中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (49): 7364-7370.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.49.010
• 运动医学动物模型 Animal models of sports medicine • 上一篇 下一篇
不同强度有氧运动周期训练疲劳模型大鼠心肌形态变化及超量恢复规律
张 静1,张丽娜2,阳仁均2,胡 尧1
- 1成都中医药大学,四川省成都市 611137;2成都体育学院,四川省成都市 610041
Morphological changes of myocardium and over-recovery law in model rats undergoing different intensities of periodic aerobic training
Zhang Jing1, Zhang Li-na2, Yang Ren-jun2, Hu Yao1
- 1Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611137, Sichuan Province, China; 2Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
有氧运动:是指人体在氧气充分供应的情况下进行的体育锻炼。即在运动过程中,人体吸入的氧气与需求相等,达到生理上的平衡状态。简单来说,有氧运动是指任何富韵律性的运动,其运动时间较长(约15 min或以上),运动强度在中等或中上的程度(最大心率的60%-80%)。有氧运动是一种恒常运动,是持续5 min以上还有余力的运动。
超量恢复理论:是在运动训练后的恢复期,机体内的磷酸原、肌糖原贮备、氧合肌红蛋白、乳酸的再利用、结构蛋白及酶蛋白等物质,通过一段时间的恢复而出现消耗的能源物质和机体的机能状态超过原来的水平的现象。在超量恢复阶段,机体内的能源物质的水平与运动训练前相比有比较大的增加,对机体工作能力的提高有很大帮助,对运动训练的安排和进行体育比赛有科学的指导意义。
文题释义:
有氧运动:是指人体在氧气充分供应的情况下进行的体育锻炼。即在运动过程中,人体吸入的氧气与需求相等,达到生理上的平衡状态。简单来说,有氧运动是指任何富韵律性的运动,其运动时间较长(约15 min或以上),运动强度在中等或中上的程度(最大心率的60%-80%)。有氧运动是一种恒常运动,是持续5 min以上还有余力的运动。
超量恢复理论:是在运动训练后的恢复期,机体内的磷酸原、肌糖原贮备、氧合肌红蛋白、乳酸的再利用、结构蛋白及酶蛋白等物质,通过一段时间的恢复而出现消耗的能源物质和机体的机能状态超过原来的水平的现象。在超量恢复阶段,机体内的能源物质的水平与运动训练前相比有比较大的增加,对机体工作能力的提高有很大帮助,对运动训练的安排和进行体育比赛有科学的指导意义。
.jpg) 文题释义:
有氧运动:是指人体在氧气充分供应的情况下进行的体育锻炼。即在运动过程中,人体吸入的氧气与需求相等,达到生理上的平衡状态。简单来说,有氧运动是指任何富韵律性的运动,其运动时间较长(约15 min或以上),运动强度在中等或中上的程度(最大心率的60%-80%)。有氧运动是一种恒常运动,是持续5 min以上还有余力的运动。
超量恢复理论:是在运动训练后的恢复期,机体内的磷酸原、肌糖原贮备、氧合肌红蛋白、乳酸的再利用、结构蛋白及酶蛋白等物质,通过一段时间的恢复而出现消耗的能源物质和机体的机能状态超过原来的水平的现象。在超量恢复阶段,机体内的能源物质的水平与运动训练前相比有比较大的增加,对机体工作能力的提高有很大帮助,对运动训练的安排和进行体育比赛有科学的指导意义。
文题释义:
有氧运动:是指人体在氧气充分供应的情况下进行的体育锻炼。即在运动过程中,人体吸入的氧气与需求相等,达到生理上的平衡状态。简单来说,有氧运动是指任何富韵律性的运动,其运动时间较长(约15 min或以上),运动强度在中等或中上的程度(最大心率的60%-80%)。有氧运动是一种恒常运动,是持续5 min以上还有余力的运动。
