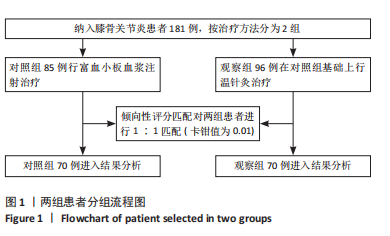
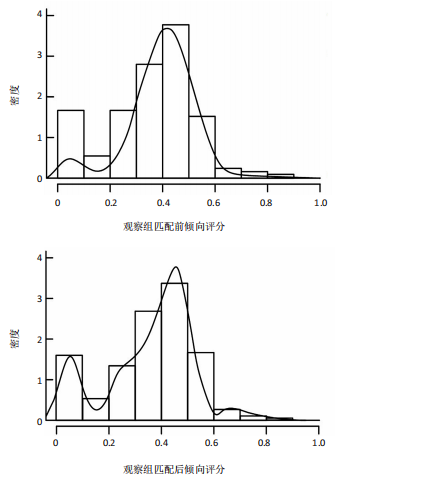
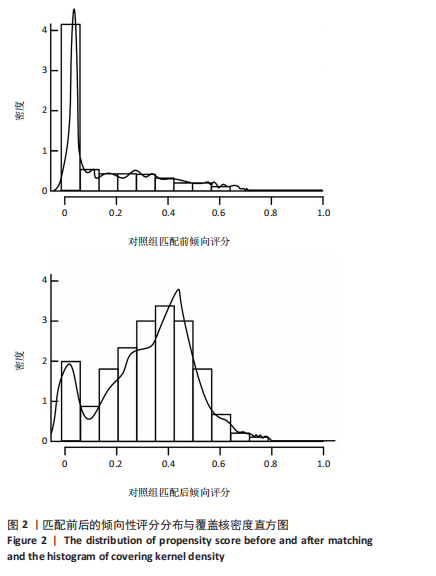
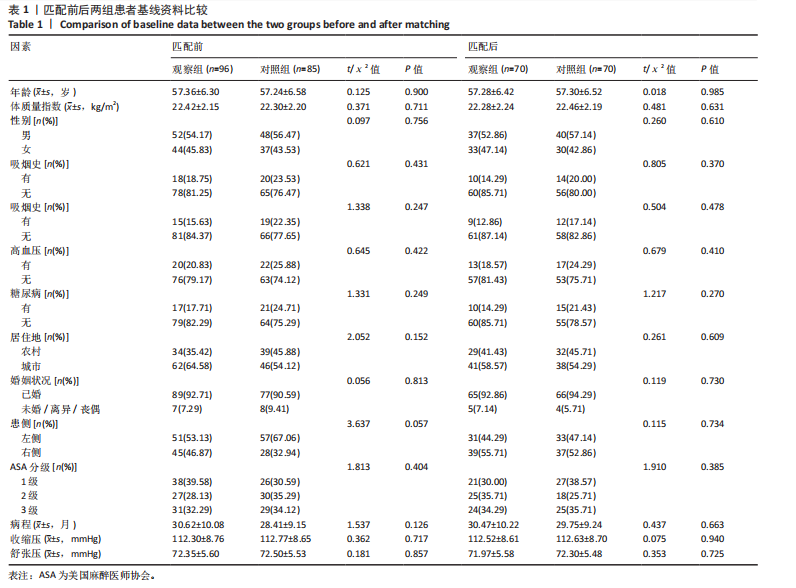
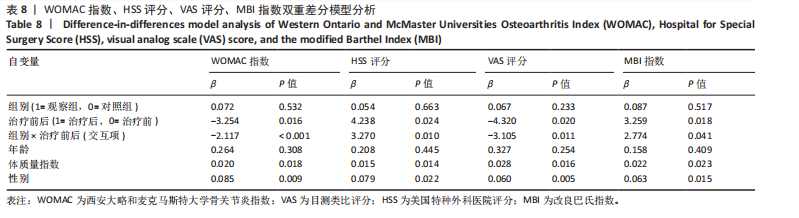
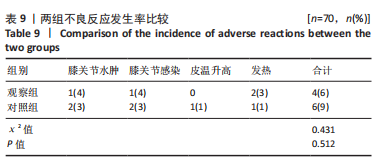
[1] 王虎, 陈顺喜, 陈益丹. 温针灸配合中药外敷治疗膝关节骨性关节炎对炎症反应及膝关节功能的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2022, 40(7):63-66.
