| [1] Raisz LG. Mechanisms and regulation of bone resorption by osteoclastic cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;79(2):287.[2] 赵铭,李博.骨形态生发蛋白圆基因修饰脂肪干细胞对去卵巢骨质疏松性大鼠骨缺损的修复作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2012, 18(8):706-708.[3] 王军.年老性骨质疏松的危险因素发病机制及防治[J].中国老年医学杂志,2008,28(18):1869-1871.[4] 王秀玲.骨质疏松症几种相关基因的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13(5):367-370.[5] 梁芝萍.骨质疏松患者与补钙[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2006, 15(14):1949.[6] Zhao Q,Shao J,Chen W.Osteoclast differentiation andgene regulation. Front Biosci. 2007;12: 2519-2529.[7] 谈志龙,任海龙,白人骁.骨质疏松症与骨代谢生化测定指标[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2006, 2(1):89-93.[8] 马静波.骨质疏松症的治疗和预防概述[J].医师进修杂志,2005, 28(5):9-11.[9] 欧阳钢,王东岩,徐小梅.针灸配合药物治疗男性骨质疏松症疗效观察[J].中国针灸,2011,31(1):23- 25.[10] Ozmen B, Kirmaz C, Aydin K, et al. Influence of the selective ostrogen receptor modulator on IL-6,TNF-alpha,TGF-beta1 and bone turnover markers in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Eur Cytekine Netw. 2007; 18(3):148-153.[11] Xian XH, Dong XB, Qin Z, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of MHC Ⅱ Exon 2 of DQA gene in cricetulus barabensis. Qufu Shifan Daxue Xuebao. 2009;35(2):98-103.[12] 蔺辉星,周振雷.Rnux2研究进展[J].中国畜牧兽医, 2009,36(2): 53-57.[13] Amorim BR, Okamura H, Yoshida K, et al. The transcript ional fact or Osterix direct ly int eracts with RNA helicase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;355( 2) : 347-351.[14] Asanuma K, Yanagida-Asanuma E, Faul C, et al. Synaptopodin orchestrates actin organization and cell motility via regulation of RhoA signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(5): 485-491.[15] Mustafa G, Khan PA, Iqbal I, et al. Simplified quantification of urinary protein excretion in children with nephrotic syndrome. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2007;17(10): 615-618.[16] Biswas A, Kumar R, Chaterjee A, et al. Quantitation of proteinuria in nephrotic syndrome by spot urine protein creatinine ratio estimation in children. Mymensingh Med J. 2009;18(1):67-71.[17] 童培建,肖鲁伟,孙益.特异性抑制ATP6i 慢病毒治疗局部骨质疏松的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2009,15(5):322-326.[18] Wei YF, Liu YL, Zhang SH, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on pIasma estrin and bone mineral density in ovariectomized rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu(Acupunct Res, Chin). 2007;32(1):38-41.[19] Strioga MM,Viswanathan S,Darinskas A,et al.Same or not the same Comparison of adipose tissue- derived versus bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem and stromal cells.Stem Celts Dev. 2012.[20] Sang IL, Duck SK, Hwa JL, et al. The Role of Thymosin Beta 4 on Odontogenic Differentiation in Human Dental Pulp Cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(4): 210-215.