| [1]Duan L,Liang Y,Ma B,et al.Epigenetic regulation in chondrocyte phenotype maintenance for cell-based cartilage repair.Am J Transl Res.2015;7(11):2127-2140.[2]Wang D,Liu W,Feng Q,et al.Effect of inorganic/organic ratio and chemical coupling on the performance of porous silica/chitosan hybrid scaffolds.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 2):969-975. [3]Brix M,Kaipel M,Kellner R,et al.Successful osteoconduction but limited cartilage tissue quality following osteochondral repair by a cell-free multilayered nano-composite scaffold at the knee. Int Orthop.2016;40(3):1-8.[4]Sanchotello M,Forriol F,Gastaldi P,et al.Time evolution of in vivo articular cartilage repair induced by bone marrow stimulation and scaffold implantation in rabbits.Int J Artif Organs. 2015;38(4):210-223.[5]Xia WY,Wei L,Lei C,et al.The experimental study of tissue engineered autologous cartilage using chitosan-gelatin complex scaffolds.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2003;83(7): 577-579.[6]Jia S,Zhang T,Xiong Z,et al.In Vivo Evaluation of a Novel Oriented Scaffold-BMSC Construct for Enhancing Full-Thickness Articular Cartilage Repair in a Rabbit Model. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145667. [7]Muhonen V,Salonius E,Haaparanta AM,et al.Articular cartilage repair with recombinant human type II collagen/polylactide scaffold in a preliminary porcine study.J Orthop Res.2016;34(5):745-753.[8]Reyes R,Delgado A,Solis R,et al.Cartilage repair by local delivery of transforming growth factor-β1 or bone morphogenetic protein-2 from a novel, segmented polyurethane/polylactic- co -glycolic bilayered scaffold.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(4):1110-1120.[9]Park JH,Jung JW,Kang HW,et al.Indirect three-dimensional printing of synthetic polymer scaffold based on thermal molding process.Biofabrication.2014;6(2):025003.[10]Rahmanianschwarz A,Held M,Knoeller T,et al.In vivo biocompatibility and biodegradation of a novel thin and mechanically stable collagen scaffold.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(4):1173-1179.[11]Wang X,Yan Y,Zhang R.Rapid prototyping as a tool for manufacturing bioartificial livers. Trends Biotechnol. 2007; 25(11):505-513.