中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 2303-2312.doi: 10.12307/2026.586
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
膝关节周围截骨治疗膝骨关节炎:治疗策略的优化
陈秋函1,2,3,杨 龙2,3,袁代柱2,3,吴展羽2,3,邹梓豪2,3,叶 川2,3
- 1贵州医科大学临床医学院,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2贵州医科大学附属医院骨科,贵州省贵阳市 550004;3贵州医科大学组织工程与干细胞研究中心,贵州省贵阳市 550004
-
收稿日期:2024-12-31接受日期:2025-03-27出版日期:2026-03-28发布日期:2025-09-28 -
通讯作者:叶川,博士生导师,主任医师,贵州医科大学附属医院骨科,贵州省贵阳市 550004;贵州医科大学组织工程与干细胞研究中心,贵州省贵阳市 550004 -
作者简介:陈秋函,男,2000年生,贵州医科大学在读硕士,主要从事关节疾病的基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:贵州省科学技术厅贵州省高层次创新人才(百层次)(黔科合平台人才[2020]6013),项目负责人:叶川
Peri-knee osteotomy for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: optimization of treatment strategies
Chen Qiuhan1, 2, 3, Yang Long2, 3, Yuan Daizhu2, 3, Wu Zhanyu2, 3, Zou Zihao2, 3, Ye Chuan2, 3
- 1Clinical Medical College, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 3Tissue Engineering and Stem Cell Research Center, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-31Accepted:2025-03-27Online:2026-03-28Published:2025-09-28 -
Contact:Ye Chuan, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Tissue Engineering and Stem Cell Research Center, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Chen Qiuhan, Master candidate, Clinical Medical College, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Tissue Engineering and Stem Cell Research Center, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Guizhou Provincial High-level Innovative Talents of Department of Science and Technology of Guizhou Province, No. [2020]6013 (to YC)
摘要:
文题释义:
膝关节周围截骨术:是一种矫正下肢力线和缓解关节负荷的骨科手术,主要应用于早中期膝骨关节炎患者或关节畸形矫正。通过调整胫骨或股骨截骨,改善关节应力分布,延缓关节置换的需求。
膝骨关节炎:是中老年人群中常见的退行性关节疾病,以关节软骨退化、骨赘形成及关节间隙狭窄为主要特征,导致患者出现疼痛、功能障碍,严重影响生活质量。随着人口老龄化进程加快,膝骨关节炎的发病率逐年升高,早期诊断和治疗策略的优化已成为骨科领域的重要研究热点。
摘要
背景:随着保膝理念的兴起,膝关节周围截骨技术凭借其矫正下肢力线、缓解关节负荷、延缓关节置换需求的优势,逐渐成为治疗早中期膝骨关节炎的重要方法。
目的:综述不同膝关节周围截骨技术的优缺点及其临床效果,为临床实践中选择合适的手术策略提供参考依据。
方法:检索PubMed数据库和中国知网2014-2024年发表的有关膝关节周围截骨治疗膝骨关节炎的相关文献,英文检索词包括“knee osteoarthritis,high tibial osteotomy,distal femur osteotomy,proximal fibula osteotomy,tibial condylar valgus osteotomy,dome shaped high tibial osteotomy,limb alignment correction,joint-preserving surgery”;中文检索词包括“膝关节骨关节炎,胫骨高位截骨术,股骨远端截骨术,腓骨近端截骨术,胫骨髁外翻截骨术,圆顶形截骨术,力线矫正,保膝手术”。按照纳入和排除标准最终纳入108篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①膝关节周围截骨在治疗膝骨关节炎中的疗效已被广泛认可。近年来,通过优化不同术式,包括胫骨高位截骨、股骨远端截骨、腓骨近端截骨,以及创新性的腘肌前经胫骨结节高位截骨,临床效果得到了显著提升。②这些术式可通过矫正下肢力线和优化膝关节负重分布,有效缓解疼痛并改善患者的功能活动;然而,术后并发症如外侧合页骨折、髌骨低位以及矫正不足等问题仍需重点关注;随着个性化截骨方案的发展,结合患者年龄、畸形来源及基础疾病的综合评估,手术的精准性和安全性进一步提高。综上所述,膝关节周围截骨术在改善膝关节功能和提升患者生活质量方面发挥了重要作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈秋函, 杨 龙, 袁代柱, 吴展羽, 邹梓豪, 叶 川. 膝关节周围截骨治疗膝骨关节炎:治疗策略的优化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312.
Chen Qiuhan, Yang Long, Yuan Daizhu, Wu Zhanyu, Zou Zihao, Ye Chuan. Peri-knee osteotomy for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: optimization of treatment strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312.
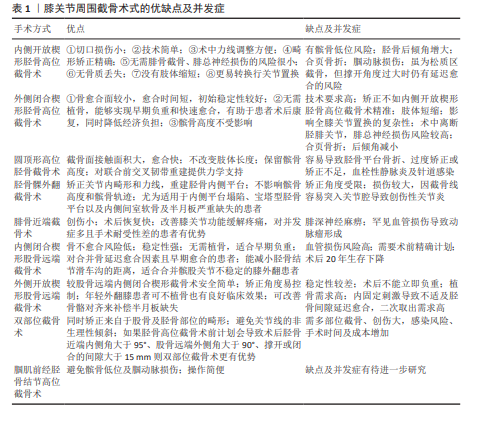
2.1 胫骨高位截骨术 胫骨高位截骨术是一种治疗膝关节内侧间室骨关节炎的有效手术方式,通过力线矫正,减少软骨和软骨下骨的受力,从而达到缓解疼痛及促进内侧间室修复达到治疗骨关节炎的目的。COVENTRY等[13]首次报道了胫骨高位截骨术在治疗膝内翻型骨关节炎中的应用。迄今为止,胫骨高位截骨术在长期随访中展现了良好的临床效果,并逐渐受到骨科领域的广泛关注。胫骨高位截骨术通过精确的术前计划,利用截骨技术纠正术前的内翻力线畸形。目前胫骨高位截骨主流术式主要有以下几种:内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术、外侧闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术、腘肌前经胫骨结节高位截骨术、圆顶形胫骨高位截骨术及胫骨髁外翻截骨术。
2.1.1 内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术 内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术是一种通过胫骨结节以上进行开放楔形截骨的手术方式,由BRETT[14]于1935年报道,也是目前胫骨高位截骨中应用最广泛的术式之一。该技术的截骨平面起于胫骨干骺端内侧,指向胫骨近端外侧的胫腓关节上缘,通过逐步撑开截骨间隙至术前计划角度完成矫正。该术式具有以下优势:①切口损伤小;②技术简单;③术中力线调整方便;④畸形矫正精确;⑤无需腓骨截骨、腓总神经损伤的风险很小;⑥无骨质丢失;⑦没有肢体缩短;⑧更易转换行关节置换。
虽然内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术具有多项优点,但也伴随一定缺点及并发症,具体如下:
(1)外侧合页骨折:当撑开高度超过11 mm时,外侧合页骨折的风险显著增加,可能导致截骨端失稳、截骨不愈合,并影响力线矫正效果[15]。TAKEUCHI等[16]报道,在104例膝关节中,5例Ⅱ型合页骨折中有2例愈合延迟。LEE等[17]研究显示,不稳定型外侧合页骨折患者的胫骨后倾角变化显著高于无外侧合页骨折患者。另有研究显示,9例不稳定型外侧合页骨折中4例术后坡度变化超过6°[18]。预防合页骨折关键在于选择适宜的合页点,NAKAMURA等[19]详细介绍了安全区的位置:①位于近端胫腓关节水平线上方,且在垂直方向上位于近端胫腓关节内侧边缘的外侧;②建议保留5-10 mm的合页宽度;③合页高度建议女性放在距胫骨平台15 mm处,男性放置在距胫骨平台20 mm处[20]。计算力学分析也验证了这些措施的有效性[21]。其他预防措施包括:①术中缓慢、渐进撑开截骨间隙以充分利用外侧合页的弹性[22];②在计划的截骨区域对侧插入1根克氏针,以避免过度切割和合页破坏[23];③从前外侧至后内侧方向插入拉力螺钉增加稳定性[24];④对矫正角度较大的病例,应使用角稳定钢板固定,避免钢板过于前内侧放置,最大程度提高近端截骨块的稳定性,并预防螺钉断
裂[25]。
(2)腘动脉损伤:腘动脉损伤虽罕见但后果严重。例如,ATTINGER等[26]报道了1例腘动脉完全破裂病例,术后即出现下肢缺血症状,术后采用自体静脉移植修补,但患者术后1年仍残留感觉障碍及疼痛。预防腘动脉损伤的主要措施包括:①正确放置拉钩:在腘肌前方放置拉钩以保护腘血管;②术前通过MRI评估血管变异;③优化截骨方向:锯片方向应稍近端胫腓关节前方,避免超过冠状面30°或指向腓骨头后方[27-28];④透视确认截骨方向及拉钩保护位置。
(3)髌骨低位:内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术在胫骨结节近端截骨存在髌骨低位风险,尤以矫正角度超过15°时显著[29],因经骨结节远端移位及术后髌腱粘连引起。髌韧带瘢痕形成进一步加重疼痛、活动受限及髌骨关节炎[30]。而避免髌骨低位最根本的方法是在髌腱止点下缘进行截骨。①胫骨结节远端单平面截骨,但容易增加骨不连及合页骨折风险[31];②双平面下行截骨术,保留结节与近端连接避免髌骨高度下降,但该术式较复杂,螺钉固定难度增加,尤其在开口增宽时[32]。
(4)后倾角增大:内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术可能无意间导致胫骨后倾角增大,增加前交叉韧带的负荷并加剧其退变[33]。这与胫骨近端呈三角形态[34]、内侧副韧带对截骨间隙的不对称牵拉、钢板位置过于偏前放置及手术切口选择等均有关系。目前常常通过精确的术前计划、细致的术中操作,并在截骨间隙后1/3放置垫块以减少后倾角增加的风险[35]。
