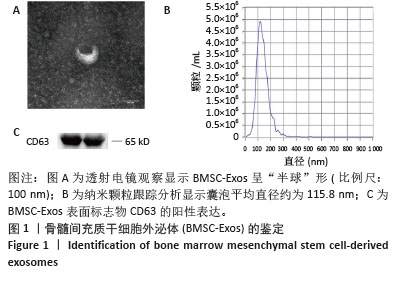
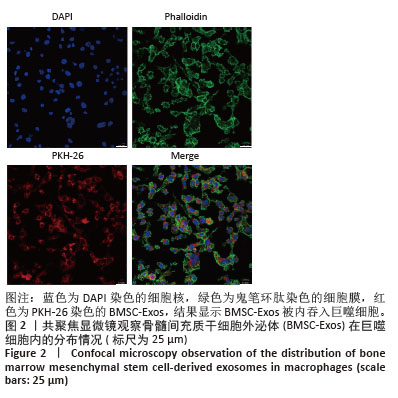
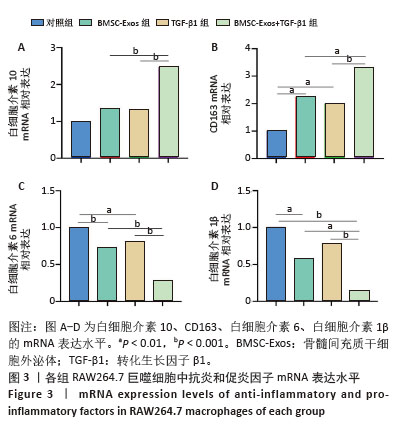
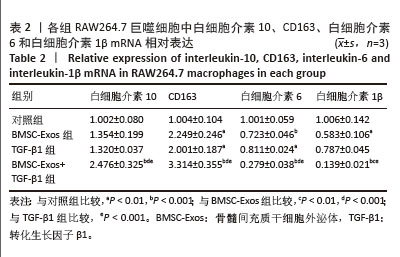
[1] MCCOY AM. Animal Models of Osteoarthritis: Comparisons and Key Considerations. Vet Pathol. 2015;52(5):803-818.
[2] ZHANG H, CAI D, BAI X. Macrophages regulate the progression of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):555-561.
[3] FURMAN BD, KIMMERLING KA, ZURA RD, et al. Articular ankle fracture results in increased synovitis, synovial macrophage infiltration, and synovial fluid concentrations of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(5):1234-1239.
[4] GORDON S, MARTINEZ FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32(5):593-604.
[5] HONSAWEK S, YUKTANANDANA P, TANAVALEE A, et al. Plasma and synovial fluid connective tissue growth factor levels are correlated with disease severity in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Biomarkers. 2012;17(4):303-308.
[6] AYRAL X, PICKERING EH, WOODWORTH TG, et al. Synovitis: a potential predictive factor of structural progression of medial tibiofemoral knee osteoarthritis -- results of a 1 year longitudinal arthroscopic study in 422 patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005; 13(5):361-367.
[7] WU CL, HARASYMOWICZ NS, KLIMAK MA, et al. The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):544-554.
[8] ATRI C, GUERFALI FZ, LAOUINI D. Role of Human Macrophage Polarization in Inflammation during Infectious Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1801.
[9] JIN Y, XU M, ZHU H, et al. Therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(19):9281-9294.
[10] YAO Z, QI W, ZHANG H, et al. Down-regulated GAS6 impairs synovial macrophage efferocytosis and promotes obesity-associated osteoarthritis. Elife. 2023;12:e83069.
[11] LI W, XU Y, CHEN W. Bone mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous lncRNA CAHM via exosomes to regulate macrophage polarization and ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Cell Res. 2022; 421(2):113408.
[12] XIE X, YANG X, WU J, et al. Exosome from indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerates repair process of ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating macrophages polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):367.
[13] OLSON SA, FURMAN BD, KRAUS VB, et al. Therapeutic opportunities to prevent post-traumatic arthritis: Lessons from the natural history of arthritis after articular fracture. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(9):1266-1277.
[14] RIGAMONTI E, ZORDAN P, SCIORATI C, et al. Macrophage plasticity in skeletal muscle repair. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:560629.
[15] AEGERTER H, LAMBRECHT BN, JAKUBZICK CV. Biology of lung macrophages in health and disease. Immunity. 2022;55(9):1564-1580.
[16] SHEN X, QIN J, WEI Z, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosome-derived lncRNA TUC339 influences the progression of osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization and chondrocyte apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;167:115488.
[17] LI Q, BARRES BA. Microglia and macrophages in brain homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18(4):225-242.
[18] TU Y, LIU J, KONG D, et al. Irisin drives macrophage anti-inflammatory differentiation via JAK2-STAT6-dependent activation of PPARγ and Nrf2 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;201:98-110.
