中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 985-992.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.07.001
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 下一篇
阿普唑仑治疗焦虑抑郁患者全膝关节置换后疼痛的安全有效性
梁 欣1,2,王 恒3,李显蓉4
- 1西南医科大学护理学院,四川省泸州市 646000;四川射洪县中医院,2手术室,3骨科,四川省遂宁市 629200;4西南医科大学附属医院胃肠外科,四川省泸州市 646000
Preoperative application of alprazolam for patients with anxiety and depression and pain after total knee arthroplasty: its safety and effectiveness
Liang Xin1, 2, Wang Heng3, Li Xian-rong4
- 1School of Nursing, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Operation Room, 3Department of Orthopedics, Shehong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Sichuan Province, Suining 629200, Sichuan Province, China; 4Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 64600, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
全膝关节置换后疼痛:全膝关节置换是骨关节炎中晚期治疗的首选手段。尽管全膝关节置换可以减少疼痛,改善运动功能,但其存在术后近远期并发症。研究提示有19%-30%接受全膝关节置换的患者在术后承受中重度的疼痛,术后疼痛导致依从性下降、镇痛药物使用过量等。目前围手术期疼痛管理存在缺乏规范化标准方案、治疗靶点较为单一、治疗滞后性等问题,因此有必要研究和发展新型疼痛管理方法。
焦虑抑郁状态:焦虑抑郁状态可以敏化中枢性疼痛。研究表明,焦虑抑郁状态可能影响全膝关节置换术后关节功能恢复,而骨科就诊患者抑郁焦虑状态存在比例较高,提示焦虑、抑郁以及疼痛相互影响,协同加重。虽然焦虑抑郁与慢性疼痛具有高度并存性,但是其具体发生机制仍不清楚。
摘要
背景:心理因素影响全膝关节置换后患者疼痛程度,干预围手术期心理状态对置换后疼痛以及关节功能的影响尚未见大量报道。
目的:观察阿普唑仑干预全膝关节置换前具有焦虑抑郁状态患者的安全性和有效性。
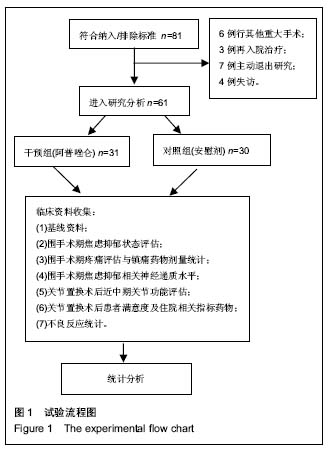
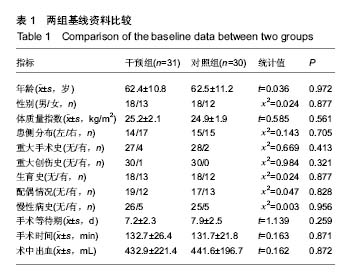
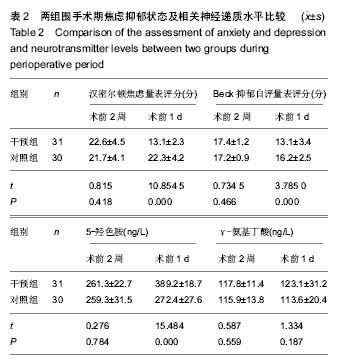
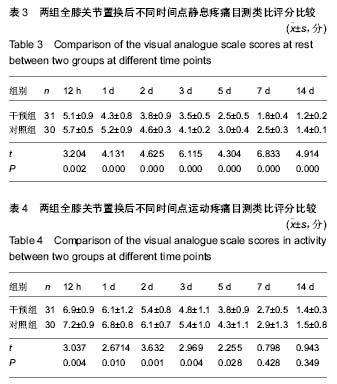
方法:选择61例单侧全膝关节置换前存在焦虑抑郁状态的患者,随机分为2组,术前2周干预组予以阿普唑仑片,对照组予以安慰剂。收集基线资料、手术相关资料,术前汉密尔顿评分和Beck抑郁量表评估焦虑抑郁状态变化,术后评估2组患者各时间点静息和活动时的疼痛评分,统计术后非类固醇镇痛药物和静脉自控镇痛泵使用情况,ELISA法检测外周血神经递质,利用相关量表评估关节置换后近中期关节功能,统计患者满意度和住院相关指标,检测药物不良反应。
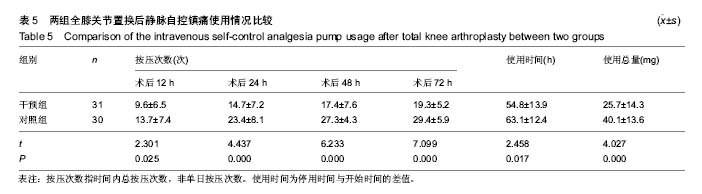
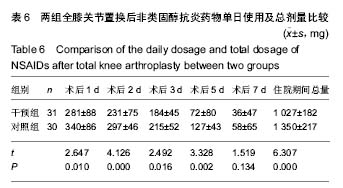
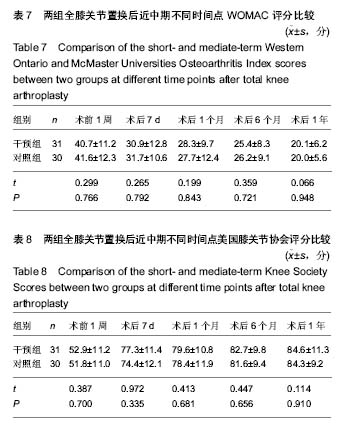
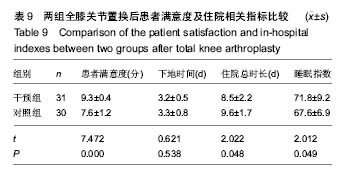
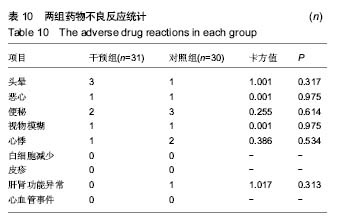
结果与结论:①应用阿普唑仑后干预组焦虑抑郁状态有显著改善;干预后2周干预组外周血5-羟色胺和γ-氨基丁酸水平上升;②术后12 h、1 d、2 d、3 d、5 d、7 d时干预组静息疼痛目测类比评分显著低于对照组(P < 0.05);术后12 h、1 d、2 d、3 d、5 d时干预组运动疼痛目测类比评分显著低于对照组(P < 0.05);③干预组镇痛泵及镇痛药物使用均显著少于对照组,镇痛药物使用剂量与术前焦虑抑郁状态具有相关性;④2组术后西安大略-麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数和美国膝关节协会评分差异无显著性意义;⑤全膝关节置换后干预组满意度、睡眠指数、住院总时长等指标优于对照组。用药期间未见明显不良反应;⑥结果提示,对于全膝关节置换前诊断为焦虑抑郁状态的患者,置换前予以阿普唑仑干预可以缓解焦虑抑郁,改善围手术期静息和运动疼痛,减少术后镇痛药物的使用,增加患者满意度。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-0552-655X(梁欣)
中图分类号:
.jpg)