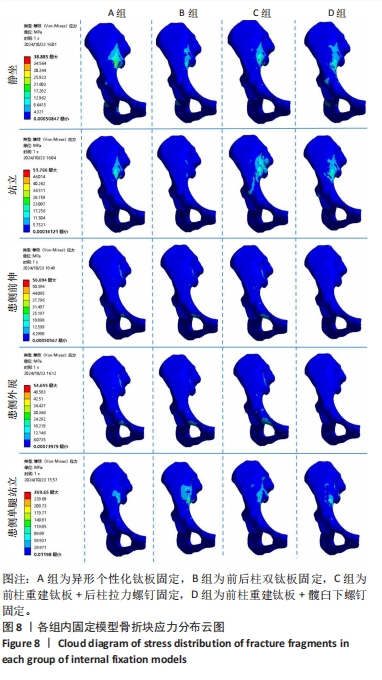
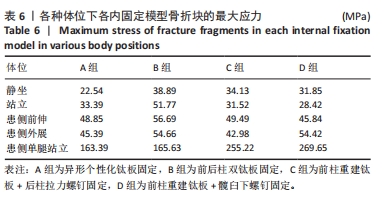
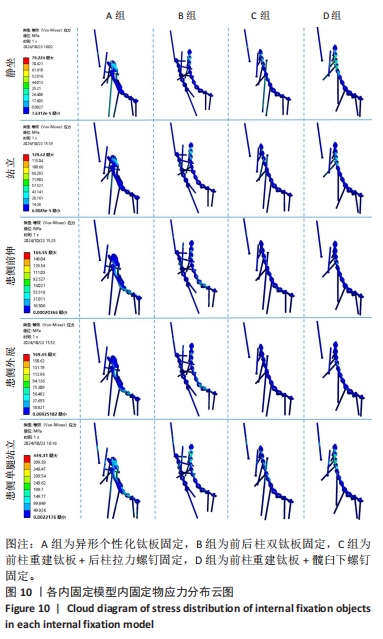
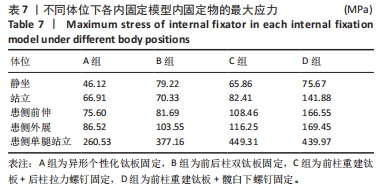
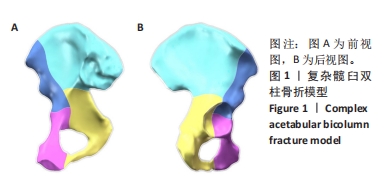
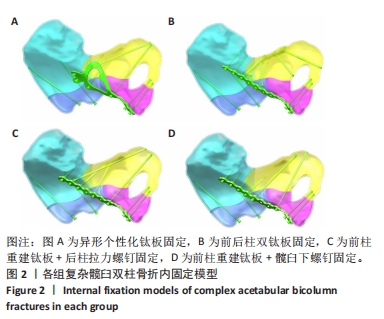
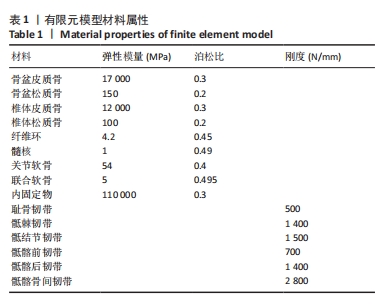
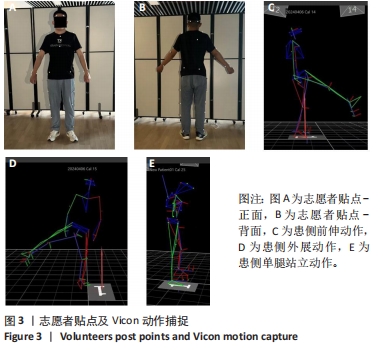
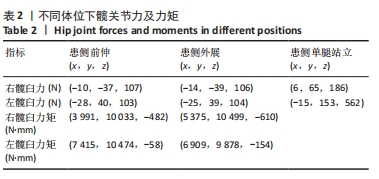
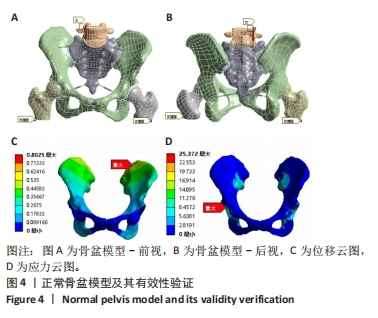
[1] LETOURNEL E. Acetabulum fractures: classification and management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;151:81-106.