[21] Liu JZ, Zhao L, Ni L, et al. The effect of synthetic α-tricalcium phosphate on osteogenic differentiation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2015; 7(9): 1588-1601.[22] Xiaojian H, Min C, Tao H. Lentivirus-mediated RNAi knockdown of the gap junction protein, Cx43, attenuates the development of vascular restenosis following balloon injury. Int J Mol Med.2015; 35(4): 885-892.[23] 苏玲,屠伟峰,陈茜,等.右美托咪定及其联合舒芬太尼预先给药对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].中华麻醉学会杂志,2013, 33(5):622-625.[24] Turnbull IR, Clark AT, Stromberg PE, et al. Effects of aging on the immunopathologic response to sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(3): 1018-1023.[25] Liu WH, Hei ZQ, Nie H, et al. Berberine ameliorates renal injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by suppression of both oxidative stress and aldose reductase. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008;121(8):706-712.[26] 王莉. 华勒变性及少突胶质前体细胞和雪旺细胞移植[D].上海交通大学, 2008.[27] 李军. 嗅鞘细胞蛛网膜下腔移植治疗脊髓损伤的实验研究[D]. 泰山医学院, 2011.[28] 王军.年老性骨质疏松的危险因素发病机制及防治[J].中国老年医学杂志, 2008,28(18):1869-1871.[29] 陈晋明,王世平,马丽珍,等.虾青素的抗氧化活性研究[J].营养学报, 2007,29(2):35-38.[30] Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, et al. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States,2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22: 465-475. [31] Bunnell BA, Estes BT, Guilak F, et al. Differentiation of adipose stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;456:155-171.[32] Tanabe N, Maeno M, Suzuki N, et al. IL-1alpha stimulates theformation of osteoclast-like cells by increasing M-CSF and PGE(2)production and decreasing OPG production by osteoblasts. Life Sci. 2005;24:615-626.[33] Park KJ,Krishnan V,O Malley BW,et al.Formation of an IKKalpha-dependent transcription complex is required for estrogen receptor-mediated gene activation.Mol Cell. 2005;18: 71-82.[34] Weitzmann MN,Pacifici R.T cells:unexpected players in the bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency and in basal bone homeostasis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1116: 360-375.[35] 甘露.间充质干细胞治疗急性肾损伤的临床应用可行性探讨[J].特别健康, 2014,3(3):39.[36] Lee SK,Kim Y,Kim SS,et al.Differential expression of cell surface proteins in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured with or without basic fibroblast growth factor containing medium. Proteomics. 2009;9(18):4389-4405.[37] 毛家玺,汤晓静.干细胞在急性肾损伤中的治疗作用及进展[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2012,13(1):86-88.[38] Xu XY, Shao N, Qiao D, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in extra mammary Paget disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8(3):3062-3068.[39] Alessandro T, Paola P. Biochemical markers in the follow up of the osteoporotic patients. Clin Cases Mineral Bone Metubol. 2012;9(2): 80-84. |
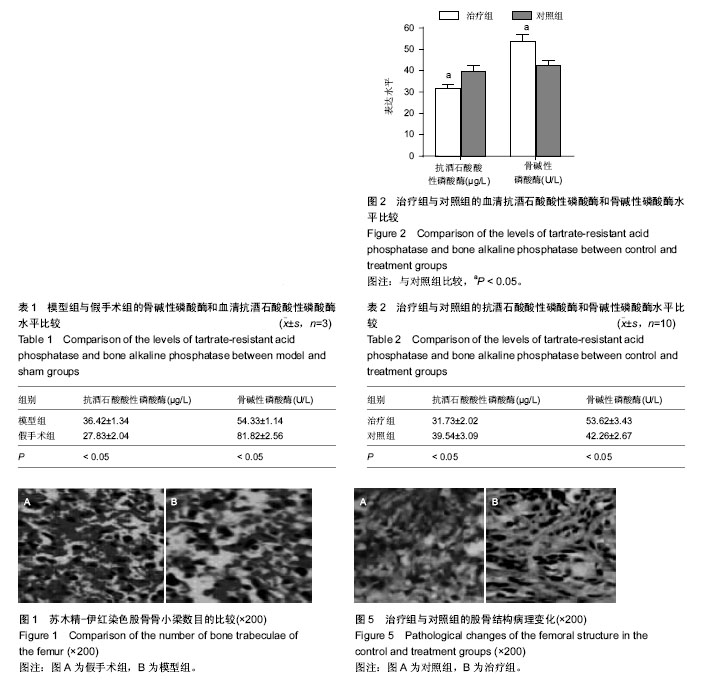
.jpg)
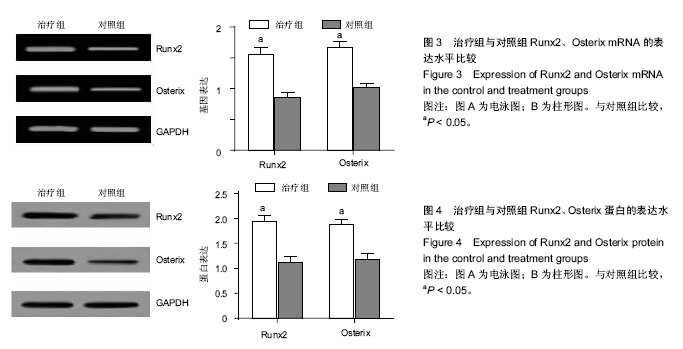
.jpg)