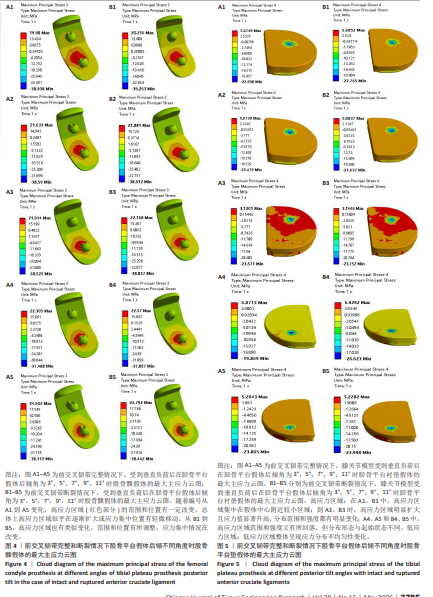
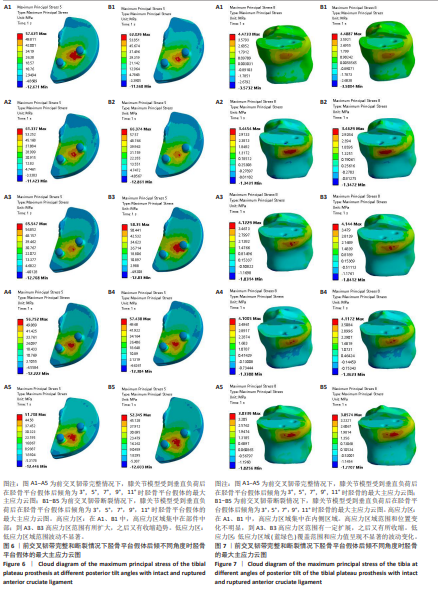
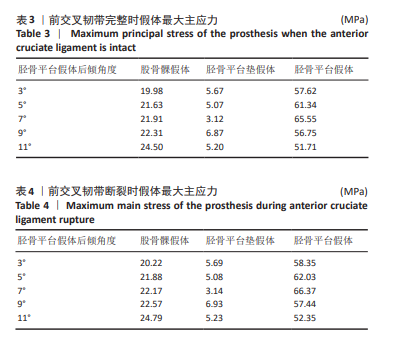
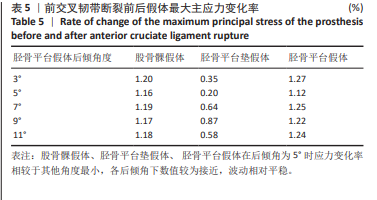
[1] 孙婧怡,高奉,钱驿,等. 前交叉韧带重建术后膝关节旋转稳定性对运动表现的影响 [J]. 中国医学科学院学报,2024,46(6):814-822.
[2] 熊昌军,左云周,严小康,等. 膝关节单髁置换术治疗高龄膝关节内侧间室骨关节炎的临床研究[J].中医正骨,2025,37(1):45-50.
[3] 李慧彬,王婷婷,张延辉,等.膝关节单髁置换术后并发症及分析[J].牡丹江医学院学报,2022,43(2):119-121.
[4] 党晓栋,熊守林,屈亚飞,等.UKA假体后倾角安装位置对衬垫磨损的影响[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(2):236-242.
[5] 翟凯,王冰,周珂,等.胫骨平台后倾角变化对单髁关节置换术后关节功能及假体生存率的影响[J].骨科,2024,15(1):18-23.
[6] 李鹏祥,赵改平,夏费一,等. 膝关节前交叉韧带断裂单髁置换生物力学特性的有限元分析 [J]. 医用生物力学,2020,35(1):70-76.
[7] 朱广铎. 单髁膝关节置换有限元分析[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院, 2016.
[8] 黄晓丹,李华,杨山,等.膝单髁置换术后髌股关节生物力学变化的相关研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2024,17(7):604-608.
[9] 樊瑜波, 王丽珍. 骨肌系统生物力学建模与仿真[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2018.
[10] COWIN SC. The mechanical and stress adaptive properties of bone. Ann Biomed Eng. 1983;11(3):263.
[11] DONZELLI PS, SPILKER RL, ATESHIAN GA, et al. Contact analysis of biphasic transversely isotropic cartilage layers and correlations with tissue failure. J Biomech. 1999;(10):1037-1047.
[12] LEROUX MA, SETTON LA. Experimental and Biphasic FEM Determinations of the Material Properties and Hydraulic Permeability of the Meniscus in Tension. J Biomech Eng. 2002;124(3):315-321.
[13] ARMSTRONG CG, LAI WM, MOW VC. An Analysis of the Unconfined Compression of Articular Cartilage. J Biomech Eng. 1984;106(2): 165-173.