除此之外,内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术的术后并发症同样也值得注意,一项基于71项研究的系统评价和荟萃分析共纳入7 836例患者,胫骨高位截骨术后总体并发症发生率为6.9%,其中最常见的术后并发症包括浅表感染(2.2%)、骨不连(1.9%)、矫正损伤(1.2%)、内固定失效(1.0%)[36]。
但是内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术作为目前临床应用最广泛的截骨术之一,通过技术优化可以有效降低风险,临床疗效已得到广泛认可。MABROUK等[37]对651例行内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术的患者进行13年随访,5年和10年的生存率分别为97.2%和91.9%,总体并发症发生率为10.3%,患者的西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数、目测类比评分、欧洲五维健康量表评分均较术前显著改善。TAKAHARA等[38]随访内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术患者93例(109个膝关节)64.2个月,术后日本骨科协会评估治疗分数和莱斯霍尔姆膝关节评分量表评分显著提升。另有研究表明,566例内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术患者10年生存率为79%,骨关节炎严重程度是全膝关节置换的主要预测因素[39]。一项针对71项研究(共纳入7 836例患者)进行的荟萃分析显示,胫骨近端开放截骨术后的5年生存率为95.5%,10年生存率为87.6%,10年以上生存率约为85%[40]。内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术的长期疗效和生存率已在多项研究中得到验证,不仅表现出高水平的中长期生存率,还显著改善了患者的疼痛、功能及生活质量。此外,还有学者使用内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术治疗自发性胫骨平台大面积骨坏死患者,发现该术式能够显著缓解疼痛并改善功能[41]。截骨手术还被认为与软骨再生有关,内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术联合软骨修复手术近年来被广泛关注,一项研究对66个膝关节进行了内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术联合软骨移植术,平均随访9.49年,关节镜评估显示在57个接受关节镜检查的膝关节中49个软骨再生率达100%,部分患者甚至出现透明软骨再生,其余8个膝关节出现部分软骨再生;所有患者疼痛、膝关节功能评分及活动能力均明显改善[42]。另一项研究通过术后1年关节镜探查提取软骨样本,结合PCR及蛋白质印迹技术发现胫骨高位截骨术通过上调磷酸化细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2基因促进了软骨再生[43]。总之,内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术是一种安全有效的术式,适用于膝骨关节炎患者,具有显著疗效和广泛应用价值。
2.1.2 外侧闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术 外侧闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术由COVENTRY等[13]首次提出,其优势包括:①骨愈合面较小,愈合时间短,初始稳定性较好;②无需植骨,能够实现早期负重和快速愈合,有助于患者术后康复,同时降低经济负担;③髌骨高度不受影响。
外侧闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术也存在一些明显的局限性:①术中需识别并保护腓总神经,近端胫腓关节离断可能增加全膝关节置换转换率并降低截骨生存率[44];②解剖结构改变增加膝关节置换复杂性;③矫正角度大时影响全膝关节置换实施;④术前需精准规划截取骨块大小,矫正精度低于内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术,存在矫正不足的风险;⑤可能造成后倾角减小[45]、肢体短缩且2次截骨创伤较大。
尽管外侧闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术存在不足,但其疗效仍获认可。FERRER等[46]随访70例膝骨关节炎患者,术后5,10年生存率分别为87.6%和75.5%,患者膝关节协会评分系统、牛津膝关节评分及目测类比评分显著改善,约30%患者因矫正不足影响生存率和满意度。外侧闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术存在一些并发症,术中并发症为5.5%,术后发症为6.9%,最常见的并发症是合页骨折(29.4%)、矫正失败(10%)、腓总神经损伤(6%)、感染(2%)和骨不连(1.2%)[36]。MAHMOUND
等[47]随访354例患者(平均年龄51岁)随访平均时间18年,发现55岁以下患者15年后全膝关节置换转换率为64%,55岁以上为85%,总体并发症发生率为6%,无腓总神经麻痹病例,在55岁以下的患者中效果显著。然而,与内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术相比,外侧闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术的应用范围相对较小。
2.1.3 腘肌前经胫骨结节高位截骨术 胫骨近端内侧高位截骨可有效矫正下肢力线,但术后可能导致髌骨低位和髌股关节外侧倾斜,特别在矫正角度较大时,同时还存在腘窝血管损伤的风险。胫骨结节远端单平面截骨能更好地避免这些问题。然而,胫骨结节远端单平面截骨术因位于皮质骨区域,增加了骨不连及骨性愈合的风险,同时由于合页侧皮质骨弹性较差,需术中进行对侧合页减压以降低合页骨折风险,这增加了手术的难度和复杂性[31]。双平面下行截骨术虽然能优化术后力线矫正稳定性,但其技术较为复杂,且存在胫骨结节骨折的风险。此外,术中可能需要额外置入螺钉以提高稳定性,增加了手术难度和潜在并发症。
基于以上的痛点,WU等[48]提出了一种创新性截骨术式,腘肌前经胫骨结节高位截骨术为单平面截骨,基于对胫骨结节髌腱止点的影像学观察及尸体解剖学验证,将胫骨结节区分为A、B、C、D区,发现髌腱止点的主体部分在A、B区,若截骨线通过C、D区时并不损伤髌腱主体,不导致髌骨低位。这一手术方式突破了既往所认为胫骨结节是截骨禁区的理念,通过腘肌覆盖截骨平面,降低了腘动脉损伤风险,展现了良好的临床潜力。然而,WU等[48]提出的一种创新性截骨术式应用时间较短,需进一步研究验证其生物力学优势和长期疗效。
2.1.4 圆顶形胫骨高位截骨术 圆顶形胫骨高位截骨术由BLAIMONT等[49]
于1975年首次报道,目前在临床实践中的应用相对较少。该术式在胫骨结节上方设计弧形截骨面,弧顶朝上,通过钻孔和骨凿完成截骨操作,旋转截骨块以实现下肢力线的精确矫
正[50]。
圆顶形胫骨高位截骨术与开放或闭合楔形截骨相比,具有以下优点:①不会引起肢体长度的变化;②其截骨面接触面积大,有助于早期负重及骨愈合;③该术式能够保留胫骨结节相对于关节线的位置,避免髌骨低位,不影响后期关节置换手术的实施[51];
④对于因闭合胫骨高位截骨矫正失败导致复发性内翻的患者,圆顶形胫骨高位截骨术可以显著改善临床症
状[52]。在合并前交叉韧带功能不全及膝关节屈曲畸形引起疼痛的患者中,联合前交叉韧带重建术也表现出一定的优势。通过减少内翻畸形引发的异常应力和降低胫骨平台后倾角,减轻了前叉韧带的负荷,为前交叉韧带的重建提供了良好的力学支持,并在短期内显示出明确的效果[53]。
圆顶形胫骨高位截骨术的缺点及并发症:①操作较为复杂;②手术暴露区域大;③截骨也不如楔形截骨方便。该术式并发症主要为血栓性静脉炎、拇长伸肌坏死、胫骨平台骨折、针道感染、过矫或欠矫[54]。目前该术式的长期随访较少,CHIANG等[55]随访16例患者共19个膝关节,平均随访时间为15年,术后5年内,大部分膝关节表现出优良的矫正效果,但术后外翻角度从12.4° 下降至7.8°,并在随访末期进一步降低。因此,矫正角度的持久性是该术式需关注的主要问题之一。
2.1.5 胫骨髁外翻截骨术 胫骨髁外翻截骨术,或称L型胫骨高位截骨术,由日本学者CHIBA[56]于1989年首次报道,主要用于治疗伴有外侧半脱位的严重晚期内侧间室骨关节炎。该术式通过设计“L”型截骨线进行矫正:纵向截骨线从胫骨外侧髁间隆起尖端向远处延伸,通常位于髌韧带的内侧;横向截骨线则从平台下约4 cm斜向腓骨头方向,2条截骨线的交点构成“L”型截骨线的顶点。
胫骨髁外翻截骨术特别适用于伴有胫骨平台塌陷、宝塔型胫骨平台及内侧软骨和半月板严重缺失的患者。其主要优点包括:①该术式在有效矫正下肢畸形的同时,可重建胫骨内侧平台,使关节线倾斜和关节内畸形得到纠正,改善关节面的匹配度,减少关节松弛,避免“跷跷板”现象[57];②在矫正过程中不会影响胫骨结节的完整性,因此不会显著改变髌骨高度或影响髌股关节轨迹,降低术后髌骨低位的发生率[58];③在治疗重度膝骨关节炎伴不稳定病例中效果优于胫骨近端内侧开放截骨[59-60];④对于膝关节外侧间隙增宽及关节线夹角增大的膝骨关节炎的患者,胫骨髁外翻截骨术能够有效地减少关节线夹角,提高关节稳定性,有良好的早期疗
效[61];⑤适用于各年龄段及各种程度的膝关节内翻骨关节炎的患者[62];⑥同对于创伤性关节炎及陈旧性的胫骨平台骨折有良好的早期临床疗效,可显著缓解膝关节疼痛并改善功能[63]。
胫骨髁外翻截骨术的局限性也较为明显,包括:①矫正角度受限:胫骨髁外翻截骨术为关节内截骨、矫正范围受限,难以实现较大程度的矫正;②纵向截骨线容易突入关节腔,增加创伤性关节炎发生的概率[64]。在股胫角> 185°的患者,单纯胫骨髁外翻截骨术可能不足以恢复正常力线,此时可能需要联合胫骨近端内侧开放截骨以优化矫正效果[60]。
2.2 腓骨近端截骨术 该术式由国内著名学者张英泽等[65]于2014年首次提出,是由中国首创的新型截骨方法,源自“膝关节不均匀沉降理论”。随着年龄增长及骨质疏松的加重,胫骨作为主要负重关节,因内侧缺乏骨性阻挡、外侧受腓骨支撑,导致负重点向内侧偏移,最终引发内侧胫骨平台的不均匀沉降,这一过程加重了膝关节力线的异常和负重中心的偏移,形成恶性循环。通过截断腓骨,削弱腓骨对外侧的支撑作用,重新分配膝关节负荷,缓解内侧膝关节内侧间室骨关节炎的症状。
腓骨近端截骨术的优点及适应证:①优化膝关节负荷分布,减轻内侧压力:计算力学研究表明,腓骨近端截骨术后可重新分配并均匀化关节应力,有效改善膝关节力学环境[66];②尸体标本研究显示,腓骨近端截骨术后胫骨整体应力未发生显著变化,但膝关节内侧间室压力显著释放,有助于减轻疼痛并改善膝关节功能[67];③优化下肢生物力学,改善踝关节对位及步态稳定性[68],步态分析证明术后患者的步态稳定性有所提高[69];④与胫骨高位截骨术相比,手术时间更短、术中出血量更少、住院时间更短且术后并发症发生率较低,对于并发症较多、手术耐受性差的患者,腓骨近端截骨术更有优势[70];⑤对于自发性膝关节骨坏死的患者,通过内侧减压显著减小骨坏死区域面积,帮助患者实现早期负重[71]。此外,腓骨近端截骨术也伴随着一些并发症,包括:①腓深神经麻痹,常常表现为足背感觉异常、麻木、一过性足下垂;②严重膝骨关节炎可能是腓骨近端截骨术后满意度下降的独立风险因
