| [1] 刘磊,孙琳, 孙记航,等.1-6岁正常小儿胸椎椎弓根形态学研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(8):713-717.
[2] Fuster S, Vega A, Barrios G, et al.Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion in the thoracolumbar spine using image-guided navigation.Neurocirugia (Astur). 2010; 21(4):306-311.
[3] 史金辉,杨慧林,王根林,等.椎弓根内固定治疗合并脊髓损伤的胸腰椎骨折[J].国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(20): 1531-1532.
[4] 刘洪涛,镇万新,朱杰诚,等.经皮椎弓根内固定术在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(16): 1227-1229.
[5] 任东风,史亚民,侯树勋,等.后路短节段椎弓根内固定治疗无神经损伤胸腰段爆裂骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2005,20(2):86-87.
[6] 张雪松,王岩,张永刚,等.全节段椎弓根螺钉与椎弓根钉、钩系统矫治单胸弯特发性脊柱侧凸的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(3):182-186.
[7] Venmans A, Klazen CA, van Rooij WJ, et al. Postprocedural CT for perivertebral cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty is not necessary-- results from VERTOS II. Neuroradiology. 2011; 53(1):19-22.
[8] 王建华,夏虹,吴增晖,等.数字骨科技术在儿童上颈椎手术中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(6): 516-519.
[9] 夏天,王雷,董双海,等.椎间孔扩大减压结合改良经椎间孔腰椎椎体间融合术治疗退变性腰椎管狭窄症(22例3年以上随访)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(24): 2242-2245.
[10] Li SG, Sheng L, Zhao H, et al. Clinical applications of computer-assisted navigation technique in spinal pedicle screw internal fixation. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009;89(11):736-739.
[11] 樊友亮,丁亮华,何双华,等.腰椎后部结构生物力学研究进展及其临床意义[J].中国医师进修杂志,2011,34(11): 75-77.
[12] Li Q, Liu Y, Chu Z, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with transpedicular intervertebral bone graft and pedicle screws fixation in injured vertebrae. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011; 25(8):956-959.
[13] 张元智,杨勇,刘瑞,等.导航模板在单侧髋关节发育不良全髋置换术中的初步应用[J].内蒙古医学院学报,2010, 32(1):21-27.
[14] Zencica P, Chaloupka R, Hladíková J, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbosacral fusion in spondylolisthesis: a retrospective radiological and clinical analysis. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010;77(2):124-130.
[15] Fan Chiang CY, Tsai TT, Chen LH, et al. Computed tomography-based navigation-assisted pedicle screw insertion for thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. Chang Gung Med J. 2012;35(4):332-338.
[16] 秦毅,李勇,李振宇,等.微创后路固定联合前路病灶清除植骨融合治疗胸腰段脊柱结核[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014, 22(7):659-661,667.
[17] Ghaith el-S, Hodgson S, Sharp M. Laser surface alloying of 316L stainless steel coated with a bioactive hydroxyapatite-titanium oxide composite. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2):83.
[18] Melo RDS, Silva PWAD, Toscano CFDS.Avaliação postural da coluna vertebral em crianças e adolescentes com deficiência auditiva.Arquivos Int Otorrinolaringol. 2011; 15(2):195-202.
[19] Puelma F,Olave E. Relaciones del Origen del Tronco Celiaco, Arterias Mesentéricas y Renales con la Columna Vertebral en Individuos Chilenos. Int J Morphol. 2010;28(4):1227-1234.
[20] 史亚民,侯树勋,韦兴,等.青少年胸椎椎弓根影像学特征及其临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003, 11(21): 1469-1472.
[21] 蔡志群,马琪峰.一期前路病灶清除钛网植入治疗胸腰椎结核[J].按摩与康复医学:下旬刊,2010,1(4): 101-102.
[22] 王建华,夏虹,吴增晖,等.数字骨科技术在儿童上颈椎手术中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(6): 516-519.
[23] 郭新军,朱振军.人工珊瑚骨内固定手术治疗脊柱结核的临床效果分析[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(10): 2628-2629,2631.
