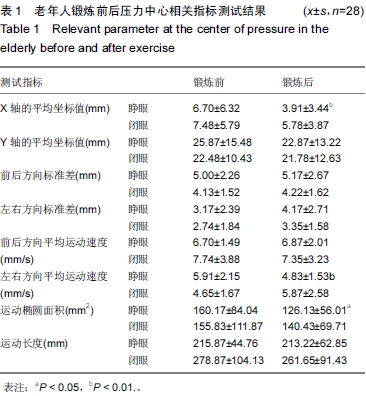
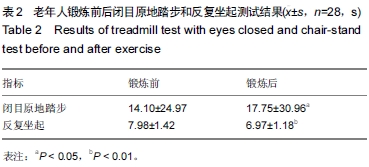
| [1] Gregg EW, Pereira MA, Casper Sen CJ. Physical activity, falls, and fractures among older adults: A review of the epidemiologic evidence. J Am Geriatr Soc.2000,48(8): 883-893.
[2] Rubenstein LZ, Josephson KR. The epidemiology of falls and syncope. Clin Geriatr Med.2002;18(2):141-158.
[3] 张敏,李彬.老年人随年龄增长骨量变化与健骨运动的研究进展[J].湖北体育科技,2005,24(3):327-329.
[4] Day L, Fildes B, Gordon I, et al. Randomized factorial trial of falls prevention among older people living in their own homes. BMJ.2002;325(7356)128-131.
[5] Barnett A, Smith B, Lord SR,et al. Community-based group exercise improves balance and reduces falls in at risk older people: a randomized controlled trial. Age Ageing.2003, 32(4):407-414.
[6] 鲍勃•安德森.拉伸:最好的运动[M].北京:北京科学技术出版社, 2010.
[7] 罗伯特•麦卡蒂 杰夫•沙兰德.易化牵伸术[M].北京:人民体育出版社,2010.
[8] 王盛,杨菊,朱奕.平衡反馈训练仪用于脑损伤偏瘫患者静态平衡测试的信度与效度研究[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2011,26(11): 1035-1038.
[9] 朱晓军,朱奕,王盛,等.三维运动分析系统用于平衡检测的信度与效度研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2012,04:315-319.
[10] 杨婷,钱兴皋,张会慧,等.平衡反馈训练仪与Berg平衡量表在评定脑卒中偏瘫患者平衡功能中的相关性[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2012,11:1011-1014.
[11] 张丽,瓮长水,彭楠,等.老年静态平衡功能定量测定及年龄相关性分析[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2011,03:258-261.
[12] 肖春梅,李阳,党繁义.老年人跌倒与平衡能力下降的相关测试指标[J].中国康复医学杂志,2003,18(8):457-459.
[13] 张雪琴,田磊.城市高龄老人上下肢力量的调查与分析[J].江苏教育学院学报:自然科学版,2009,26(4):32-33.
[14] 赵媛,王燕,徐旭东,刘雅莉.太极拳运动对老年人平衡功能和跌倒预防效果的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志,2013,03:339-345.
[15] 姚波,金建明,霍文璟,等.老年人下肢伸膝肌力对平衡功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2006,28(7):466-468.
[16] 张彩芳.太极拳对老年人平衡能力的影响研究[D].北京:首都体育学院,2011.
[17] 张丽芬.八段锦对老年人平衡能力的影响研究[D].北京:首都体育学院,2012.
[18] 庞丹丹.太极拳运动对中老年人静态平衡能力影响的实验研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2011.
[19] 周崇山.太极拳运动与健身秧歌对部分中老年妇女平衡能力影响的对比研究[D].石家庄,河北师范大学,2007.
[20] 李静.不同运动项目提高老年人平衡能力的调查[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(18):2678-2679.
[21] 朱东,李立,邱丕相,等.上海市区太极拳练习者膝关节疼痛调查分析[J].中国运动医学杂志,2011,30(9): 820-824.
[22] 张胜年,林中宝,袁泳虹.背向行走训练对老年人静态平衡能力及步态的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2008,27(3):304-307.
[23] 李红川,实施弹力带柔性抗阻训练对中老年女性肌肉力量和平衡能力的影响研究[D].成都:成都体育学院,2012.
[24] 刘剑.抗阻伸膝和跖屈练习对老年人柔韧与平衡能力的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2010,33(7):48-50.
[25] 张帆,王长生,叶志强.不同拉伸方式对股后肌群柔韧素质影响的对比试验研究[J].天津体育学院学报,2014,01:61-65+70.
[26] 吕乙林,袁运平,刘永东.动静态伸展运动在高校田径技术教学中的实验研究[J].首都体育学院学报,2003.15(1):78-81.
[27] 李志敢,陈教忠.准备运动引入肌肉静态拉伸对少儿运动能力的影响[J].广州体育学院学报,2005,25(3):18-21.
[28] 王红梅,刘尧.动静力牵拉运动对大学生体质影响的实验研究[J].辽宁体育科技,2006,28(3):27-28.
[29] 邓敏韬.PNF拉伸法对游泳专项学生肩关节柔韧性及肌肉力量训练效果的实验研究[D].天津体育学院,2013.
[30] 刘静.不同拉伸方式作用下下肢刚度与爆发力的关系[D].北京体育大学,2013.
[31] 刘苾川,杜加华,易燕,等.针刺配合牵张运动治疗运动性肌肉拉伤疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2009,24(4):372-373.
[32] Kirmizigil B, Ozcaldiran B, Colakoglu M. Effects of three different stretching techniques on vertical jumping performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2014, 28(5):1263-1271.
[33] Beltrão NB1, Ritti-Dias RM2, Pitangui AC, et al. Correlation between Acute and Short-Term Changes in Flexibility Using Two Stretching Techniques. Int J Sports Med. 2014.
[34] 俞晓杰,吴毅.运动疗法在膝关节骨关节炎中的应用[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2005,27:559-561.
[35] 侯曼,侯佳,王汉玉.36-89岁老年人下肢力量的测试研究[J].中国体育科技,2002,38(6):27-28.
[36] 高炳宏.力量训练、有氧训练和两者结合训练对不经常锻炼的老年人柔韧性的影响[J].上海体育科研,2003(1):67.
[37] Margaret K. Mak, PhD, Pui Ling Ng, MSc. Mediolateral Sway in Single-Leg Stance Is the Best Discriminator of balance performance for Tai-Chi Practitioners.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003;84:683-686.
|