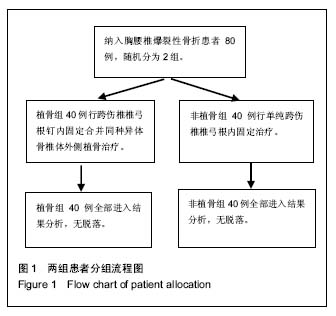
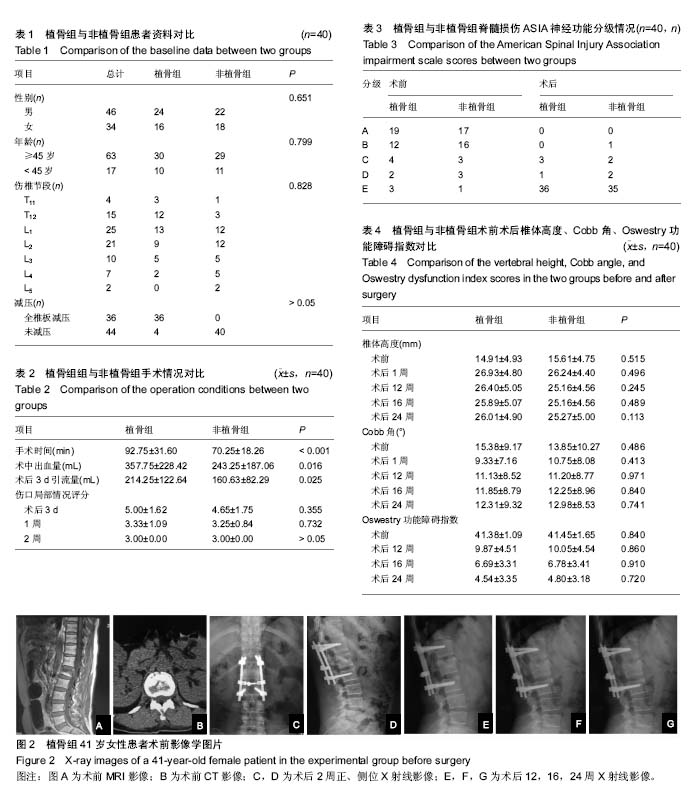
| [1] Tropiano P, Huang RC, Louis CA, et al. Functional and radiographic outcome of thoracolumbar and lumbar burst fractures managed by closed orthopaedic reduction and casting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(21):2459-2465.[2] 凌仕勇,陈军. 经伤椎与跨伤椎椎弓根螺钉复位固定治疗单节段胸腰椎骨折疗效比较[J]. 中国现代医生, 2016,54(12):58-61.[3] Scheer JK, Bakhsheshian J, Fakurnejad S, et al. Evidence-Based Medicine of Traumatic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review of Operative Management across 20 Years. Global Spine J. 2015;5(1): 73-82.[4] Fakurnejad S, Scheer JK, Patwardhan AG, et al. Biomechanics of thoracolumbar burst fractures: methods of induction and treatments. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(12): 2059-2064.[5] Anghel S, Petrisor M, Buicu CF, et al. Predictive factors for postoperative deformity in thoracolumbar burst fractures: a statistical approach. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49 (2):133-138.[6] Deng Z, Zou H, Cai L. The retrospective analysis of posterior short-segment pedicle instrumentation without fusion for thoracolumbar burst fracture with neurological deficit. Scientific World J. 2014;2014:457634.[7] Kim KW, Cho KJ, Kim SW, et al. A nation-wide, outpatient-based survey on the pain, disability, and satisfaction of patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Asian Spine J. 2013;7 (4):301-307.[8] Chen D, An ZQ, Song S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with conservative treatment in patients with chronic painful osteoporotic spinal fractures. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21 (3):473-477.[9] Oner FC, Wood KB, Smith JS, et al. Therapeutic decision making in thoracolumbar spine trauma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35 (21 Suppl):S235-244.[10] Vaccaro AR, Lehman RA Jr, Hurlbert R J, et al. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30 (20):2325-2333.[11] Krappinger D, Kastenberger TJ, Schmid R. [Augmented posterior instrumentation for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body fractures]. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;24 (1):4-12.[12] Javadi SA, Naderi F. The long-term efficacy of pedicular screw fixation at patients suffering from thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit. Asian J Neurosurg. 2015;10 (4):286-289.[13] Tomii M, Mizuno J, Takeda M, et al. Thoracolumbar extradural arachnoid cyst--three surgical case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2013;53 (2):129-133.[14] McCormack T, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19(15):1741-1744.[15] 孙天胜. 《新鲜胸腰段脊柱脊髓损伤评估与治疗》的专家共识[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21 (11):963-968.[16] Knop C, Fabian HF, Bastian L, et al. Late results of thoracolumbar fractures after posterior instrumentation and transpedicular bone grafting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26 (1):88-99.[17] Chou PH, Ma HL, Wang ST, et al. Fusion may not be a necessary procedure for surgically treated burst fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spines: a follow-up of at least ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96 (20):1724-1731.[18] Defino HL, Canto FR. Low thoracic and lumbar burst fractures: radiographic and functional outcomes. Eur Spine J. 2007;16 (11):1934-1943.[19] Liu CL, Wang ST, Lin HJ, et al. AO fixateur interne in treating burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1999;62 (9):619-625.[20] Kim YM, Kim DS, Choi ES, et al. Nonfusion method in thoracolumbar and lumbar spinal fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36 (2):170-176.