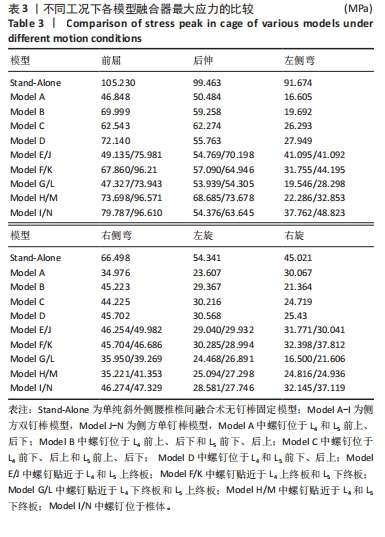
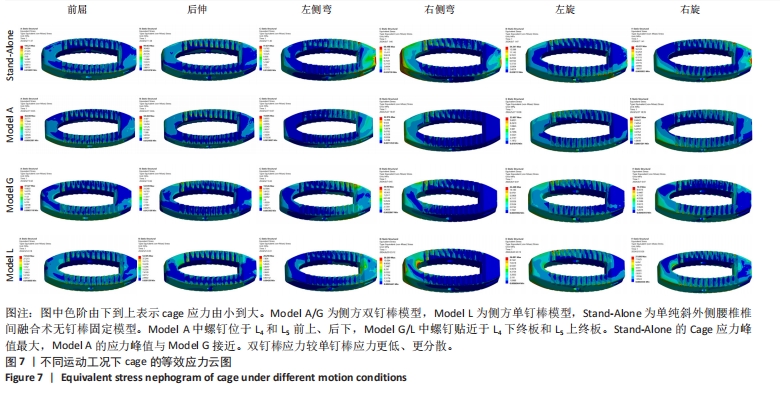
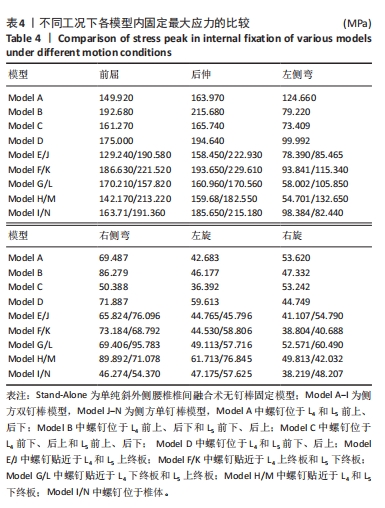
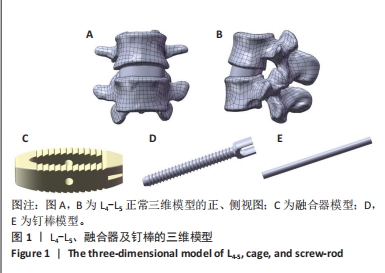
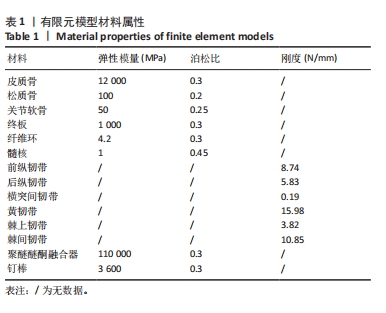
[1] SOUSLIAN FG, PATEL PD. Review and analysis of modern lumbar spinal fusion techniques. Brit J Neurosurg. 2021;38(1):61-67.
[2] MAYER HM. A new microsurgical technique for minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 1997;22(6):691-699; discussion 700.
[3] SILVESTRE C, MAC-THIONG JM, HILMI R, et al. Complications and Morbidities of Mini-open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in 179 Patients. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(2):89-97.
[4] LI X, DONG Y, ZHOU H, et al. Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion at L5-S1 Segment Through an Approach Between the Psoas Muscle and the Great Vessels. J Vis Exp. 2024;(203): doi: 10.3791/65684.
[5] 高志扬,王京,黄毓凯,等.斜外侧入路腰椎椎间融合术的临床进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2024,34(7):774-779.