超量恢复理论:是在运动训练后的恢复期,机体内的磷酸原、肌糖原贮备、氧合肌红蛋白、乳酸的再利用、结构蛋白及酶蛋白等物质,通过一段时间的恢复而出现消耗的能源物质和机体的机能状态超过原来的水平的现象。在超量恢复阶段,机体内的能源物质的水平与运动训练前相比有比较大的增加,对机体工作能力的提高有很大帮助,对运动训练的安排和进行体育比赛有科学的指导意义。摘要
背景:“超量恢复理论”是运动训练的基础理论,而有关内脏的超量恢复研究较少,心脏在有氧运动训练后的超量恢复更是鲜见报道。
目的:观察不同有氧运动周期训练后大鼠心肌组织的形态改变,以及心脏功能在训练结束后连续72 h的恢复规律。
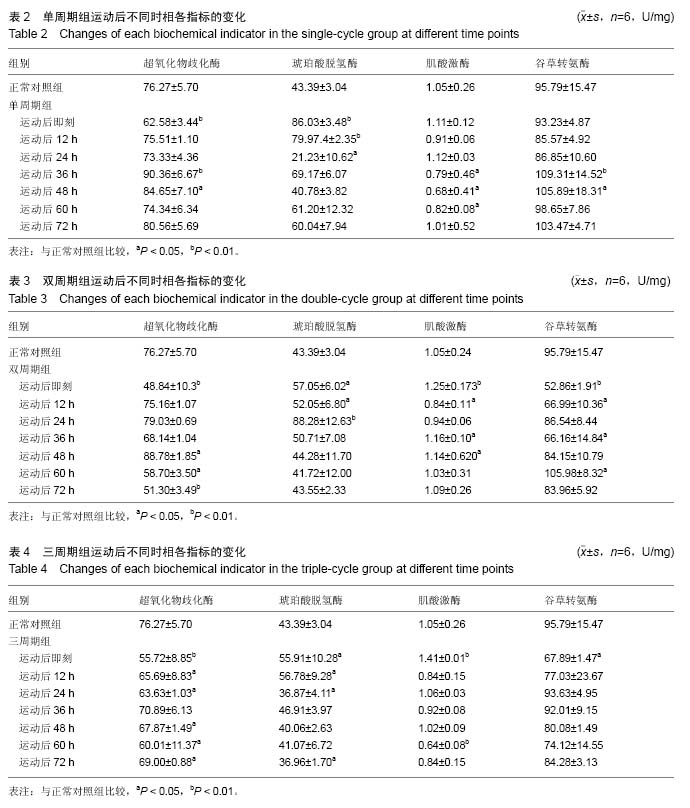
方法:将132只SD大鼠随机分为正常对照组(n=6)、单周期组(n=42)、双周期组(n=42)及三周期组(n=42),后3组按照递增负荷的方式(从负重3%到负重6%)进行为期1周的适应性游泳,然后进行以有氧运动为主的游泳运动模型,按各自不同运动量的训练周期对大鼠进行周期性游泳训练,单周期组的训练强度最小,三周期组训练强度最大,双周期组训练强度居中。训练后于设定时间点进行取材,测定心肌组织肌酸激酶、超氧化物岐化酶、琥珀酸脱氢酶、谷草转氨酶的变化;取左心尖部分组织经包埋切片后行苏木精-伊红染色观察。
结果与结论:①运动后即刻:随着训练强度的增大,心肌组织的病理改变更明显;②单周期组超氧化物岐化酶、琥珀酸脱氢酶、谷草转氨酶出现超量恢复,且显著高于正常对照组(P < 0.05),其超量恢复出现在运动后12-36 h;双周期组各指标均出现超量恢复,显著高于正常对照组(P < 0.05),其超量恢复出现时间点在运动后24-48 h;三周期组仅琥珀酸脱氢酶在12 h出现超量恢复(P < 0.05),其余指标均未出现超量恢复,且各项指标在整个恢复过程中持续低迷,疑似出现过度疲劳;③结果表明,三周期组训练强度过大,单周期及双周期组训练安排以双周期较好,建议实际有氧运动训练采用双周期训练模式。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4286-0215(胡尧)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
有氧运动:是指人体在氧气充分供应的情况下进行的体育锻炼。即在运动过程中,人体吸入的氧气与需求相等,达到生理上的平衡状态。简单来说,有氧运动是指任何富韵律性的运动,其运动时间较长(约15 min或以上),运动强度在中等或中上的程度(最大心率的60%-80%)。有氧运动是一种恒常运动,是持续5 min以上还有余力的运动。
超量恢复理论:是在运动训练后的恢复期,机体内的磷酸原、肌糖原贮备、氧合肌红蛋白、乳酸的再利用、结构蛋白及酶蛋白等物质,通过一段时间的恢复而出现消耗的能源物质和机体的机能状态超过原来的水平的现象。在超量恢复阶段,机体内的能源物质的水平与运动训练前相比有比较大的增加,对机体工作能力的提高有很大帮助,对运动训练的安排和进行体育比赛有科学的指导意义。
文题释义:
有氧运动:是指人体在氧气充分供应的情况下进行的体育锻炼。即在运动过程中,人体吸入的氧气与需求相等,达到生理上的平衡状态。简单来说,有氧运动是指任何富韵律性的运动,其运动时间较长(约15 min或以上),运动强度在中等或中上的程度(最大心率的60%-80%)。有氧运动是一种恒常运动,是持续5 min以上还有余力的运动。
超量恢复理论:是在运动训练后的恢复期,机体内的磷酸原、肌糖原贮备、氧合肌红蛋白、乳酸的再利用、结构蛋白及酶蛋白等物质,通过一段时间的恢复而出现消耗的能源物质和机体的机能状态超过原来的水平的现象。在超量恢复阶段,机体内的能源物质的水平与运动训练前相比有比较大的增加,对机体工作能力的提高有很大帮助,对运动训练的安排和进行体育比赛有科学的指导意义。