| [1]Yang K,Zhang Y,Zhang N,et al.Recent progress of small intestinal submucosa in application research of tissue repair and reconstruction.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013;27(9):1138-1143.[2]Lu HK,Ren AJ,Sun XL,et al.Compound graft of porcine small intestinal submucosa with Schwann cells to reconstruct injured cavernous nerves and restore erectile function. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue.2010;16(9):834-839.[3]Shi L,Ronfard V.Biochemical and biomechanical characterization of porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS): a mini review.Int J Burns Trauma.2013;3(4):173-179.[4]Horiguchi A.Editorial comment to outcome of small intestinal submucosa graft for repair of anterior urethral strictures.Int J Urol.2013;20(6):629-630.[5]Villoldo GM,Loresi M,Giudice C,et al.Histologic changes after urethroplasty using small intestinal submucosa unseeded with cells in rabbits with injured urethra.Urology.2013; 81(6): 1380-1381.[6]孙慧哲,田伟,曾亮,等.参考猪小肠黏膜下基质海绵的制备[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(21):3110-3116.[7]董鸿鸣,柏树令.小鼠骨髓基质干细胞的培养及常见的组化染色方法[J].中国医科大学学报,2004,33(4):294-298.[8]卢洪凯,任安吉,孙晓璐,等.复合雪旺细胞的猪小肠粘膜下层对大鼠海绵体神经损伤勃起功能恢复的实验研究[J].中华男科学杂志,2010(9):834-839.[9]张开刚,曾炳芳,张长青.小肠粘膜下层的制备及细胞相容性的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(4):344-348.[10]Ding JX,Zhang XY,Chen LM,et al.Vaginoplasty using acellular porcine small intestinal submucosa graft in two patients with Meyer-von-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome: a prospective new technique for vaginal reconstruction.Gynecol Obstet Invest.2013;75(2):93-96.[11]苏琰,张长青,张开刚,等.小肠粘膜下层与雪旺细胞生物相容性的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(2):153-156.[12]Lin HK,Godiwalla SY,Palmer B,et al.Understanding roles of porcine small intestinal submucosa in urinary bladder regeneration: identification of variable regenerative characteristics of small intestinal submucosa.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2014;20(1):73-83. [13]Roos S,Wyder M,Candi A,et al.Binding studies on isolated porcine small intestinal mucosa and in vitro toxicity studies reveal lack of effect of C.perfringens beta-toxin on the porcine intestinal epithelium.Toxins(Basel).2015;7(4):1235-1252.[14]Ramos CM,Francisco JC,Olandoski M,et al.Myocardial regeneration after implantation of porcine small intestinal submucosa in the left ventricle.Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc.2014; 29(2):202-213. [15]Winskel H,Ratitamkul T,Charoensit A.The role of tone and segmental information in visual-word recognition in Thai.Q J Exp Psychol(Hove).2017;70(7):1282-1291. [16]Yi JS,Lee HJ,Lee HJ,et al.Rat peripheral nerve regeneration using nerve guidance channel by porcine small intestinal submucosa.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2013;53(2):65-71.[17]Mondalek FG,Lawrence BJ,Kropp BP,et al.Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 September 30. Published in final edited form as: Biomaterials.Biomaterials. 2008;29(9): 1159-1166.[18]Iwasaki J,Hata T,Uemoto S,et al.Portocaval shunt for hepatocyte package: challenging application of small intestinal graft in animal models.Organogenesis.2013;9(4):273-279.