[2] KELLY J, LADURNER A, RICKMAN M. Surgical management of acetabular fractures–a contemporary literature review. Injury. 2020;51(10):2267-2277.
[3] 刘潇,李明,刘建恒,等.髋臼双柱骨折的治疗现状[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(2):126-131.
[4] 吴华川,倪卫东.累及髋臼双柱骨折的手术治疗策略[J].检验医学与临床,2017,14(21):3276-3278.
[5] 吴海洋,蔡贤华,刘曦明,等.第二代动力化前路方形区钛板螺钉固定髋臼骨折有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(14): 1297-1301.
[6] 汪伟基,高希林,季明华,等.合并股骨头中心性脱位的髋臼骨折手术治疗分析[J].西北国防医学杂志,2015,36(3):196-198.
[7] 黄进成,刘曦明,蔡贤华,等.髋臼双柱骨折内固定生物力学稳定性的有限元分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2014,16(3):236-239.
[8] 古金山,杨朝晖,栗树伟.单一前路与前后联合入路治疗髋臼双柱骨折的力学分布差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(33):5254-5258.
[9] 赵德伟,田丰德.单纯髋臼前后缘发育不良的解剖学与临床研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2008(1):101-104.
[10] WU H,SHAO Q,SONG C, et al.Personalized three-dimensional printed anterior titanium plate to treat double-column acetabular fractures:a retrospective case-control.study. Orthop Surg. 2020; 12(4):1212-1222.
[11] LUBOVSKY O, PELEG E, JOSKOWICZ L, et al. Acetabular orientation variability and symmetry based on CT scans of adults[J].Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2010;5(5):449-54.
[12] 温湘源.3D打印个性化翼型接骨板治疗髋臼骨折生物力学研究及其临床应用[D].广州:南方医科大学,2020.
[13] LAWRENCE DA, MENN K, BAUMGAERTNER M, et al. Acetabular fractures: anatomic and clinical considerations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201(3):W425-436.
[14] 吴咏德,蔡贤华,刘曦明,等.前路钛板加方形区螺钉治疗髋臼双柱骨折的坐位生物力学分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2013,15(2):152-156.
[15] 许玉林,沈师,卓乃强,等.髋臼后柱骨折3种不同钢板固定后站立及坐立位下的生物力学比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(6): 826-830.
[16] 许文泉.一体化翼型接骨板固定复杂髋臼骨折的三维有限元分析及对比研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2022.
[17] 潘昌武,刘曦明,蔡贤华,等.微型联合重建接骨板内固定治疗髋臼后壁骨折坐位下的三维有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015, 23(2):160-164.
[18] 程莹莹,梁畅,许鹏,等.不同固定方案的腰椎后路椎间融合术生物力学有限元分析[J].北京化工大学学报(自然科学版),2024, 51(3):88-97.
[19] BULAQI HA, MASHHADI MM, SAFARI H, et al. Dynamic nature of abutment screw retightening: finite element study of the effect of retightening on the settling effect. J Prosthet Dent. 2015;113(5):412-419.
[20] 林冠林,陈庄洪,蔡贤华,等. 动力化前路方形区钛板螺钉系统固定伴有对侧骨盆前环不稳的髋臼双柱骨折的站位有限元分析[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(2):388-390.
