中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (21): 3163-3170.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.21.018
• 材料力学及表面改性 material mechanics and surface modification • 上一篇 下一篇
基于CT颅内动脉瘤支架的表面剪切应力分析
魏 赫,木合塔尔•克力木,刘小月
- 新疆大学机械工程学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830047
Surface shear stress of intracranial aneurysm stent based on CT data
Wei He, Muhetaer Kelimu, Liu Xiao-yue
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 剪切应力:物体由于外因(载荷、温度变化等)而变形时,在它内部任一截面(剪切面)的两方出现的相互作用力,称为“内力”。内力的集度,即单位面积上受到的内力称为“应力”。应力可分解为垂直于截面(剪切面)的分量,称为“正应力”或“法向应力”;相切于截面(剪切面)的分量,称为“剪切应力”。 支架置入后血管再狭窄:再狭窄问题主要由于作为异物的支架置入人体血管并撑开后,对血管内壁细胞造成了一定的损伤,触发人体自愈功能,血管内壁的大量平滑肌再次从新组织朝损伤部位移动,同时支架置入一定时间后,血液内的血小板在支架表面汇聚并释放相应的因子,导致了支架置入血管后再狭窄问题的出现。
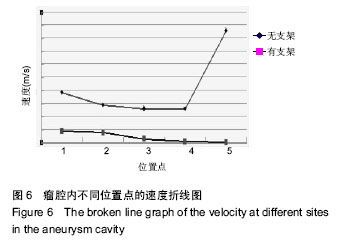
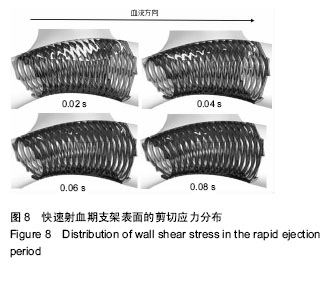
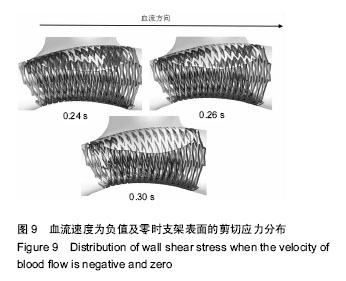
背景:动脉瘤中置入支架后血液流动状态的改变,为研究支架置入后再狭窄的发生提供了前提和条件,而数值模拟分析是一种很好的技术手段。 目的:探究支架置入对个体化颅内动脉瘤血液动力学的影响,以及支架表面剪切应力的分布特征。 方法:依据1例颅内动脉瘤患者的CT影像数据,进行数据的提取、优化,建立个体化颅内动脉瘤实体化模型;设计矩形截面螺旋形支架的三维模型,并通过布尔运算,得到带有支架的动脉瘤模型,并通过对该模型支架表面剪切应力的分布情况来分析再狭窄发生的可能。 结果与结论:通过探究不同血流速度与血液黏度对支架表面剪切应力的影响发现,在同一个时刻中支架表面大于40 Pa的剪切应力区域,随血流速度和血液黏度的增大而增大;而剪切应力不足0.5 Pa的区域,随血液黏度的增大有所减小,当速度为0时分布最大。该支架对于动脉瘤的生长或破裂起到了抑制作用,但发生再狭窄的区域很大,需要对支架进行优化或从新选型,以使支架的剪切应力保持在0.5-40 Pa的理想范围之中,并保证在心动周期的不同时刻里剪切应力的脉动变化尽可能减小,以达到防止支架置入后发生血管内部的再狭窄目的。
中图分类号:



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)