素[72];③罕见动脉损伤导致动脉瘤形成[73]。这些不良反应可以通过后续的治疗得到缓解[74]。
临床研究显示,腓骨截骨术近期疗效显著,能够改善腓骨头至胫骨平台的垂直距离、Kellgren-Lawrence分级、上胫腓关节角度以及美国特种外科医院膝关节评分较术前明显改善,可显著提高膝关节功能,缓解疼痛,延缓关节置换时间[75]。腓骨近端截骨术被认为是一种治疗膝骨关节炎的可靠方式,不仅短期疗效明确,中长期随访中满意度也较高,甚至有研究认为腓骨截骨术可作为晚期膝骨关节炎患者的一种治疗选择[76]。
2.3 股骨远端截骨术 股骨远端截骨术被推荐作为外侧骨关节炎的替代治疗方法,通常在畸形水平进行矫正。然而研究表明,当外翻畸形超过12°或关节面水平倾斜超过10°时,矫形部位更应该选在股骨,否则有胫骨半脱位的可能[77]。股骨远端截骨术的主要术式有内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术和外侧张开楔形股骨远端截骨术。
2.3.1 内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术 该术式通过从股骨远端内侧切下楔形骨块并对合截骨部位,实现下肢力线的矫正[78]。目前,内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术是治疗膝外翻最常见的截骨手术方式之一,其优势主要包括:①保留骨量:该术式保留了更多的骨量,可以矫正较大角度的外翻畸形,截骨区域骨面直接接触,提供了更稳定的结构,降低骨不愈合与骨不连发生率,对于早期需负重、吸烟、神经病变、骨质条件差以及肥胖的患者有较好的适应性[79];②改善髌骨关节稳定性:有研究表明,内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术可通过缩小胫骨结节与胫骨沟的距离改善髌骨不稳,对合并髌股关节不稳定的膝外翻患者具有潜在益处[80]。同时,内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术也存在一些不足之处:①术前计划要求精确:与撑开截骨相比,股骨远端外侧张开楔形截骨术式相对复杂,需2次截骨,需依赖精确的术前计划,以确保截除骨块大小的准确性;②股骨内侧血管损伤风险较外侧更高[81]。
CARBAL等[82]随访22例接受股骨远端内侧闭合楔形截骨术治疗的患者长达15年,结果显示所有患者均达到良好的矫正效果,均未需要翻修为全膝关节置换术。另一项中长期随访研究表明,在平均11年的随访时间内,57例行股骨远端内侧闭合楔形截骨术的患者中,仅4例需行全膝关节置换翻修手术,且所有主观评分(膝关节协会评分系统、膝关节损伤和骨关节炎结局评分、Tenger 膝关节功能评分、目测类比评分)在最后随访时均较术前显著改善[83]。STERNHEIM
等[84]对接受股骨远端内侧闭合截骨术治疗的41例(45例)患者进行长期随访,10,15,20年生存率分别为90%,79%及21.5%,20年生存率明显下降。多数患者在20多年以后接受了全膝关节置换。目前随着3D打印技术的发展,SHI等[85]报道了3D打印技术引导下实施内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术治疗膝外侧间室骨关节炎和外翻畸形的结果,与常规手术相比,3D打印技术可以明显提高闭合楔形截骨手术准确度、缩短手术时间及减少透视次数。总体而言,内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术是一种安全且有效的治疗膝关节外翻性骨关节炎的手术方式。
2.3.2 外侧开放楔形股骨远端截骨术 其手术方法是通过大腿外侧切开股骨远端1/3区域,在外侧髁和股骨干骺端进行楔形截骨[86-87]。该术式的主要优点包括:①相对于闭合截骨而言仅需一次截骨、通过撑开控制矫正角度相对简单;②对于外侧半月板损伤或者缺损的患者,通过改善骨骼对齐,补充半月板功能的缺失,从而减少软骨的进一步磨损[83];③适合膝外翻合并韧带松弛的年轻患者。
外侧开放楔形股骨远端截骨术的缺点也较明显:①结构稳定性较差:与内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术相比结构稳定性和刚度较低[88],其术后通常不能立即负重;②骨愈合时间较长:单平面开放截骨和钢板可能刺激髂胫束,这延长了截骨区域骨性愈合的时间,有二次取出内固定的必要[89];③不愈合率、骨折和骨不连发生率相对较高,因此大多数情况下需要植骨[90]。但KOLB等[91]对22例年轻膝外翻患者实施外侧开放楔形股骨远端截骨术,均未进行植骨,且术后获得了良好的骨愈合。他们认为,对于年轻患者,不植骨同样是一种安全可靠的选择。CANCE等[92]随访了38例行外侧开放楔形股骨远端截骨术的患者,共62个膝关节,平均随访时间(15.2±4.4)年,并发症发生率为26%,5,10年生存率分别为92.1%和78.9%,患者满意度较高。一项Meta分析研究表明,外侧开放楔形股骨远端截骨术和内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术在临床疗效及并发症发生率方面无显著差
异[93]。外侧开放楔形股骨远端截骨术和内侧闭合楔形股骨远端截骨术的术后存活率分别为81.5%(平均随访8.8年)和90.5%(平均随访4.5年),存活率与随访时间显著相关,但与具体手术技术无关。两种技术最常见的并发症为术后疼痛和内固定引起的不适。手术方式的选择应综合考虑患者个体特点及术者经验。
2.4 双部位截骨术 传统截骨手术多仅矫正单部位畸形,研究表明胫骨畸形仅占30%,而其他畸形可能来源于股骨、关节内或组合畸形[94]。准确的畸形分析对于识别畸形部位以及防止矫正后非生理性关节线方向的形成至关重要。尽管胫骨近端截骨术是治疗内侧膝骨关节炎最常用的手术方式,并且临床效果良好[95-96],但单部位截骨可能导致40%的过度矫正,影响治疗效果并增加并发症风险[97-98]。关节线倾斜的变化常常让骨科医生处于两难的境地,如果接受矫形过后带来的继发畸形,则存在损害膝关节稳定性和改变膝关节生物力学的风险[99]。三维有限元分析表示关节线倾斜超过5°时,关节软骨可能会承受有害的剪切应力[100]。
为克服这些挑战,BABIS等[101]提出采用胫骨近端截骨术和股骨远端截骨术的双部位截骨组合。目前研究认为如果胫骨高位截骨术前计划会导致术后胫骨近端内侧角> 95°、股骨远端外侧角> 90°、撑开或闭合的间隙> 15 mm则应考虑行双部位截骨,以实现平衡的矫正并维持生理性的关节线倾斜[102]。在胫骨与股骨存在联合畸形的情况下,目前通常采用胫骨近端内侧开放截骨与股骨远端外侧闭合截骨的组合方式进行矫正,双部位截骨术具有以下两大优势:首先,必要的截骨间隙开口可以大幅缩小,如果仅进行胫骨截骨,某些情况下的开口高度可能会超过20 mm,而双部位截骨术通过分散矫正,减少了过大开口带来的风险,例如延迟愈合或骨不连;其次,在双部位截骨中使用股骨截骨形成的楔形骨块作为填充物,可在多数病例中实现快速骨愈合。这种方法不仅避免了胫骨截骨单独扩大的情况,还减少了合页骨折等并发症的发生,从而显著提高手术效果[101]。双部位截骨短期临床效果明确,SCHUSTER等[103]对41例患者进行平均(11.4±3.6)个月的随访,发现术后肢体对齐以及临床评分(国际膝关节文献委员会评分系统、牛津膝关节评分、膝关节损伤和骨关节炎结局评分和Tenger膝关节功能评分)均较术前显著改善,并且整体并发症发生率低于2%。RUPP等[104]报道,双部位截骨术后7个月重返运动和工作的患者比率较高,分别为96%和90%。CLARK等[105]对22例(24膝)行双部位截骨术的患者进行了长达(26.1±7.7)年的随访,从双部位截骨转为全膝关节置换术的平均时间为(14.1±6.5)年,70.8%的膝关节在双部位截骨术后10年以上转为全膝关节置换,全膝关节置换术后功能未受影响。尽管双部位截骨需要多次截骨,创伤较大,增加手术风险和成本,但较低的并发症发生率和优异的短期疗效使它成为治疗膝骨关节炎的可靠选择。

| [1] COURTIES A, KOUKI I, SOLIMAN N, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2024: epidemiology and therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32(11):1397-1404. [2] LI J, FU S, GONG Z, et al. Mri-based texture analysis of infrapatellar fat pad to predict knee osteoarthritis incidence. Radiology. 2022;304(3):611-621. [3] MISSERI G, GREGORETTI C, LO BIANCO G. Review of evaluation and treatment of knee pain. Jama. 2024;331(8):706-707. [4] ZHU S, QU W, HE C. Evaluation and management of knee osteoarthritis. J Evid Based Med. 2024;17(3):675-687. [5] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. Jama. 2021;325(6): 568-578. [6] CLARK GP. Treatment options for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in adults. JAAPA. 2023;36(11):1-6. [7] COPP EH, GALE TH, BYRAPOGU VKC, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty approximates healthy knee kinematics more closely than total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2024;42(11):2514-2524. [8] BOZKURT M, PULATKAN A, RANDELLI PS, et al. What are the indications for tibial and femoral osteotomies around the knee? J Arthroplasty. 2025;40(2S1):S156-S158. [9] HUANG Y, LOBENHOFFER P, JIANG XY. Development of knee-preserving osteotomy in China. Sci Bull (Beijing). 