[21] Jindal N, Sankhala SS, Bachhal V. The role of fusion in the management of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine treated by short segment pedicle screw fixation: a prospective randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(8): 1101-1106.[22] Sanderson PL, Fraser RD, Hall DJ, et al. Short segment fixation of thoracolumbar burst fractures without fusion. Eur Spine J. 1999;8 (6):495-500.[23] Lakshmanan P, Jones A, Mehta J, et al. Recurrence of kyphosis and its functional implications after surgical stabilization of dorsolumbar unstable burst fractures. Spine J. 2009;9 (12):1003-1009.[24] Yaldiz C, Asil K, Ozkal B, et al. Thoracolumbar burst fractures requiring instrumented fusion: Should reducted bone fragments be removed? A retrospective study. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2015;49 (6):358-366.[25] Muller U, Berlemann U, Sledge J, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit by indirect reduction and posterior instrumentation: bisegmental stabilization with monosegmental fusion. Eur Spine J. 1999;8 (4):284-289.[26] Chang KW, Chen HC, Chen YY, et al. Sagittal translation in opening wedge osteotomy for the correction of thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31 (10):1137-1142.[27] Toyone T, Tanaka T, Kato D, et al., The treatment of acute thoracolumbar burst fractures with transpedicular intracorporeal hydroxyapatite grafting following indirect reduction and pedicle screw fixation: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31 (7):E208-214.[28] Alanay A, Acaroglu E, Yazici M, et al. Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26 (2):213-217.[29] Knop C, Fabian HF, Bastian L, et al. Fate of the transpedicular intervertebral bone graft after posterior stabilisation of thoracolumbar fractures. Eur Spine J. 2002;11 (3):251-257.[30] Ma Y, Li X, Dong J. Is it useful to apply transpedicular intracorporeal bone grafting to unstable thoracolumbar fractures? A systematic review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154(12):2205-2213.[31] 史晓林,张昊,刘磊,等. 椎弓根置钉修复胸腰椎骨折合并脊髓损伤:选择性损伤节段及全部固定节段植骨融合的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20 (17):2488-2495.[32] Leferink VJ, Zimmerman KW, Veldhuis EF, et al. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures: radiological results of transpedicular fixation combined with transpedicular cancellous bone graft and posterior fusion in 183 patients. Eur Spine J. 2001;10 (6):517-523.[33] 贾金龙,杨庆国,张银顺,等.椎体减压植入物内固定修复胸腰椎爆裂性骨折:随访验证后路途径更安全[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(22):3531-3537.[34] Wang L, Wang Y, Yu B, et al. Comparison of cranial facet joint violation rate between percutaneous and open pedicle screw placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94 (5):e504.[35] Ito Z, Imagama S, Kanemura T, et al. Bone union rate with autologous iliac bone versus local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF): a multicenter study. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 (5):1158-1163.[36] Myeroff C, Archdeacon M. Autogenous bone graft: donor sites and techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(23): 2227-2236.[37] Tomford WW. Bone allografts: past, present and future. Cell Tissue Bank. 2000;1(2):105-109.[38] Miller LE, Block JE. Safety and effectiveness of bone allografts in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36 (24):2045-2050.[39] Bakhsheshian J, Dahdaleh NS, Fakurnejad S, et al. Evidence-based management of traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures: a systematic review of nonoperative management. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;37(1):E1.[40] 高峰,张智达,任应清,等. 胸腰椎爆裂性骨折后路内固定手术中融合与非融合手术疗效的比较研究[J]. 中国现代医生, 2017, 55(2):56-59. |
.jpg)
.jpg)