[12]Hoque ME,Chuan YL,Pashby I.Extrusion based rapid prototyping technique: An advanced platform for tissue engineering scaffold fabrication.Biopolymers.2012;97(2): 83-93.[13]Chen L,Zhu WM,Fei ZQ,et al.The study on biocompatibility of porous nHA/PLGA composite scaffolds for tissue engineering with rabbit chondrocytes in vitro.Biomed Res Int.2013;2013: 412745.[14]Islam A,Yasin T,Gull N,et al.Evaluation of selected properties of biocompatible chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) blends.Int J Biol Macromol.2016;82:551-556.[15]Jaipaew J,Wangkulangkul P,Meesane J,et al.Mimicked cartilage scaffolds of silk fibroin/hyaluronic acid with stem cells for osteoarthritis surgery: Morphological, mechanical, and physical clues.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016; 64:173-182.[16]Qi BW,Yu AX,Zhu SB,et al.Chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel combined with Ad-hTGF-β1 transfected mesenchymal stem cells to repair rabbit articular cartilage defects.Exp Biol Med (Maywood).2013;238(1):23-30. [17]Morille M,Toupet K,Montero-Menei CN,et al. PLGA-based microcarriers induce mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis and stimulate cartilage repair in osteoarthritis.Biomaterials. 2016;88:60-69.[18]Kanimozhi K,Khaleel Basha S,Sugantha Kumari V. Processing and characterization of chitosan/PVA and methylcellulose porous scaffolds for tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:484-491.[19]Kanimozhi K,Khaleel BS,Sugantha KV.Processing and characterization of chitosan/PVA and methylcellulose porous scaffolds for tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:484-491.[20]Vikingsson L,Sancho-Tello M,Ruiz-Sauri A,et al.Implantation of a polycaprolactone scaffold with subchondral bone anchoring ameliorates nodules formation and other tissue alterations.Int J Artif Organs.2016;38(12):659-666.[21]Vicentini DS,Smania A,Laranjeira MCM.Chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) films containing ZnO nanoparticles and plasticizers. Mater Sci Eng C.2010;30(4):503-508.[22]Nava MM,Draghi L,Giordano C,et al.The effect of scaffold pore size in cartilage tissue engineering.J Appl Biomater Funct Mater.2016;14(3):e223-229.[23]Han F,Zhou F,Yang X,et al.A pilot study of conically graded chitosan-gelatin hydrogel/PLGA scaffold with dual-delivery of TGF-beta1 and BMP-2 for regeneration of cartilage-bone interface.