2023;68(2):125-128. [10] OU Y, XIONG T, LI N, et al. Knee arthroscopy has limited effects on relieving local symptoms of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis of data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(1):443-451. [11] XIONG S, QU Y, REN J, et al. Effect of prosthetic joint line installation height errors on insert wear in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023;40(6):1192-1199. [12] 中国医院协会临床新技术应用专业委员会, 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组, 等. 中国膝关节周围截骨下肢力线矫正术治疗膝关节骨关节炎临床指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(23):1655-1672. [13] COVENTRY MB. Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1965;47:984-990. [14] BRETT A. Operative correction of genu recurvatum. JBJS. 1935;17(4):984-989. [15] SONG KY, KOH IJ, KIM MS, et al. Early experience of lateral hinge fracture during medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy: incidence and clinical outcomes. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(2): 161-169. [16] TAKEUCHI R, ISHIKAWA H, KUMAGAI K, et al. Fractures around the lateral cortical hinge after a medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a new classification of lateral hinge fracture. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(1):85-94. [17] LEE SS, NHA KW, LEE DH. Posterior cortical breakage leads to posterior tibial slope change in lateral hinge fracture following opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019; 27(3):698-706. [18] SONG JH, BIN SI, KIM JM, et al. Risk factors for increase in posterior slope after medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022;10(11): 23259671221137042. [19] NAKAMURA R, KOMATSU N, FUJITA K, et al. Appropriate hinge position for prevention of unstable lateral hinge fracture in open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-b(10):1313-1318. [20] KIM SM, BIN SI, KIM JM, et al. Lateral distance from the osteotomy hinge point to the tibial cortex is associated with lateral hinge fracture type and fracture occurrence time after medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2024;40(3):890-895. [21] OSMANI HT, GUPTA R, EARL R, et al. Finite element analysis confirms the optimal apex position in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy to avoid lateral hinge fracture. J Exp Orthop. 2024;11(4):e70042. [22] GULAGACI F, JACQUET C, EHLINGER M, et al. A protective hinge wire, intersecting the osteotomy plane, can reduce the occurrence of perioperative hinge fractures in medial opening wedge osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020; 28(10):3173-3182. [23] MA HH, LOBENHOFFER P, YANG JC. The benefits of a percutaneous supplemental screw to reinforce the hinge of a medial open wedge tibial osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(7):3707-3713. [24] NAKAMURA R, KOMATSU N, FUJITA K, et al. Anteromedial plating without filling the gap in open wedge high tibial osteotomy may increase the risk of screw breakage, which can be reduced by medial plating and bone-substitute insertion. J Orthop Sci. 2023; 28(2):416-425. [25] TAKEUCHI R, WOON-HWA J, ISHIKAWA H, et al. Primary stability of different plate positions and the role of bone substitute in open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2017;24(6):1299-1306. [26] ATTINGER MC, BEHREND H, JOST B. Complete rupture of the popliteal artery complicating high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop. 2014;11(4):192-196. [27] KIM J, ALLAIRE R, HARNER CD. Vascular safety during high tibial osteotomy: a cadaveric angiographic study. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(4):810-815. [28] KANG T, LEE DW, PARK JY, et al. Sawing toward the fibular head during open-wedge high tibial osteotomy carries the risk of popliteal artery injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(5):1365-1371. [29] JINGBO C, MINGLI F, GUANGLEI C, et al. Patellar height is not altered when the knee axis correction is less than 15 degrees and has good short-term clinical outcome. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(6):536-546. [30] OTSUKI S, MURAKAMI T, OKAMOTO Y, et al. Risk of patella baja after opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(3):2309499018802484. [31] HAN C, LI X, TIAN X, et al. The effect of distal tibial tuberosity high tibial osteotomy on postoperative patellar height and patellofemoral joint degeneration. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):466. [32] PARK SB, KIM JS, JEONG HW, et al. Medially and distally inserted tuberosity screw fixation of the osteotomized tubercle is safe and effective in retro-tubercular bi-planar opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023; 31(4):1571-1582. [33] KIM GB, KIM KI, SONG SJ, et al. Increased posterior tibial slope after medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy may result in degenerative changes in anterior cruciate ligament. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(9):1922-1928. [34] SCHUBERT I, FERNER F, DICKSCHAS J. The effect of open-wedge and closed-wedge high tibial osteotomies on the tibial posterior slope-a study of two hundred seventy-nine cases. Int Orthop. 