[2] 洪秀娥, 张霖云, 林旺, 等. 基于扶阳理论督灸联合温针灸治疗阳虚寒凝型膝关节骨关节炎疗效观察[J]. 中国针灸,2022,42(12): 1357-1362.
[3] 张茜玥, 李昀姝, 赵杰瑞, 等. 中医药联合富血小板血浆治疗膝骨关节炎进展[J]. 中药材,2024,47(1):261-267.
[4] 武永利, 李龙, 刘君伟, 等. 温针灸抑制NLRP3炎症小体激活改善兔膝骨关节炎的软骨损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(20): 3202-3208.
[5] 徐旭, 张丽丽, 马红梅, 等. 温针灸联合加味阳和汤治疗老年膝关节骨性关节炎临床疗效及对炎症因子水平的影响[J]. 湖北中医药大学学报,2021,23(5):89-92.
[6] AKPABIO A, AKINTAYO R, YERIMA A, et al. Frequency, pattern, and associations of generalized osteoarthritis among Nigerians with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40(8):3135-3141.
[7] 中华医学会骨科学分会. 骨关节炎诊治指南(2007年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2007,27(10):793-796.
[8] ATERFIELD J, SIM J. Clinical assessment of pain by the visual analogue scale. Br J Ther Rehabil. 2013;3(2):94-97.
[9] 何栩,彭倩,路怀民,等. 温针灸治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效及对膝关节功能的影响[J]. 河北中医,2021,43(9):1537-1540,1545.
[10] LUAN L, BOUSIE J, PRANATA A, et al. Stationary cycling exercise for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2021;35(4):522-533.
[11] LIU B, XU HY, ZHANG R, et al. An Update on Clinical Utility of Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography in Knee Osteoarthritis. J Ultrasound Med. 2023;42(7):1413-1422.
[12] 晋帅锋, 乔晋琳, 丁宇, 等. 针刀联合富血小板血浆注射疗法治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效研究[J]. 世界中医药,2022,17(15): 2203-2206.
[13] 杨亚崇, 帅世超, 岳立辉, 等. 富血小板血浆治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的研究进展[J]. 中国输血杂志,2023,36(1):90-93.
[14] BENNELL KL, PATERSON KL, METCALF BR, et al. Effect of Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma vs Placebo Injection on Pain and Medial Tibial Cartilage Volume in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: The RESTORE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021;326:2021-2030.
[15] BELK JW, LIM JJ, KEETER C, et al. Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis Who Receive Platelet-Rich Plasma or Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate Injections Have Better Outcomes Than Patients Who Receive Hyaluronic Acid: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arthroscopy. 2023;39:1714-1734.
[16] BELK JW, KRAEUTLER MJ, HOUCK DA, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Sports Med. 2021; 49:249-260.
[17] 李迩, 吴俊敏, 李思远, 等. 射频电极刃针松解术治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效观察[J]. 时珍国医国药,2023,34(8):1920-1922.
[18] PARK YB, KIM JH, HA CW, et al. Clinical Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection and Its Association With Growth Factors in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Clinical Trial As Compared With Hyaluronic Acid. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49:487-496.
[19] 冯雷, 邰东旭. 温针灸联合中药熏蒸对膝关节骨性关节炎骨代谢指标及炎性因子的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2022,49(1):150-154.
[20] 谈倩, 李佳, 李柏村, 等. 温针灸减轻膝骨性关节炎大鼠软骨组织的氧化损伤和炎性反应[J]. 针刺研究,2022,47(4):321-328.
[21] 杨荣荣, 郭萍, 张惠环. 基于膝关节功能、疼痛程度及生活质量评价温针灸辅助治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2024,51(7):152-155.
