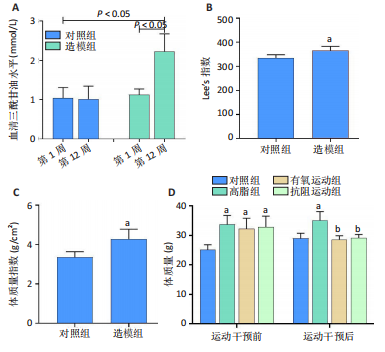
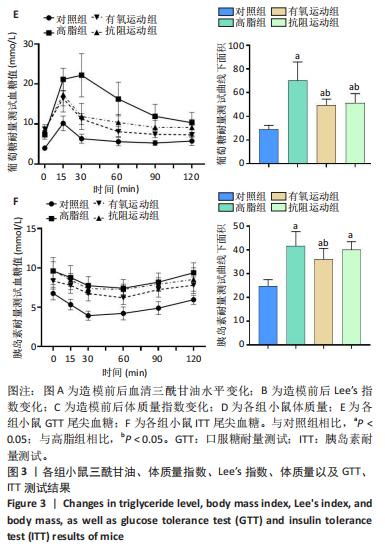
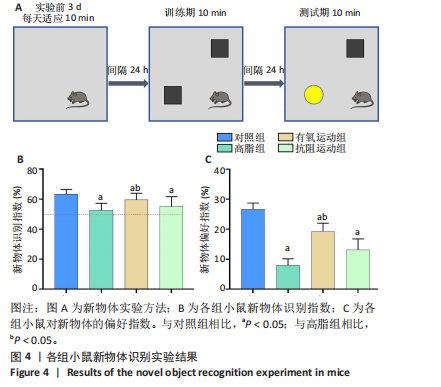
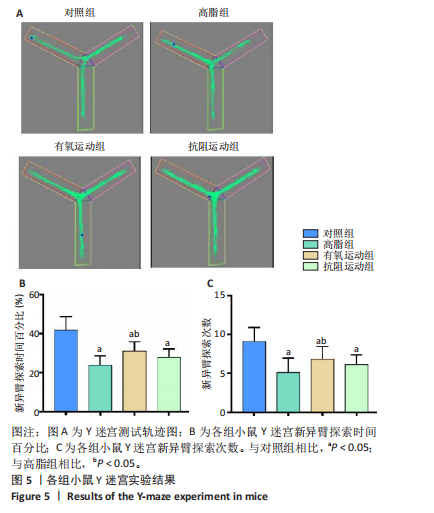
[1] GHOSH P, FONTANELLA RA, SCISCIOLA L, et al. Obesity-induced neuronal senescence: Unraveling the pathophysiological links. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;101:102533.
[2] QI Y, WANG X. The Role of Gut Microbiota in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetes: Lessons from Animal Models and Humans. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):922.
[3] TANG C, WANG Y, XU Z, et al. The relationships between high-fat diet and metabolic syndrome: Potential mechanisms. Food Bioscience. 2024; 59:104261.
[4] BOWMAN K, THAMBISETTY M, KUCHEL GA, et al. Obesity and Longer Term Risks of Dementia in 65-74 Year Olds. Age Ageing. 2019;48(3): 367-373.
[5] KULLMANN S, HENI M, HALLSCHMID M, et al. Brain Insulin Resistance at the Crossroads of Metabolic and Cognitive Disorders in Humans. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1169-1209.
[6] TYAGI A, PUGAZHENTHI S. Targeting Insulin Resistance to Treat Cognitive Dysfunction. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(6):2672-2691.
[7] CAI M, WAN J, CAI K, et al. The mitochondrial quality control system: a new target for exercise therapeutic intervention in the treatment of brain insulin resistance-induced neurodegeneration in obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2024;48(6):749-763.
[8] 钟莎莎,刘奇,王强,等.肥胖引发低度炎症导致认知障碍的机制研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2024,21(8):32-35.
[9] HUANG X, HUSSAIN B, CHANG J. Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27(1):36-47.
[10] WANG X, GE A, CHENG M, et al. Increased hypothalamic inflammation associated with the susceptibility to obesity in rats exposed to high-fat diet. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012:847246.
[11] VADINI F, SIMEONE PG, BOCCATONDA A, et al. Liraglutide improves memory in obese patients with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2020;44(6):1254-1263.
[12] ZHANG Z, ZHANG B, WANG X, et al. Olfactory Dysfunction Mediates Adiposity in Cognitive Impairment of Type 2 Diabetes: Insights From Clinical and Functional Neuroimaging Studies. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(7): 1274-1283.
[13] 李炎,刘鹏飞,刘学伟,等.开心散改善小鼠肥胖相关认知障碍的机制研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2024,30(1):46-52.
[14] SALMAN HB, SALMAN MA, YILDIZ AKAL E. The effect of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on weight loss and cognitive function in overweight or obese individuals on weight-loss diet. Nutr Hosp. 2022;39(4):803-813.
[15] 张鹏鹏.持续和间歇运动上调PGC-1α/Irisin/BDNF表达改善肥胖小鼠认知功能障碍[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2023,39(9): 1346-1355.