2020;44(6): 1077-1082. [35] NOYES FR, GOEBEL SX, WEST J. Opening wedge tibial osteotomy: the 3-triangle method to correct axial alignment and tibial slope. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(3):378-387. [36] MILTENBERG B, PUZZITIELLO RN, RUELOS VCB, et al. Incidence of complications and revision surgery after high tibial osteotomy: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2024; 52(1):258-268. [37] MABROUK A, RISEBURY M, YASEN S. High survivorship and low complication rate in a single-centre series of 651 medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy cases with a mean follow-up of 13 years. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024;32(3):736-749. [38] TAKAHARA Y, NAKASHIMA H, ITANI S, et al. Mid-term results of medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy based on radiological grading of osteoarthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(1):149-158. [39] PRIMEAU CA, BIRMINGHAM TB, LEITCH KM, et al. Total knee replacement after high tibial osteotomy: time-to-event analysis and predictors. Cmaj. 2021;193(5):E158-E166. [40] LOKE R WK, CHAN YK, LIM YH, et al. Conversion to total knee arthroplasty after high tibial osteotomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthop J Sports Med. 2025;13(2):23259671241310963. [41] SAKAKIBARA Y, MUKAI R, SHIMOYAMA K, et al. Treating extensive spontaneous osteonecrosis of the tibia by the medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy procedure: a case report. Cureus. 2024;16(8):e67336. [42] JUNG WH, SAHU V, SEO M, et al. Cartilage regeneration and long term survival in medial oa knee patients treated with hto and oats. J Orthop. 2024;57:120-126. [43] WU J, ZHAO B, LUO W, et al. Arthroscopy combined with high tibial osteotomy promotes cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2023;31(1):10225536231165357. [44] SáNCHEZ-SOLER J, COELHO A, TORRES-CLARAMUNT R, et al. Proximal tibiofibular dislocation in closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy increases the risk of medium and long-term total knee replacement. J Clin Med. 2021;10(13):2743. [45] CHENG X, LIU F, XIONG F, et al. Radiographic changes and clinical outcomes after open and closed wedge high tibial osteotomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):179. [46] FERRER RIVERO R, PUJOL O, FERRER RIVERO J, et al. Closing wedge high tibial osteotomy: an old-fashioned technique? Survival, clinical and radiological outcomes of a case series analysis. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2024;68(4):336-343. [47] MAHMOUD A, GARBA B, MCMENIMAN T, et al. Lateral closing wedge high-tibial osteotomy is a long-lasting option for patients under the age of 55 with medial compartment osteoarthritis. J Exp Orthop. 2024;11(4):e70040. [48] WU Z, YUAN D, HUA D, et al. Precise patellar tendon insertion protection and osteotomy surface advantage of transtibial tuberosity-high tibial osteotomy. Orthop Surg. 2023; 15(2):639-647. [49] BLAIMONT P, BURNOTTE J, HALLEUX P. Prearthrosis of the knee. Pathogeny, biomechanics, and preventive treatment. Acta Orthop Belg. 1975;41(2):177-200. [50] SUNDARAM NA, HALLETT JP, SULLIVAN MF. Dome osteotomy of the tibia for osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(5):782-786. [51] BASIONY HA, ELTRAIGY SA, ABOUZIED MS, et al. The use of dome shaped osteotomy and plating in correction of genu varum. Benha J Appl Sci. 2024;9(1):45-53. [52] GAMA DF, CABRAL J, VALE M, et al. Dome-shaped osteotomy for revision of failed closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019;7(7): 2325967119857047. [53] TAKAHASHI T, WATANABE S, HINO M, et al. Excellent short-term results of dome-shaped high tibial osteotomy combined with all-inside anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Exp Orthop. 2023;10(1):69. [54] KARAISMAILOGLU B, KUYUBASI SN, KARAISMAILOGLU TN. Dome-shaped high tibial osteotomy with semi-circular Ilizarov pin fixator: Mid- to long-term results of a novel technique. Knee. 2020;27(5): 1618-1626. [55] CHIANG H, HSU HC, JIANG CC. Dome-shaped high tibial osteotomy: a long-term follow-up study. J Formos Med Assoc. 2006; 105(3):214-219. [56] CHIBA G. New tibial osteotomy for severe osteoarthritis of the knee with teeter effect. J Jpn Orthop Assoc. 1992;66: 798. [57] HIGUCHI T, KOSEKI H, YONEKURA A, et al. Comparison of radiological features of high tibial osteotomy and tibial condylar valgus osteotomy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):409. [58] KIM Y, KLEY K, ISHIJIMA M, et al. Medial tibial condylar valgus osteotomy improve clinical outcomes and effectively corrects significant tibial varus deformities without compromising joint line obliquity or patellar heigh. