| [1]费小琛,颜永年,熊卓,等.骨组织工程PLGA/TCP复合材料的性能研究[J].材料导报,2003,17(12): 76-79.[2]贾帅军,孟国林,刘建,等.胶原修饰快速成形PLGA/TCP人工骨支架体外生物相容性研究[J].科学技术与工程, 2009,9(12):3207-3211.[3]Tali R, Yael KI, Emil R, et al. Chondrogenesis of hMSC in affinity-bound TGF-beta scaffolds. Biomaterials.2012;33(3): 751-761.[4]黄永辉,夏青,沈铁城,等. 人骨髓间充质干细胞接种纳米晶胶原骨构建组织工程骨[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2008,5(1): 1-3.[5]Kim HJ, Kim UJ, Kim HS, et al. Bone tissue engineering with premineralized silk scaffolds. Bone.2008;42(6): 1226-1234.[6]Robert F.Service.Tissue engineers build new bone. Science. 2000;289 (5984) :1498-1500.[7]Langer R, Vacanti JP.Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260: 920-926.[8]Martin I, Wendt D, Heberer M.The role of bioreactors in tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol.2004;22(2) :80-86.[9]Chen HC, Hu YC.Bioreactors for tissue engineering. Biotechnol Lett.2006;28 (18) :1415-1423.[10]Bilodeau K, Mantovan D.Bioreactors for tissue engineering: focus on mechanical constraints. A comparative review. Tissue Eng.2006;12(8):2367-2383.[11]王妍,伍活廉,张丽君,等. 一种生物反应罐;中国, 201420151906. 9[P].2014-11-12.[12]刘晓晨,贾文霄,金格勒,等.MRI、CT、X线对兔腰椎融合术后的比较性实验研究[J].中国医学计算机像,2011,17(1):75-79.[13]韩耀坤,贾秀月,娄大力,等.同种异体骨髓基质干细胞治疗骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国病案,2012,13(8):61-63.[14]车向新,曹俊,黄小林,等.自制诱导型人工骨材料修复兔颅骨缺损实验研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2013,23(14):11-17.[15]王飞,王妍,程律莎,等. hMSCs的成骨定向分化及与PLGA/TCP的相容性[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版,2014, 42(11): 143-148.[16]Wang F,Zhang LJ, Wang Y,et al. Feeder-Culture Bioreactors Inducing Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Polylactic Glycolic Acid/Tricalcium Phosphate (PLGA/TCP) Scaffolds. Journal of biomaterials and tissue engineering. 2015;5(7): 557-564.[17]Das S,Hollister S,Flangan C.Freeform fabrication of Nylon-6 tissue engineering scaffolds.Rapid Prototyping J.2003;9(1): 43-49.[18]Nam YS,Park TG.Biodegradable poiymeric microcellular foams by modified thermally induced phase separation method.Biomaterials.1999;20(19):1783-1790.[19]Mikos AG, Thorsen AJ, Czerwonka LA, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Poly (L -Lactic Acid) Foams. Polymer. 1994;35(5):1068-1077.[20]Doshi J, Reneker DH. Electrospinning Process and Applications of Electrospun Fibers. Electrostatics. 