[19]Liu Z,Feng X,Wang H,et al.Carbon nanotubes as VEGF carriers to improve the early vascularization of porcine small intestinal submucosa in abdominal wall defect repair.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:1275-1286. [20]Hoeppner J,Marjanovic G,Helwig P,et al.Extracellular matrices for gastrointestinal surgery: ex vivo testing and current applications.World J Gastroenterol.2010;16(32):4031-4038.[21]Song Z,Peng Z,Liu Z,et al.Reconstruction of abdominal wall musculofascial defects with small intestinal submucosa scaffolds seeded with tenocytes in rats.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(13-14):1543-1553. [22]Lin HK,Godiwalla SY,Palmer B,et al.Understanding roles of porcine small intestinal submucosa in urinary bladder regeneration: identification of variable regenerative characteristics of small intestinal submucosa.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2014;20(1):73-83. [23]Mondalek FG,Lawrence BJ,Kropp BP,et al.Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 September 30.Published in final edited form as: Biomaterials.Biomaterials.2008;29(9):1159-1166. [24]Nakatsu H,Ueno T,Oga A,et al.Influence of mesenchymal stem cells on stomach tissue engineering using small intestinal submucosa.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(3): 296-304. [25]Orlando G,Wood KJ,De Coppi P,et al.Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 May 1. Published in final edited form as: Ann Surg.Ann Surg.2012;255(5):867-880. [26]Lam MT,Wu JC.Author manuscript;available in PMC 2013 September 1. Published in final edited form as: Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2012;10(8): 1039-1049. [27]Patil PB,Chougule B, Kumar VK,et al.Recellularization of acellular human small intestine using bone marrow stem cells.Stem Cells Transl Med.2013;2(4):307-315. [28]Shimazu T,Villena J,Tohno M,et al.Immunobiotic Lactobacillus jensenii elicit anti-inflammatory activity in porcine intestinal epithelial cells by modulating negative regulators of the toll-like receptor signaling pathway.Infect Immun.2012;80:276-288. [29]Villena J,Suzuki R,Fujie H,et al.Immunobiotic Lactobacillus jensenii modulates toll-like receptor 4-induced inflammatory response via negative regulation in porcine antigen presenting cells.Clin Vaccine Immunol.2012;19:1038-1053.[30]Villena J,Kitazawa H.Role of Toll-like Receptors in the Modulation of Intestinal Inflammation by Immunobiotics.Probiotics: Immunobiotics and Immunogenics,2013:89-127.[31]Villena J,Aso H,Alvarez S,et al.Porcine Toll-Like Receptors and Their Crosstalk with Immunobiotics: Impact in the Regulation of Gut Inflammatory Immunity.Probiotics: Sources, Types and Health Benefits,NOVA Science Publishers,Inc., New York,2012:53-84.[32]Chiba E,Tomosada Y,Vizoso-Pinto MG,et al.Immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus improves resistance of infant mice against respiratory syncytial virus infection.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;17:373-382. |
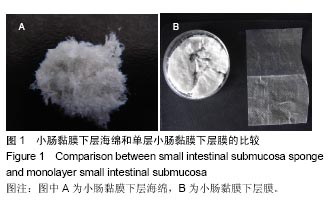
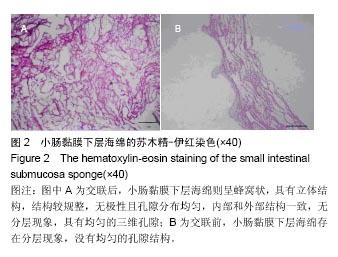
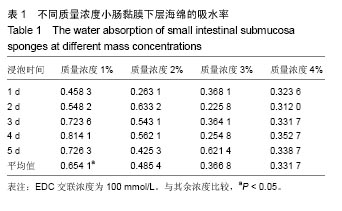
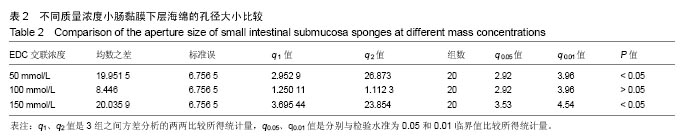
.jpg)

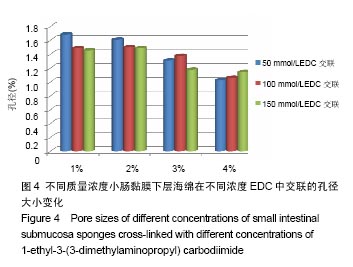

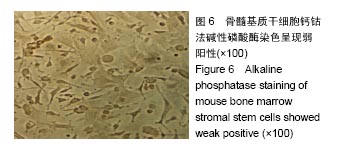

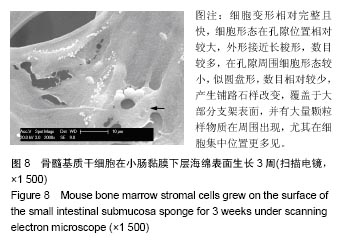
.jpg)