[19] ZHU F, CHEN Y, LI J, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Myocardial Infarction Injury via miR-24-3p-Promoted M2 Macrophage Polarization. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2022;6(11):e2200074.
[20] AUDRITO V, SERRA S, BRUSA D, et al. Extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) promotes M2 macrophage polarization in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2015;125(1): 111-123.
[21] BLIDDAL H. Definition, pathology and pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ugeskr Laeger. 2020;182(42):V06200477.
[22] XIE J, HUANG Z, YU X, et al. Clinical implications of macrophage dysfunction in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:36-44.
[23] HE J, CAO W, AZEEM I, et al. Epigenetics of osteoarthritis: Histones and TGF-β1. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;510:593-598.
[24] ARABPOUR M, SAGHAZADEH A, REZAEI N. Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107823.
[25] MANTOVANI A, SICA A, SOZZANI S, et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(12):677-686.
[26] WANG Y, YU D, LIU Z, et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1):189.
[27] MANTOVANI A, BISWAS SK, GALDIERO MR, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 2013;229(2):176-185.
[28] WYNN TA, CHAWLA A, POLLARD JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446): 445-455.
[29] ZHANG J, RONG Y, LUO C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):25138-25152.
[30] PANG L, JIN H, LU Z, et al. Treatment with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Nanovesicle-Containing Gelatin Methacryloyl Hydrogels Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Modulating Chondrogenesis and Macrophage Polarization. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(17):e2300315.
[31] SCHMITTGEN TD, LIVAK KJ. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(6):1101-1108.
[32] SMITH PK, KROHN RI, HERMANSON GT, et al. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985;150(1):76-85.
[33] LUO M, ZHAO F, CHENG H, et al. Macrophage polarization: an important role in inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15: 1352946.
[34] CASSETTA L, CASSOL E, POLI G. Macrophage polarization in health and disease. ScientificWorldJournal. 2011;11:2391-2402.
[35] SICA A, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):787-795.
[36] ABE C, BHASWANT M, MIYAZAWA T, et al. The Potential Use of Exosomes in Anti-Cancer Effect Induced by Polarized Macrophages. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):1024.
[37] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;877:173090.
[38] CHEN Y, DONG P, ZHANG X. Research advance on the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in sepsis. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023;35(2):212-216.
[39] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440.
[40] GINHOUX F, GUILLIAMS M. Tissue-Resident Macrophage Ontogeny and Homeostasis. Immunity. 2016;44(3):439-449.
[41] ZHAI Z, CUI T, CHEN J, et al. Advancements in engineered mesenchymal stem cell exosomes for chronic lung disease treatment. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):895.
[42] ZHANG B, GONG J, HE L, et al. Exosomes based advancements for application in medical aesthetics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10: 1083640.
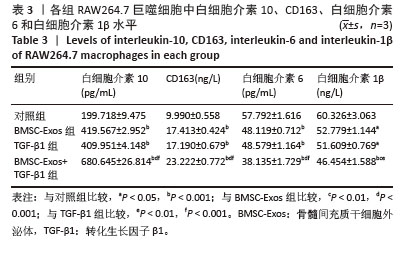
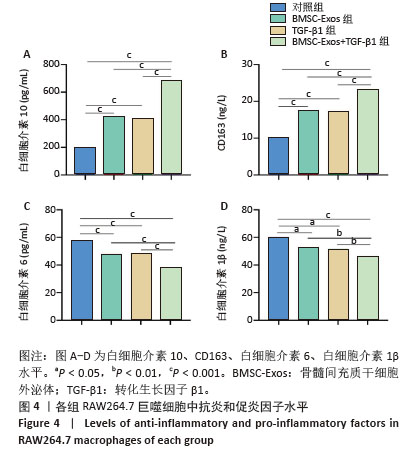
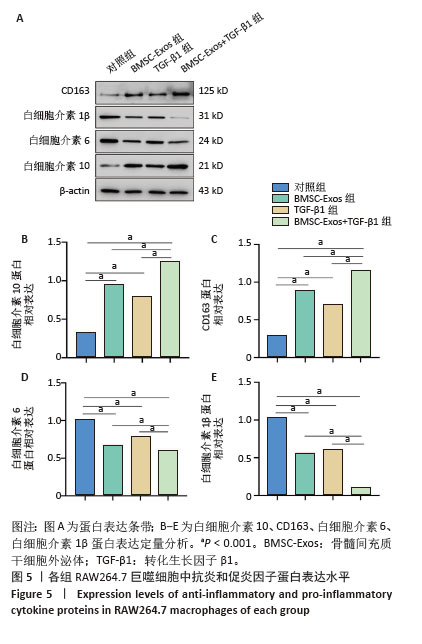
|