[22] 付聪聪, 张美丽, 王晓宁, 等. 当归通痹汤联合温针灸阳陵泉对膝骨性关节炎患者膝关节液炎性因子及血液黏滞度的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2024,44(6):1382-1385.
[23] JIN S, GUAN X. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the comparative curative effects of warm acupuncture and other traditional Chinese medicines in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Palliat Med. 2022;11:708-716.
[24] 王甜, 顾彦冬. 正骨推拿联合温针灸对膝骨性关节炎(寒湿痹阻型)患者的步态及炎性相关因子水平的影响[J]. 天津中医药,2024, 41(7):875-879.
[25] YAGI M, TANIGUCHI M, TATEUCHI H, et al. Properties of the iliotibial band and their relationships with gait parameters among patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2023;41:1177-1185.
[26] COSTA LAV, LENZA M, IRRGANG JJ, et al. How Does Platelet-Rich Plasma Compare Clinically to Other Therapies in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51:1074-1086.
[27] BARIA MR, VASILEFF WK, BORCHERS J, et al. Treating Knee Osteoarthritis With Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid Combination Therapy: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2022; 50:273-281.
[28] OEDING JF, VARADY NH, FEARINGTON FW, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Alternative Injections for Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Systematic Review and Statistical Fragility Index-Based Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Sports Med. 2024;52(12):3147-3160.
[29] LEWIS E, MERGHANI K, ROBERTSON I, et al. The effectiveness of leucocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma injections on symptomatic early osteoarthritis of the knee: the PEAK randomized controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2022;104-B:663-671.
[30] GU C, MAO Y, DONG H, et al. Nomogram in Knee Instability: 3D Gait Analysis of Knee Osteoarthritis Patients. Indian J Orthop. 2022; 56:1554-1564.
[31] 包杭生, 冯宗权, 邹勇根. 基于步态分析探究骨补丸干预老年膝骨关节炎患者炎症因子表达[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2024,44(2):331-334.
[32] 张帅攀, 朱清广, 程艳彬, 等. 易筋经功法干预膝骨关节炎患者步态生物力学的随机对照试验[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2023,38(10): 5081-5086.
[33] 李永杰, 付申宇, 夏渊, 等. 膝骨关节炎女性伸膝肌力、步态时空参数与峰值膝关节屈曲/内收力矩关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(9):1354-1358.
[34] PFEUFER D, MONTEIRO P, GILILLAND J, et al. Immediate Postoperative Improvement in Gait Parameters following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Can Be Measured with an Insole Sensor Device. J Knee Surg. 2022;35:692-697.
[35] BATAILLER C, LORDING T, NAAIM A, et al. No difference of gait parameters in patients with image-free robotic-assisted medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty compared to a conventional technique: early results of a randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:803-813.
[36] BACON KL, FELSON DT, JAFARZADEH SR, et al. Gait Alterations and Association With Worsening Knee Pain and Physical Function: A Machine Learning Approach With Wearable Sensors in the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024;76:984-992.
[37] WANG Z, LU J, LI Z, et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Measures in the Infrapatellar Fat Pad in Older Adults: Associations with Knee Pain, Radiographic Osteoarthritis, Kinematics, and Kinetics of the Knee. Acad Radiol. 2024;31:3315-3326.
[38] 李宏恩, 马恺, 石春花, 等. 步态分析用于膝骨性关节炎诊断与功能评定的研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2024,28(2):281-286.
[39] IWASAKI K, OHKOSHI Y, HOSOKAWA Y, et al. Higher Association of Pelvis-Knee-Ankle Angle Compared With Hip-Knee-Ankle Angle With Knee Adduction Moment and Patient-Reported Outcomes After High Tibial Osteotomy. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51:977-984.
[40] 马淑敏, 高谦, 徐峰, 等. 膝骨关节炎患者股四头肌功能水平及髋关节步态运动学特征分析[J]. 中国康复,2023,38(6):345-349.
[41] TAWY GF, BIANT LC, MCNICHOLAS MJ. Gait kinematics and knee stability 10-years following posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty comparable to healthy adults >55. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024;32:54-63.
|