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2024:104030.doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2024.104030. [59] HIGUCHI T, KOSEKI H, YONEKURA A, et al. Comparison of short-term clinical outcomes between open-wedge high tibial osteotomy and tibial condylar valgus osteotomy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):98. [60] WANG X, SHI L, ZHANG R, et al. Salvage of severe knee osteoarthritis: efficacy of tibial condylar valgus osteotomy versus open wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):451. [61] 胡健, 陈礼阳, 刘丙立. 胫骨髁外翻截骨术的应用进展[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2023, 29(5):436-439. [62] TERAMOTO T, HARADA S, TAKENAKA N, et al. Tibial condylar valgus osteotomy (tcvo): surgical technique and clinical results for knee osteoarthritis with varus deformity. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;22:101589. [63] 金宇杰, 周晓强, 孙超, 等. 胫骨髁外翻截骨术治疗创伤性膝关节炎的早期临床疗效分析[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2023,20(2):22-27. [64] WANG X, ZHANG R, ZHENG X, et al. Geometrical analysis of the opening gap after tibial condylar valgus osteotomy for proper hinge point selection. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(23):1267. [65] 张英泽, 李存祥, 李冀东, 等. 不均匀沉降在膝关节退变及内翻过程中机制的研究[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2014,35(2): 218-219. [66] MORALES AVALOS JE, MORALES-AVALOS R, MARTíNEZ-GUAJARDO KV, et al. How effective is proximal fibular osteotomy in redistributing joint pressures? Insights from an hto comparative in-silico study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):333. [67] BALDINI T, ROBERTS J, HAO J, et al. Medial compartment decompression by proximal fibular osteotomy: a biomechanical cadaver study. Orthopedics. 2018;41(4):e496-e501. [68] GUO J, ZHANG L, QIN D, et al. Changes in ankle joint alignment after proximal fibular osteotomy. PLoS One. 2019;14(3): e0214002. [69] LI X, CAO Y, CAO Z, et al. Gait improvement in patients with knee osteoarthritis after proximal fibular osteotomy. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:1869922. [70] WU ZX, REN WX, WANG ZQ. Proximal fibular osteotomy versus high tibial osteotomy for treating knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):470. [71] CHEN YS, ANG MD, YANG CY, et al. Proximal fibular osteotomy relieves pain in spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: a retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(30):e29585. [72] FU C, WANG F, ZHU Y, et al. Severe medial osteoarthritis predicts patient dissatisfaction after proximal fibular osteotomy: a mid- to long-term follow-up study. Int Orthop. 2024; 48(1):95-101. [73] CHEN YS, YANG CY, CHANG CW, et al. Anterior tibial artery pseudoaneurysm as a rare technical complication after corrective fibular osteotomy: a case report. Patient Saf Surg. 2022;16(1):25. [74] 明立功, 孟维娜, 明朝戈, 等. 膝关节骨性关节炎腓骨近端截骨治疗的并发症分析及对策[J]. 实用手外科杂志,2022, 36(1):66-69. [75] QIN D, CHEN W, WANG J, et al. Mechanism and influencing factors of proximal fibular osteotomy for treatment of medial compartment knee osteoarthritis: A prospective study. J Int Med Res. 2018; 46(8):3114-3123. [76] 王丰坤, 林文蔚, 杨国栋, 等. 腓骨近端截骨术治疗高龄、晚期膝关节骨性关节炎患者的临床效果[J]. 精准医学杂志, 2021,36(5):382-385+390. [77] KAYAALP ME, APSELOFF NA, LOTT A, et al. Around-the-knee osteotomies part 1: definitions, rationale and planning-state of the art. J isakos. 2024;9(4):645-657. [78] BARNAVON T, ODRI G A, VENDEUVRE T, et al. Medial closing-wedge distal femoral varus osteotomy: symptoms and functional impact in cases of associated patellofemoral osteoarthritis. A two-year follow-up prospective pilot study. Knee. 2020;27(3): 615-623. [79] SHERMAN SL, THOMPSON SF, CLOHISY JCF. Distal femoral varus osteotomy for the management of valgus deformity of the knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;26(9): 313-324. [80] WATRINET J, JOERGENS M, BLUM P, et al. Tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove distance is significantly decreased by medial closing wedge distal femoral osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024;32(2): 287-294. [81] DUERR RA, HARANGODY S, MAGNUSSEN RA, et al. Technique for biplanar lateral opening wedge distal femoral osteotomy in the valgus knee. Arthrosc Tech. 2020;9(9): e1323-e1333. [82] CABRAL PB, ASTUR DC, FREITAS EV, et al. Closing-wedge distal femoral osteotomies-retrospective study. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2019;54(2):198-201. [83] UBOLDI FM, TRAVI M, TRADATI D, et al. Medial closure supracondylar femoral osteotomy: an effective solution for long-term treatment of arthritic valgus knee? J Orthop Traumatol. 2021;22(1):35. [84] STERNHEIM A, GARBEDIAN S, BACKSTEIN D. Distal femoral varus osteotomy: unloading the lateral compartment: long-term follow-up of 45 medial closing wedge osteotomies. Orthopedics. 2011;34(9):e488-e490. [85] SHI J, LV W, WANG Y, et al. Three dimensional patient-specific printed cutting guides for closing-wedge distal femoral osteotomy. Int Orthop. 