植床,然后取同样大小和厚度的角膜材料浅层角膜片,缝于患者角膜的创面上。
Ⅲ类植入性医疗器械:是最高级别的医疗器械,也是必须严格控制的医疗器械,是指植入人体,用于支持、维持生命,对人体具有潜在危险,对其安全性、有效性必须严格控制的医疗器械。
背景:角膜修复材料可修复角膜损伤,这种产品在进入临床试验之前需要评估其有效性,但现阶段尚缺乏标准化的有效性评估方法。
目的:建立并验证兔角膜真菌感染模型和角膜移植实验方法。
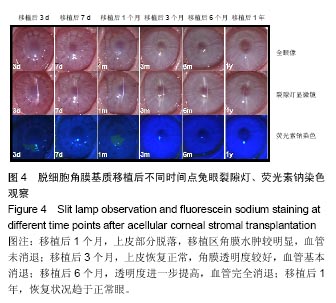
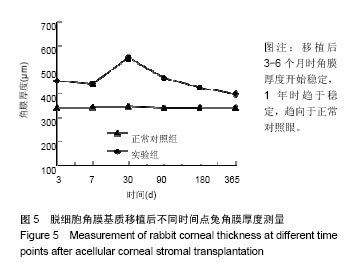
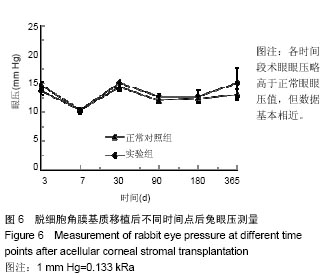
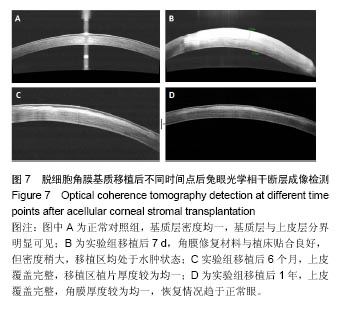
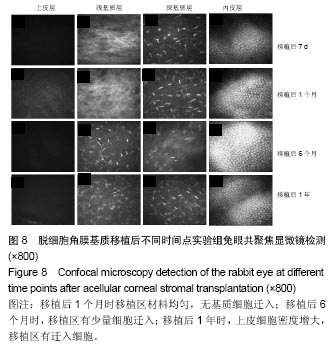
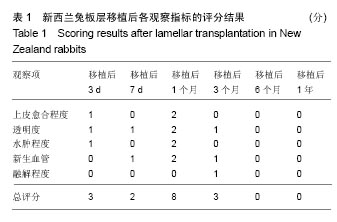
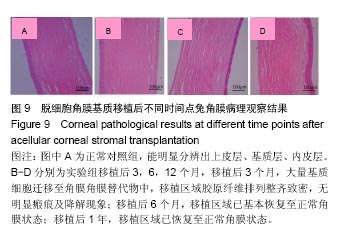
方法:取新西兰大白兔12只,建立左眼角膜真菌感染模型(实验组),右眼作为正常对照。模型建立2周后,左眼进行脱细胞猪角膜基质移植,移植后定期进行裂隙灯显微镜、角膜厚度、眼压、共聚焦显微镜及光学相干断层成像等检测,评估角膜修复材料透明度、上皮愈合程度、水肿程度、角膜新生血管程度、角膜修复材料融解程度;移植后3,6,12个月,进行角膜病理组织观察。
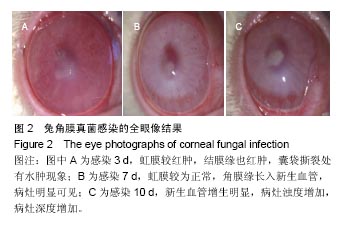
结果与结论:①实验组移植后1个月时角膜厚度明显增高,移植3-6个月时角膜厚度开始稳定,1年时趋于稳定,趋向于正常眼;②实验组眼压始终接近于正常眼;③光学相干断层成像显示,移植后7 d,角膜修复材料与植床贴合良好;移植后6个月上皮覆盖完整,移植区植片厚度较为均一;移植后1年恢复情况趋于正常眼;④共聚焦显微镜显示,移植后1个月时,移植区材料均匀;移植后6个月时,移植区有少量细胞迁入;移植后1年时,上皮细胞密度增大,移植区有迁入细胞,但少于正常眼;⑤移植后1年,角膜修复材料几近完全透明,可认为此角膜修复材料治疗感染性角膜溃疡有效;未发生排斥反应,表明该角膜修复材料的治愈性良好;⑥移植后3个月,大量基质细胞迁移至角膜角膜替代物中,移植区域胶原纤维排列整齐、致密,无明显瘢痕及降解现象;移植后6个月时,移植区域已基本恢复至正常角膜状态;移植后1年,移植区域已恢复至正常角膜状态,生物相容性很好;⑦结果表明,实验建立的兔角膜真菌感染模型和角膜移植实验方法可作为评价此类角膜材料有效性的动物模型和方法。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)