1995; 35(2-3):151-160.[21]Hutmacher DW, Schantz T, Zein I, et al. Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling. J Biomed Mater Res.2001;55(2):203-216.[22]Li S. Hydrolytic degradation characteristics of aliphatic polyesters derived from lactic and glycolic acids. J Biomed Mater Res.1999;48(3):342-353.[23]Attawia MA, Herbert KM, Laurencin CT. Osteoblast-like cell adherance and migration through 3-dimensional porous polymer matrices. BiochemBiophys Res Commun. 1996;8(1):63-75. [24]陈思诗,杨庆,沈新元,等.溶剂浇铸-粒子沥滤法制备PBS/PCL组织工程支架[J]. 东华大学学报,2009,35(4):391-395.[25]Huang YC,Mooney DJ.Gas foaming to fabricate polymer scaffolds in tissue engineering. Scaffoldings in tissue engineering.2005:159.[26]Bose S, Vahabzadeh S, Bandyopadhyay A.Bone tissue engineering using 3D Printing. Materials Today.2013;16 (12) :496-504.[27]Tarafder S,Balla VK,Davies NM.Microwave Sintered 3D Printed Tricalcium Phosphate Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2013;7(8): 631–641.[28]Cox SC, Thornby JA, Gibbons GJ, et al.3D printing of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds intended for use in bone tissue engineering applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;47:237-247.[29]Inzana A, Olvera D, Fuller M.3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials.2014;35(13):4026-4034.[30]宋克东,刘庆天,李香琴,等.新型旋转式生物反应器内三维组织工程骨的构建[J].生物化学与生物物理进展, 2004,31(11): 996-1005.[31]Rauh J,Milan F,Günther KP.Bioreactor systems for bone tissue engineering.Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews.2011; 17(4):263-280.[32]Zhang ZY, Teoh SH, Teo EY, et al.A comparison of bioreactors for culture of fetal mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering .Biomaterials.2010;31(33) :8684-8695.[33]Nishi M,Matsumoto R,Dong J,et al.Engineered bone tissue associated with vascularization utilizing a rotating wall vessel bioreactor.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(2):421-427.[34]陈孝平,汪建平.外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2013: 634-635. |
.jpg)

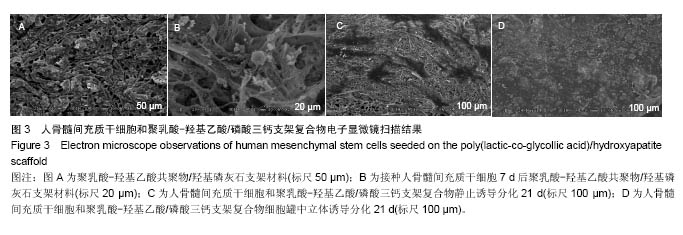
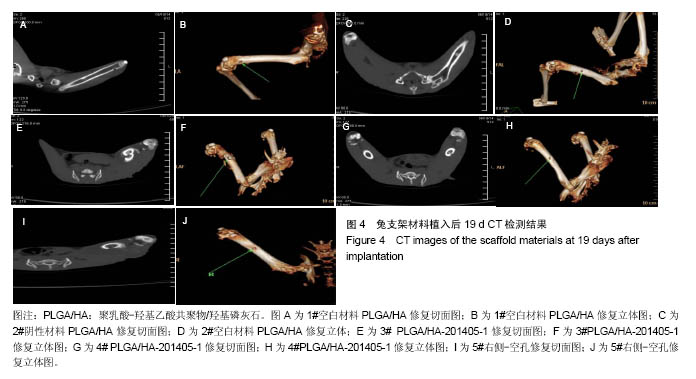
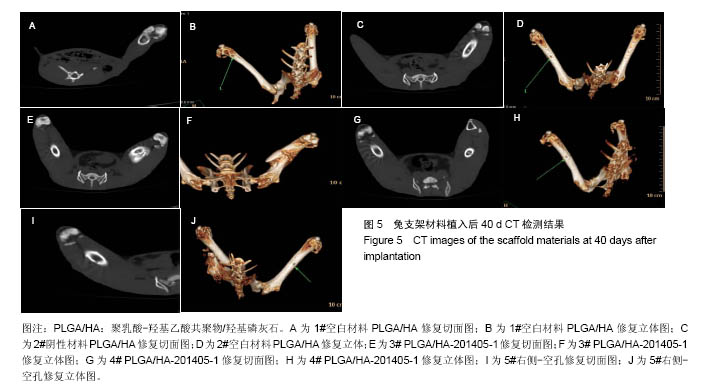
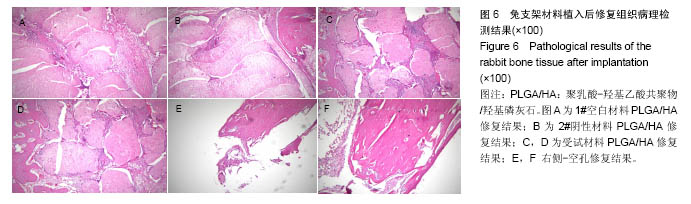
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)