| [1] Chotai S, Parker SL, Sielatycki JA, et al. Impact of old age on patient-report outcomes and cost utility for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion surgery for degenerative spine disease. Eur Spine J. 2017. doi:10.1007/s00586-016-4835-3.[2] Boissière L, Moal B, Gille O, et al. Lumbar spinal muscles and spinal canal study by MRI three-dimensional reconstruction in adult lumbar spinal stenosis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2016.10.025.[3] Kreiner DS, Hwang SW, Easa JE, et al. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Spine J. 2014;14:180-191.[4] Schüppel J, Weber F. Retrospective matched-pair cohort study on effect of bisegmental fenestration versus hemilaminectomy for bisegmental spinal canal stenosis at L3-L4 and L4-L5. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2017. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1597617.[5] Ulrich NH, Burgstaller JM, Pichierri G, et al. Decompression surgery alone versus decompression plus fusion in symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis: a Swiss prospective multi-center cohort study with 3 years of follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002068.[6] Gil-Salú JL, López-Escobar M, Gómez-Cárdenas E, et al. Calcification of the thoracic yellow ligament as a cause of myelopathy. Rev Neurol. 2002;34:750-753.[7] Thomé C, Börm W, Meyer F. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: current strategies in diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2008;105:373-379.[8] Shen L, Fang L, Qiu Y, et al. Study on different surgical approaches for acute lumber disk protrusion combined with cauda equina syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:8875-8880. [9] Spadaro A, Ciarrocchi I, Masci C, et al. Effects of intervertebral disc disorders of low back on the mandibular kinematic: kinesiographic study. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:569.[10] Losiniecki AJ, Serrone JC, Keller JT, et al. Lumbar ligamentum flavum: spatial relationships to surrounding anatomical structures and technical description of en bloc resection. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2013;74:388-392. [11] Seki S, Kawaguchi Y, Ishihara H, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis due to a large calcified mass in the ligamentum flavum. Asian Spine J. 2013;7:236-241. [12] Amirouche F, Solitro GF, Magnan BP. Stability and spine pedicle screws fixation strength-a comparative study of bone density and insertion angle. Spine Deform. 2016;4:261-267. [13] Baldawa S, Shivpuje V. Migratory low velocity intradural lumbosacral spinal bullet causing cauda equina syndrome: report of a case and review of literature. Eur Spine J. 2016; doi: 10.1007/s00586-016-4913-6.[14] Burke SM, Hwang SW, Safain MG, et al. Iatrogenic spinal cord injury during removal of the inferior articular process in the presence of ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Case Rep Surg. 2016. doi:10.1155/2016/2318759. [15] Ha KY, Kim SI, Kim YH, et al. Predictive factors for postoperative follow-up: which patients are prone to loss to follow-up after spinal surgery? Clin Spine Surg. 2016. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000465.[16] Safak AA, Is M, Sevinc O, et al. The thickness of the ligamentum flavum in relation to age and gender. Clin Anat. 2010;23:79-83. [17] Steffee AD, Biscup RS, Sithowski DJ. Segmental spine plates with pedicle screw fixation a new internal fixation device for disorders of the lumbar and thoracolumbar spine. Clin Orthop. 1986;203:45.[18] Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Doornik A, et al. Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987;12:160-166.[19] Scoles PV, Linton AE, Latimer B, et al. Vertebral body and posterior element morphology: the normal spine in middle life. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;13:1082-1086.[20] Amonoo-Kuofi HS. Age-related variations in the horizontal and vertical diameters of the pedicles of the lumbar spine. J Anat. 1995;186:321-328.[21] Du LJ, Li JJ. Correlative study on the radius and deflection of pedicle of vertebrae and thoracic vertebrae in Chinese adult men. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2009;19:545-549.[22] Cui XG, Ding ZH, Cai JF. Radiographic anatomy study of the relationship between the root and the pedicle of thoracolumbar spinous process. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2004;1296-1298.[23] Altinkaya N, Yildirim T, Demir S, et al. Factors associated with the thickness of the ligamentum flavum: is ligamentum flavum thickening due to hypertrophy or buckling? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36:E1093-E1097. [24] Abbas J, Hamoud K, Masharawi YM, et al. Ligamentum flavum thickness in normal and stenotic lumbar spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35:1225-1230.[25] Zeng ZY, Jiang CY, Song YX, et al. Imaging measurement and clinical significance of lumbar vertebral lamina and articular process. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2009;27:420-425.[26] Li Z. Minimally invasive closed reduction and internal fixation with fully threaded headless cannulated compression screws for repair of distal radius fracture: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Clin Transl Orthop. 2016;1:58-63.[27] Wu T, Zhang GQ. Minimally invasive treatment of proximal humerus fractures with locking compression plate improves shoulder function in older patients: study protocol for a prospective randomized controlled trial. Clin Transl Orthop. 2016;1:51-57.[28] Yin PB, Long AH, Shen J, et al. Treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fracture with proximal femoral medial sustainable intramedullary nails: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Clin Transl Orthop. 2016;1(2):44-50.[29] 阿良德,张广元,闫红秀,等.联合神经阻滞麻醉对老年全髋关节置换术中应激及置换后免疫功能的影响:随机对照临床试验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(39):5892-5897. |
.jpg)
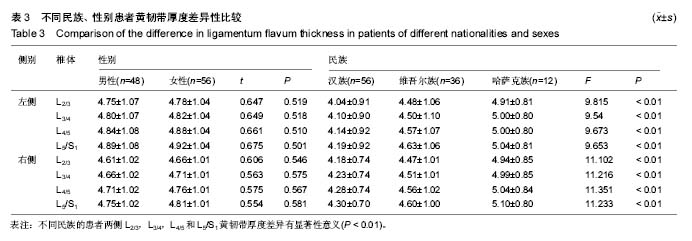
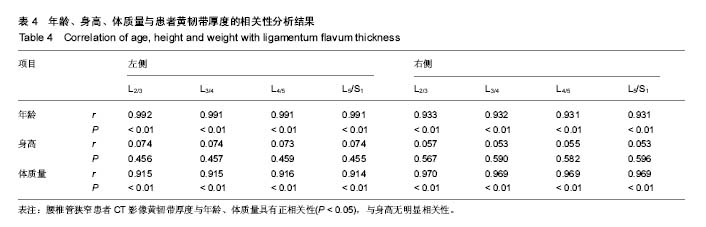
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)