[16] LIM G, LEE H, LIM Y. Potential Effects of Resistant Exercise on Cognitive and Muscle Functions Mediated by Myokines in Sarcopenic Obese Mice. Biomedicines. 2022;10(10):2529.
[17] ZHANG H, LIANG JL, WU QY, et al. Swimming Suppresses Cognitive Decline of HFD-Induced Obese Mice through Reversing Hippocampal Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and BDNF Level. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2432.
[18] HAO S, DEY A, YU X, et al. Dietary obesity reversibly induces synaptic stripping by microglia and impairs hippocampal plasticity. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;51:230-239.
[19] SHERAFATI-MOGHADAM M, PAHLAVANI HA, DARYANOOSH F, et al. The effect of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on protein expression in Flexor Hallucis Longus (FHL) and soleus (SOL) in rats with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022;21(2):1499-1508.
[20] HORNBERGER TA JR, FARRAR RP. Physiological hypertrophy of the FHL muscle following 8 weeks of progressive resistance exercise in the rat. Can J Appl Physiol. 2004;29(1):16-31.
[21] ZHENG Y, QIN Z, TSOI B, et al. Electroacupuncture on Trigeminal Nerve-Innervated Acupoints Ameliorates Poststroke Cognitive Impairment in Rats with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion: Involvement of Neuroprotection and Synaptic Plasticity. Neural Plast. 2020;2020: 8818328.
[22] 李子木,梁维凤,常晶晶,等.白介素-1β基因敲除对小鼠行为的影响[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2024,47(9):1224-1231.
[23] 杨斌,张丽芝,陈琦芳,等.减重手术改善肥胖症认知功能障碍及其机制[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2023,50(10):2373-2384.
[24] MCLEAN FH, GRANT C, MORRIS AC, et al. Rapid and reversible impairment of episodic memory by a high-fat diet in mice. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11976.
[25] ZHUANG H, YAO X, LI H, et al. Long-term high-fat diet consumption by mice throughout adulthood induces neurobehavioral alterations and hippocampal neuronal remodeling accompanied by augmented microglial lipid accumulation. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;100:155-171.
[26] ELZINGA SE, HENN R, MURDOCK BJ, et al. cGAS/STING and innate brain inflammation following acute high-fat feeding. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1012594.
[27] MARYAM K, ALI H. Aerobic and resistance exercises affect the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway, and hippocampal neuron density of high-fat diet-induced obese elderly rats. Physiol Behav. 2023;264:114140.
[28] PARK HS, PARK SS, KIM CJ, et al. Exercise Alleviates Cognitive Functions by Enhancing Hippocampal Insulin Signaling and Neuroplasticity in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1603.
[29] SPITZ AZ, GAVATHIOTIS E. Physiological and pharmacological modulation of BAX. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43(3):206-220.
[30] PANTIYA P, THONUSIN C, CHUNCHAI T, et al. Higher untrained fitness exerts a neuroprotection in Independence to caloric restriction or exercise in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Exp Neurol. 2023;365:114416.
[31] YU H, LIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):209.
[32] NAKAHIRA K, HASPEL JA, RATHINAM VA, et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(3):222-230.
[33] BAI J, LIU F. The cGAS-cGAMP-STING Pathway: A Molecular Link Between Immunity and Metabolism. Diabetes. 2019;68(6):1099-1108.
[34] LI Y, BAI D, LU Y, et al. The crude guava polysaccharides ameliorate high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice via reshaping gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;213:234-246.
[35] SANG T, GUO C, GUO D, et al. Suppression of obesity and inflammation by polysaccharide from sporoderm-broken spore of Ganoderma lucidum via gut microbiota regulation. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;256:117594.
[36] ZHEN H, HU Y, LIU X, et al. The protease caspase-1: Activation pathways and functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;717:149978.
[37] CAI X, CHEN J, XU H, et al. Prion-like polymerization underlies signal transduction in antiviral immune defense and inflammasome activation. Cell. 2014;156(6):1207-1222.
[38] 雷森林,谌晓安,陈平,等.脑源性神经营养因子介导帕金森病的运动防治:作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(25):5454-5468.
[39] 雷森林,陈平,谌晓安.运动调控BDNF表达改善阿尔茨海默病的潜在作用机制研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2024,46(6):1249-1262.
[40] SEGUELLA L, PESCE M, CAPUANO R, et al. High-fat diet impairs duodenal barrier function and elicits glia-dependent changes along the gut-brain axis that are required for anxiogenic and depressive-like behaviors. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):115.
[41] YAN P, LIU H, ZHOU T, et al. Crosstalk of Synapsin1 palmitoylation and phosphorylation controls the dynamicity of synaptic vesicles in neurons. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(9):786.
[42] MA W, LU K, LIANG HM, et al. Synapsin 1 Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment and Neuroinflammation in Rats with Alzheimer’s Disease: An Experimental and Bioinformatics Study. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2023;20(9):648-659.
[43] 刘森,陈征,高欣冉,等.高脂饮食对大鼠海马形态及突触相关蛋白Synapsin-1表达的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2021,56(6):862-866.
[44] HUDMON A, SCHULMAN H. Neuronal CA2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: the role of structure and autoregulation in cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:473-510.
|