[14] PE AE, CALVO B, MARTÍNEZ MA, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint. J Biomech. 2006;39(9):1686-1701.
[15] 马童, 薛华明, 文涛, 等. 单髁置换术应用于骨关节炎合并前交叉韧带缺失的三维有限元研究[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2019, 16(3):12-17.
[16] 张震, 董跃福, 苏宏飞, 等. 轻度OA膝关节有限元解剖模型的构建及其力学分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(5):439-443.
[17] 王献抗, 张月静, 杨友, 等. 单间室膝关节假体衬垫在步态载荷下的磨损性能仿真分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(12): 1831-1835.
[18] 刘牧子,沈鑫,谢荣辉,等. 单髁置换术胫骨假体后倾角的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(11):1033-1037.
[19] 刘军,陈慧,甄平,等.人工关节假体的摩擦学研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(18):1670-1674.
[20] 刘蒙飞,陈刚,史易晗,等.骨质疏松患者单髁置换过程中股骨假体置入位置优化的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(3):464-470.
[21] 郝琳,李正远,陈圣洪,等.前交叉韧带完整性对内侧活动平台膝关节单髁置换术短中期疗效的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2024,38(9):1071-1078.
[22] 曾伟清,肖子鹏,唐刚健,等.镜下前交叉韧带重建联合固定平台单髁置换术的早中期临床疗效观察[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2024,21(2):38-42.
[23] PFEIFFER FM. The use of finite element analysis to enhance research and clinical practice in orthopedics. J Knee Surg. 2016; 29:149-158.
[24] PANDY MG, SHELBURNE KB. Theoretical analysis of ligament and extensor-mechanism function in the ACL-deficient knee. Clin Biomech. 1998;13(2):98-111.
[25] WANG H, YAO G, HE K, et al. ACL reconstruction combined with anterolateral structures reconstruction for treating ACL rupture and knee injuries: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024; 12:1437684-1437684.
[26] 马广文, 黄斐, 吴云峰, 等. 胫骨后倾截骨对活动平台单髁关节置换术疗效的影响[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(4):302-304.
[27] LO PRESTI M, RASPUGLI GF, REALE D, et al. Early failure in medial unicondylar arthroplasty: Radiographic analysis on the importance of joint line restoration. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(9):860-865.
[28] SEKIGUCHI K, NAKAMURA S, KURIYAMA S, et al. Effect of tibial component alignment on knee kinematics and ligament tension in medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2019; 8(3):126-135.
[29] KOH YG, PARK KM, KANG KW, et al. Finite element analysis of the influence of the posterior tibial slope on mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2021;29:116-125.
[30] MOGLO K, SHIRAZI-ADL A. Biomechanics of passive knee joint in drawer: load transmission in intact and ACL-deficient joints. Knee. 2003;10(3):265-276.
[31] SUERO EM, CITAK M, CROSS MB, et al. Effects of tibial slope changes in the stability of cruciate ligament deficient knees: fixed bearing medial unicompartmental arthroplasty. Knee. 2012;19:365-369.
[32] MAK-HAM L, TP DF, SH PY, et al. Knee stability assessment on anterior cruciate ligament injury: Clinical and biomechanical approaches. Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation, Ther Technol(SMARTT). 2009; 1(1):20.
[33] CHEN Z, HAN J, ZHANG J, et al. Tibial post loading increases the risk of aseptic loosening of posterior-stabilized tibial prosthesis. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. J Eng Med. 2024;238(8-9): 9544119241272756.
[34] VEECKMANS P, GEORIS P, THIRION T. [Aseptic loosening due to osteolytic reaction to polyethylene of a total knee prosthesis]. Rev Med Liege. 2023;78(1):12-16.
[35] KUN QN, PENG XW, QI G, et al. High-grade pivot-shift phenomenon after anterior cruciate ligament injury is associated with asymmetry of lateral and medial compartment anterior tibial translation and lateral meniscus posterior horn tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(11):3700-3707.
[36] HASHIM S, JONES GG. Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction and Medial Unicompartmental Knee Replacement. J Orthop Case Rep. 2024;14(5):121-125.
[37] QI Y, SUN H, FAN Y, et al. Three dimensional finite element analysis of the influence of posterior tibial slope on the anterior cruciate ligament and knee joint forward stability. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2018;31(4):629-636.
[38] 张子恒,齐岩松,徐永胜. 有限元分析技术在膝关节骨性关节炎诊疗中的应用进展[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志,2024,9(2):96-101.
[39] 陆振宝,王启金,许庆山,等. 初次骨水泥型单髁置换术中的骨水泥用量分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2024,39(10):1077-1079.
[40] 苑冲锋. 关节外科手术患者感染情况监测及影响因素分析[J]. 临床研究,2018,26(9):11-13. |