2019;43(3):619-624. [86] COVENTRY MB. Proximal tibial varus osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the lateral compartment of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(1):32-38. [87] PILONE C, ROSSO F, COTTINO U, et al. Lateral opening wedge distal femoral osteotomy for lateral compartment arthrosis/overload. Clin Sports Med. 2019;38(3):351-359. [88] ISMAILIDIS P, SCHMID C, WERNER J, et al. Distal femoral osteotomy for the valgus knee: indications, complications, clinical and radiological outcome. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(10):6147-6157. [89] SAITHNA A, KUNDRA R, GETGOOD A, et al. Opening wedge distal femoral varus osteotomy for lateral compartment osteoarthritis in the valgus knee. Knee. 2014;21(1):172-175. [90] BERTHA N, MANFRE MG, CHIN G, et al. Osteotomies of the knee for valgus malalignment. JBJS Rev. 2025;13(2). doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.24.00189. [91] KOLB A, ISAK V, HOBUSCH GM, et al. Distal femoral varus osteotomy: results of the lateral open-wedge technique without bone grafting. Int Orthop. 2019;43(10):2315-2322. [92] CANCE N, BATAILLER C, LORDING T, et al. Ten-year minimal follow-up of lateral opening wedge distal femoral osteotomy for lateral femorotibial osteoarthritis: good survivorship and high patient satisfaction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2025; 33(2):675-685. [93] DIAZ CC, LAVOIE-GAGNE OZ, KNAPIK DM, et al. Outcomes of Distal Femoral Osteotomy for Valgus Malalignment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Closing Wedge Versus Opening Wedge Techniques. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(3):798-811. [94] FEUCHT MJ, WINKLER PW, MEHL J, et al. Isolated high tibial osteotomy is appropriate in less than two-thirds of varus knees if excessive overcorrection of the medial proximal tibial angle should be avoided. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021; 29(10):3299-3309. [95] OLLIVIER B, BERGER P, DEPUYDT C, et al. Good long-term survival and patient-reported outcomes after high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(11):3569-3584. [96] FERREIRA A, JACQUET C, GUY S, et al. Distal femoral osteotomy planning: reversed miniaci’s method is more accurate than dugdale and paley methods. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2024;110(1):103697. [97] GOSHIMA K, SAWAGUCHI T, SHIGEMOTO K, et al. Comparison of clinical and radiologic outcomes between normal and overcorrected medial proximal tibial angle groups after open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(10): 2898-2908.e1. [98] TSUJI M, AKAMATSU Y, KOBAYASHI H, et al. Joint line convergence angle predicts outliers of coronal alignment in navigated open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(6):707-715. [99] WANG D, WILLINGER L, ATHWAL KK, et al. Knee joint line obliquity causes tibiofemoral subluxation that alters contact areas and meniscal loading. Am J Sports Med. 2021; 49(9):2351-2360. [100] NAKAYAMA H, SCHRöTER S, YAMAMOTO C, et al. Large correction in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with resultant joint-line obliquity induces excessive shear stress on the articular cartilage. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6):1873-1878. [101] BABIS GC, AN KN, CHAO EY, et al. Double level osteotomy of the knee: a method to retain joint-line obliquity. Clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(8):1380-1388. [102] ALVES P, VAN ROOIJ F, KURATLE T, et al. Consistent indications, targets and techniques for double-level osteotomy of the knee: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(12): 4078-4087. [103] SCHUSTER P, RATHGEB F, MAYER P, et al. Double level osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis and bifocal varus malalignment has excellent short-term results while maintaining physiologic radiographic joint parameters. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(8):3124-3132. [104] RUPP MC, MUENCH LN, EHMANN YJ, et al. Improved clinical outcome and high rate of return to low-impact sport and work after knee double level osteotomy for bifocal varus malalignment. Arthroscopy. 2022; 38(6):1944-1953. [105] CLARK SC, SIMON KN, SARIS DBF, et al. Double-level osteotomy (dlo) for varus deformity results in over a decade of mean survival without compromising subsequent total knee arthroplasty function at a mean 26-year follow-up. J Exp Orthop. 2025;12(1): e70140. [106] LI K, SUN F, GUO H, et al. Comparison of clinical, imaging and second-look arthroscopic outcomes between varus knee patients with and without preoperative tibial varus deformity after medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2024; 46:117-127. [107] DONG C, ZHAO C, WANG F. Clinical benefit of high tibial osteotomy combined with the intervention of platelet-rich plasma for severe knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):405. [108] CHUI EC, MAK KK, NG RH, et al. Computer-aided high tibial osteotomy-a comparative study of commonly used 3d printing technology and navigation application. Orthop Surg. 2025;17(2):593-602. |
| [1] | 赵非凡, 曹玉净. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折内固定失效的危险因素与应对策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2323-2333. |