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(7): 1344-1353.[24]Chu J,Zeng S, Gao L,et al.Poly (L-lactic acid) porous scaffold-supported alginate hydrogel with improved mechanical properties and biocompatibility.Int J Artif Organs. 2016;39(8):435-443.[25]Olubamiji AD,Izadifar Z,Si JL,et al.Modulating mechanical behaviour of 3D-printed cartilage-mimetic PCL scaffolds: influence of molecular weight and pore geometry. Biofabrication. 2016;8(2):025020.[26]Dvir T,Tsur-Gang O,Cohen S.“Designer”scaffolds for tissue engineering and regeneration. Israel J Chem. 2005;45(4): 487-494.[27]Bian W,Lian Q,Li D,et al.Morphological characteristics of cartilage-bone transitional structures in the human knee joint and CAD design of an osteochondral scaffold. Biomed Eng Online. 2016;15(1):82. [28]Zhu W,Guo D,Peng L,et al.Repair of rabbit cartilage defect based on the fusion of rabbit bone marrow stromal cells and Nano-HA/PLLA composite material.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017;45(1):115-119. [29]Li X,Ding J,Zhang ZZ,et al.Kartogenin-Incorporated Thermogel Supports Stem Cells for Significant Cartilage Regeneration.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;8(8): 5148-5159.[30]Yao Q,Nooeaid P,Detsch R,et al.Bioglass(R)/chitosan- polycaprolactone bilayered composite scaffolds intended for osteochondral tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(12):4510-4518.[31].Liao J,Shi K,Ding Q,et al.Recent developments in scaffold-guided cartilage tissue regeneration. J Biomed Nanotechnol.2014;10(10):3085-3104.[32]Gaaz T,Sulong A,Akhtar M,et al.Properties and Applications of Polyvinyl Alcohol,Halloysite Nanotubes and Their Nanocomposites.Molecules.2015;20(12):19884.[33]Rodriguez-Vazquez M,Vega-Ruiz B,Ramos-Zuniga R,et al. Chitosan and Its Potential Use as a Scaffold for Tissue Engineering in Regenerative Medicine.Biomed Res Int.2015; 2015:821279. |
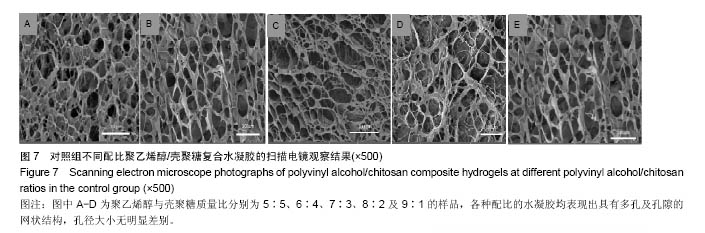
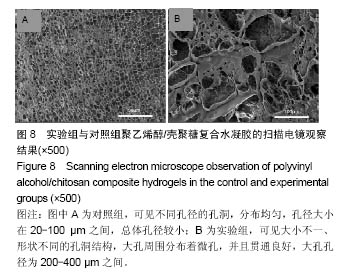
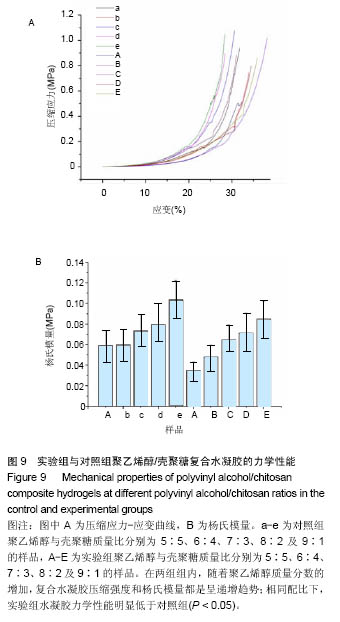
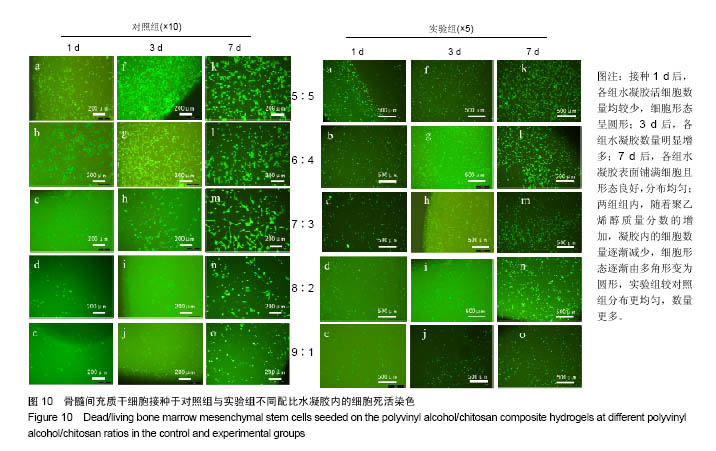
.jpg)

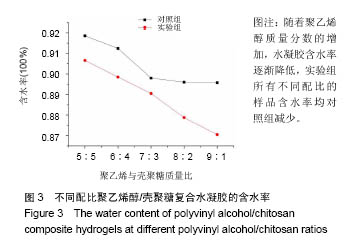
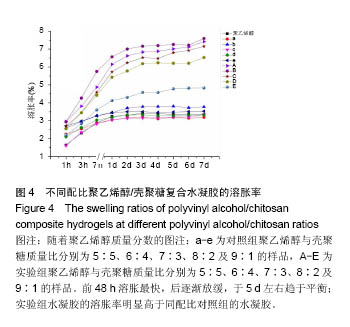
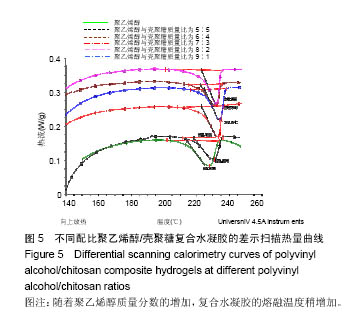
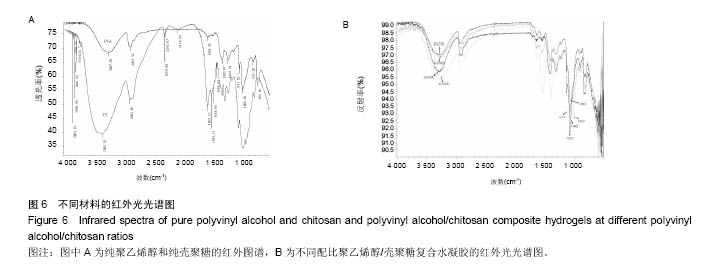
.jpg)
.jpg)