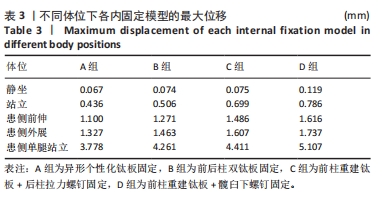
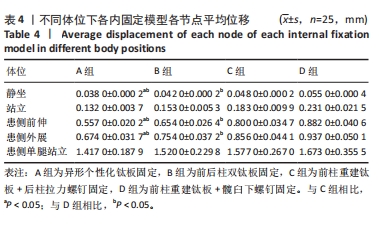
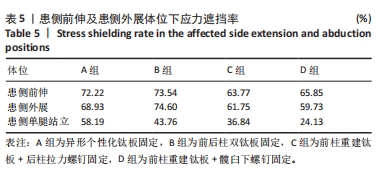
[21] 朱李梅,李明,徐爱君,等. 髋臼双柱骨折四种固定方式的生物力学比较及临床意义[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(9):2217-2220.
[22] 赵季伟,何金山,周岳来,等.髋臼后壁骨折3种内固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(10):1009-1013.
[23] 樊艳平,雷建银,刘海波,等.站位骨盆有限元模型的建立[J].太原理工大学学报,2015,46(1):124-128.
[24] 代元元.髋臼骨折内固定方式的模拟生物力学及有限元分析[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2016.
[25] 郭东鸿,童凯,王钢. 五种内固定方式固定髋臼后柱骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(6):529-535.
[26] 邵启鹏,蔡贤华,吴海洋,等.前柱伴后半横形髋臼骨折三种固定的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(22):2067-2071.
[27] NUSSER M, HOLSTIEGE J, KALUSCHA R, et al. Return to work after fractures of the pelvis and the acetabulum. Z Orthop Unfall. 2015; 153(3):282-288.
[28] 张志海,孙思佳,张绍安.单一髂腹股沟入路治疗髋臼双柱骨折的疗效分析[J].现代临床医学,2021,47(2):103-105.
[29] 李连欣,王利民,王晓梅.髋臼双柱骨折的诊疗进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2023,25(10):721-725.
[30] 张永强,章莹,夏远军,等. 髋臼部T形骨折四种不同内固定方式的生物力学有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2017,35(3):312-317.
[31] PIERANNUNZII L, FISCHER F, TAGLIABUE L, et al. Acetabular both-column fractures: essentials of operative management. Injury. 2010; 41(11):1145-1149.
[32] YANG Y, ZOU C, FANG Y. The Stoppa combined with iliac fossa approach for the treatment of both-column acetabular fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15: 1-7.
[33] YU X, GUO Y, KANG Q, et al. Effects and mechanisms of mechanical stress on secondary fracture healing. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013;18(4):1344-1348.
[34] 蔡成阔,石博文,计国旗,等.环形外固定架对长骨斜形骨折断端固定效果的生物力学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(22):1646-1646.
[35] TIANVE L, PENG Y, JINGII X, et al. Finite element analysis of different internal fixation methods for the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108658.
[36] 王序全,吴梅英,李起鸿.应力环境与骨折愈合[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,1999(1):40-44.
[37] PROVENCHER M, BAHNEY C, WORKING Z, et al. The Life of a Fracture: Biologic Progression, Healing Gone Awry, and Evaluation of Union. JBJS Rev. 2020;8(8):e1900221.
[38] PAUL GR, VALLASTER P, RUEGG M, et al. Tissue-level regeneration and remodeling dynamics are driven by mechanical stimuli in the microenvironment in a post-bridging loaded femur defect healing model in mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:856204.
[39] 丁晓红,徐世鹏,段朋云,等.骨折内固定接骨板生物力学评价及结构设计方法研究进展[J].上海理工大学学报,2022,44(5):429-439+472.
[40] 季东升.骨盆重建板的预弯塑形研究与有限元分析[D].天津:天津科技大学,2020.
[41] CARTER DR, BEAUPRE GS, GIORI NJ, et al. Mechanobiology of skeletal regeneration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(355 Suppl):S41-55.
|