| [2] | 蒋祥龙, 厉中山, 车同同. 低频脉冲电磁场在肌肉修复与增长中的应用效果和作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2350-2360. |
| [3] | 刘金龙, 阿卜杜吾普尔•海比尔, 白 臻, 苏丹阳, 苗 鑫, 李 菲, 杨晓鹏. 不同非手术方法治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸效果的系统综述与网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2370-2379. |
| [4] | 曹 涌, 滕虹良, 邰鹏飞, 李骏达, 朱腾旗, 李兆进. 细胞因子和卫星细胞在肌肉再生中的相互作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [5] | 李林臻, 焦泓焯, 陈伟南, 张铭哲, 王建龙, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清对脂多糖诱导人软骨细胞炎症损伤的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [6] | 顾富城, 杨美鑫, 吴伟欣, 蔡玮俊, 钦洋溢, 孙铭一, 孙 健, 耿秋东, 李 楠, . 龟鹿二仙胶对膝骨关节炎大鼠肠道菌群的影响:机器学习与16S rDNA分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [7] | 李晓敏, 田向东, 王朝鲁. 单平面胫骨高位截骨:股腓角作为力线矫正的参考标志[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 570-576. |
| [8] | 管昱杰, 赵 彬 . 人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [9] | 谭凤怡, 谢嘉敏, 潘振锋, 张新旭, 郑泽态, 曾祉莹, 周艳芳. 胶原蛋白联合微针治疗皮肤光老化的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 451-458. |
| [10] | 郭敬文, 王庆伟, 何子俊, 胡梓航, 陈 志, 朱 荣, 王煜明, 刘文菲, 罗庆禄. 不同浓度硅基生物陶瓷关节腔内注射治疗大鼠膝骨关节炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 288-295. |
| [11] | 韩亚澎, 高 俊, 钮云伟, 邓恩甲. 骨碎补总黄酮介导骨相关细胞程序性死亡的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 3091-3099. |
| [12] | 叶 伟, 江冬福, 庄接林, 赖华新. 温针灸与富血小板血浆注射治疗膝骨关节炎:步态参数及关节功能恢复评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 2975-2985. |
| [13] | 李宜金, 黎嘉澔, 张海涛, 黄艺伟, 陈锦伦, 曾意荣, 冯文俊. 关节康片干预软骨稳态保护膝骨关节炎小鼠关节软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 2994-3004. |
| [14] | 毛苏杰, 高 洁, 潘壮丽. 免疫细胞在训练诱导应激应答中协同调节炎症反应、肌肉再生和代谢稳态[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(10): 2671-2680. |
| [15] | 马 驰, 王 宁, 陈 拥, 魏志晗, 刘逢纪, 朴成哲. 3D打印个体化截骨导板结合定制钢板在开放楔形胫骨高位截骨中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
随着保膝理念的兴起及保留原生关节的需求,一些侵入性较小的手术方式,如关节镜手术、膝关节周围截骨术(股骨或胫骨截骨术)和单髁置换术,在临床实践中得到广泛应用。这些手术通过保留膝关节的整体结构,有效延缓甚至避免了全膝关节置换术的实施[8]。膝关节周围截骨术作为保膝手术的一类,通过矫正下肢不正常的力线,从根本上解决了力线异常这一重要病因,从而有效减轻膝关节内侧或外侧间室的负重,改善关节的力学分布,延缓骨关节炎进展,显著改善患者的功能和生活质量[9]。
膝关节周围截骨术的出现是保守治疗与全膝关节置换之间的过渡。相比之下,关节镜手术虽然对症状较轻的患者短期疗效较好,但无法像截骨术那样通过矫正力线改善膝关节的生物力学结构,难以从根本上缓解病因[10]。单髁膝关节置换术虽然创伤较小,但术后活动需要受限,以减少假体磨损[11],而膝关节周围截骨术通过保留原生关节及本体感觉,使患者术后活动不受显著限制。随着新型内植入物材料(如TomoFix钢板)的应用及术式(如双平面截骨术)的不断优化,膝关节周围截骨术得到了巨大的应用与发展。根据2021年发布的《中国膝关节周围截骨下肢力线矫正术治疗膝关节骨关节炎临床指南》[12],膝关节周围截骨术的适应证包括:①男性患者年龄< 65岁,女性患者年龄< 60岁;②体质量指数< 27.5 kg/m²;③Kellgren-Lawrence分级为Ⅲ级以下;④对侧关节间隙基本正常;⑤内翻畸形> 5°或外翻畸形> 10°;⑥术前膝关节活动范围> 100°,屈曲挛缩< 15°的患者。
此文旨在综述膝关节周围截骨的术式特点及临床疗效,为其临床应用提供参考。
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2024年10月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索年限 主要为2014-2024年,同时引用部分远期经典文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库、中国知网。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词包括“knee osteoarthritis,high tibial osteotomy,distal femur osteotomy,proximal fibula osteotomy,tibial condylar valgus osteotomy,dome shaped high tibial osteotomy,limb alignment correction,joint-preserving surgery”;中文检索词包括“膝关节骨关节炎,胫骨高位截骨术,股骨远端截骨术,腓骨近端截骨术,胫骨髁外翻截骨术,圆顶形截骨术,力线矫正,保膝手术”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、病例报告、系统评价和荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 手工检索引用文献中价值较高的参考文献,阅读评估是否符合纳入标准。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.2.1 纳入标准 纳入膝关节周围截骨术治疗膝骨关节炎相关的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①不符合研究主题;②文章质量低、来源不够权威的文献;③无法查看全文的文献;④观点过于陈旧的文献。
1.3 文章质量评估与数据提取 共检索到中英文文献969篇,包括英文文献768篇、中文文献201篇。选择与文章内容相关性大、观点新颖并具有价值的文章进行讨论与分析,排除与研究目的及内容相差较大、观点过时且重复的文献,按入选标准严格筛选后最终纳入108篇文献进行综述。见图2。
向[107]。同时随着技术的改良(截骨手术的创新及改良、内固定材料的更新以及内固定结构的拓扑优化等)、计算机辅助设计及3D打印技术的应用为保膝截骨的微创化、精准化及标准化提供了新的技术手段[108]。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 在总结既往研究成果的基础上,此文对多种膝关节周围截骨术式的优缺点及临床疗效进行了系统梳理,力求为临床实践提供全面参考。
3.3 综述的局限性 此次综述主要基于近年来国内外文献分析,尽管检索了较多高质量研究,但由于涉及术式和并发症的多样性,部分观点可能存在区域性偏差。此外,虽然一些应用较早的截骨术式已有相关的长期疗效随访报道,但仍不全面,大部分新兴术式由于临床应用时间较短,长期疗效和潜在并发症尚未完全明确,在后续研究中应进一步关注新兴术式的长期效果和传统术式的远期数据补充,以持续推动膝关节周围截骨术的发展和完善。
3.4 该综述的意义 膝关节周围截骨术作为治疗膝骨关节炎的关键手段,可通过力线重建有效延缓关节置换需求,并显著改善患者功能和生活质量。此次综述系统总结了不同截骨术式的优缺点和临床疗效,为术式选择和优化提供了科学依据。此文展望了个性化截骨方案在未来膝骨关节炎患者中的发展前景,个性化截骨方案需要综合考虑患者的年龄、畸形来源部位、基础疾病和并发症等因素。在制定治疗策略时,将微创技术、快速康复措施和促进软骨再生与修复的理念融入个性化治疗方案,从而进一步提高治疗效果,该综述的结果有助于提升临床实践水平。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
文题释义:#br# 膝关节周围截骨术:是一种矫正下肢力线和缓解关节负荷的骨科手术,主要应用于早中期膝骨关节炎患者或关节畸形矫正。通过调整胫骨或股骨截骨,改善关节应力分布,延缓关节置换的需求。#br# 膝骨关节炎:是中老年人群中常见的退行性关节疾病,以关节软骨退化、骨赘形成及关节间隙狭窄为主要特征,导致患者出现疼痛、功能障碍,严重影响生活质量。随着人口老龄化进程加快,膝骨关节炎的发病率逐年升高,早期诊断和治疗策略的优化已成为骨科领域的重要研究热点。#br# #br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
此次研究深入探讨了膝关节周围截骨手术的不同术式,全面分析了每种手术方法的术式特点、临床应用价值以及创新性。文章不仅回顾了经典的开放楔形截骨术和闭合楔形截骨术,详细讨论了它们的术式特点、并发症及其处理策略,并进行了系统性的对比分析,评估了这些手术方式在治疗膝关节骨关节炎中的疗效、技术难题与挑战。此外,该文章还关注了近年来新兴的截骨技术,分析其临床价值和术式优化的潜力。为当前膝关节周围截骨手术领域做了对应总结,并为未来的研究和临床实践提供了重要参考。本文的独特之处在于,不仅总结了现有的手术技术和研究进展,还关注了截骨术后软骨再生及生物效应的新兴理念。这一创新视角为截骨术的应用范围提供了新的拓展方向。文章通过结合现有文献和最新的研究成果,提出了针对不同患者群体的个性化术式选择策略,尤其是在选择适应症和优化治疗方案方面进行了精细的分类。这一创新性分析不仅为临床决策提供了重要的证据支持,也为个性化保膝治疗提供了科学依据,推动了膝关节治疗领域的进一步发展。
#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||