[24] Park JH, Jeon SR, Roh SW, et al. The safety and accuracy of freehand pedicle screw placement in the subaxial cervical spine: a series of 45 consecutive patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(4):280-285.
[25] 陈世忠.椎间融合器与单纯椎间植骨法治疗退变性腰椎滑脱症的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010, 25(5):439-440.
[26] 邓必权,胡华,滕宇,等.椎弓根螺钉复位内固定后单纯植骨融合与椎间融合器融合治疗腰椎滑脱症的疗效比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(7):1823-1825.
[27] Botolin S, Merritt C, Erickson M. Aseptic loosening of pedicle screw as a result of metal wear debris in a pediatric patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(1): E38-42.
[28] 叶斌,孟祥龙,刘玉增,等.徒手置钉技术在脊柱畸形矫正中的准确性与安全性研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2014,12(1): 25-34.
[29] Larson AN, Polly DW Jr, Guidera KJ, et al. The accuracy of navigation and 3D image-guided placement for the placement of pedicle screws in congenital spine deformity. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012; 32(6):e23-29.
[30] Zwingmann J, Hauschild O, Bode G, et al. Malposition and revision rates of different imaging modalities for percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation following pelvic fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133(9):1257-1265.
[31] 池永龙,徐华梓,林焱,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的初步探讨[J].中华外科杂志,2004,42(21): 1307-1311.
[32] Zhang QS, Lü GH, Wang XB, et al. The significance of removing ruptured intervertebral discs for interbody fusion in treating thoracic or lumbar type B and C spinal injuries through a one-stage posterior approach. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e97275.
[33] 吴静,茅金宝,孔祥云,等.导航与普通透视对手术室医务人员放射量的对比分析[J].医学影像学杂志,2013,23(10): 1631-1634.
[34] Van de Kelft E, Costa F, Van der Planken D, et al. A prospective multicenter registry on the accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral levels with the use of the O-arm imaging system and StealthStation Navigation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(25):E1580-1587.
[35] Villavicencio AT, Serxner BJ, Mason A, et al. Unilateral and bilateral pedicle screw fixation in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: radiographic and clinical analysis. World Neurosurg. 2015;83(4):553-559.
[36] 叶斌,孟祥龙,刘玉增,等.徒手置钉技术在脊柱畸形矫正中的准确性与安全性研究[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2014,12(1): 25-34.
[37] Allam Y, Silbermann J, Riese F, et al. Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in thoracic spine: comparison between free hand and a generic 3D-based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):648-653.
[38] Tse EY, Cheung WY, Ng KF, et al. Reducing perioperative blood loss and allogeneic blood transfusion in patients undergoing major spine surgery.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(13): 1268-1277.
[39] Ee WW, Lau WL, Yeo W, et al. Does minimally invasive surgery have a lower risk of surgical site infections compared with open spinal surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(6):1718-1724.
[40] Zwingmann J, Hauschild O, Bode G, et al. Malposition and revision rates of different imaging modalities for percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation following pelvic fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(9):1257-1265. |
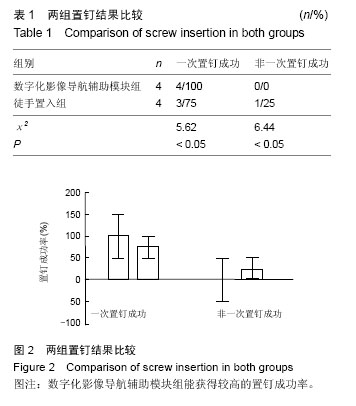
.jpg)
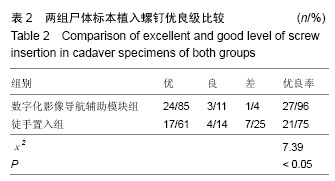
.jpg)
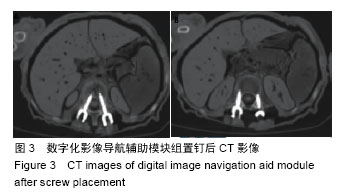
.jpg)