[6] 魏晋鹏,常峰.斜外侧入路腰椎椎间融合术临床应用研究进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2023,21(1):50-56.
[7] 陈胜,顾俊,王春明,等.单边腰椎斜侧方入路椎间融合术治疗腰椎退行性疾病的临床疗效分析[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2022,42(12):1750-1754.
[8] LI R, LI X, ZHOU H, et al. Development and Application of Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):355-365.
[9] 李生鋆,范顺武,赵凤东. OLIF的临床应用与研究进展[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(1):18-24.
[10] 侯坤鹏,赵泉来,吴天亮,等.斜外侧入路腰椎融合内固定的生物力学稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):5362-5368.
[11] ZENG ZY, CHEN PQ, ZHAO X, et al. Analysis of the causes of cage subsidence after oblique lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2024;37 (1):33-44.
[12] 葛鑫,徐宏光,刘晨,等.腰椎退行性病单独腰椎斜外侧椎体间融合术的并发症[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(3):193-198.
[13] 高显达,马雷,赵若宇,等. 单节段斜外侧腰椎间融合术后腰痛的危险因素分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(18):1342-1349.
[14] CAI XY, BIAN HM, CHEN C, et al. Biomechanical study of oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) augmented with different types of instrumentation: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022; 17(1):269.
[15] GUO HZ, TANG YC, GUO DQ, et al. Stability evaluation of oblique lumbar interbody fusion constructs with various fixation options:A finite element analysis based on three-dimensional scanning models. World Neurosurg. 2020;138:e530-e538.
[16] ZHANG S, LIU Z, LU C, et al. Oblique lateral interbody fusion combined with different internal fixations for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spine disease: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):206.
[17] TARAWNEH AM, SALEM KM. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing the Accuracy and Clinical Outcome of Pedicle Screw Placement Using Robot-Assisted Technology and Conventional Freehand Technique. Glob Spine J. 2020;11(4): 575-586.
[18] HAO J, TANG X, JIANG N, et al. Biomechanical stability of oblique lateral interbody fusion combined with four types of internal fixations: finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1260693.
[19] OUYANG P, TAN Q, HE X, et al. Computational comparison of anterior lumbar interbody fusion and oblique lumbar interbody fusion with various supplementary fixation systems: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):4.
[20] WU MT, CHUNG TT, CHEN SC, et al. Oblique lateral interbody fusion in heterogenous lumbar diseases: Anterolateral screw fixation vs. posterior percutaneous pedicle screw fixation - A single center experience. Front Surg. 2022:9:989372.
[21] GUO Y, WANG X, LI Y, et al. Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion with Anterolateral Screw Fixation Is as Effective as with Posterior Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation in Treating Single-Segment Mild Degenerative Lumbar Diseases. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e934985.
[22] 李柱海,曾建成,王贤帝,等.斜外侧腰椎椎间融合术联合前路内固定治疗退行性腰椎滑脱症的疗效分析[J].中国临床新医学, 2023,16(3):213-218.
[23] LI R, LIU Y, ZHU Y, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of oblique lumbar interbody fusion with anterolateral screw and rod instrumentation in osteopenia patients: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):760.
[24] KANEDA K, ABUMI K, FUJIYA M. Burst fractures with neurologic deficits of the thoracolumbar-lumbar spine. Results of anterior decompression and stabilization with anterior instrumentation. Spine. 1984;9(8): 788-795.
[25] LU T, LU Y. Comparison of Biomechanical Performance Among Posterolateral Fusion and Transforaminal, Extreme, and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;129:e890-e899.
[26] XU H, JU W, XU N, et al. Biomechanical comparison of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with 1 or 2 cages by finite-element analysis. Neurosurgery. 2013;73:s198-s205.
[27] 中国康复医学会脊柱脊髓专业委员会腰椎研究学组. 腰椎侧方椎间融合术应用中国专家共识[J]. 中华医学杂志,2021,101(3):199-204.
[28] PAN CC, LEE CH, CHEN KH, et al. Comparative Biomechanical Analysis of Unilateral, Bilateral, and Lateral Pedicle Screw Implantation in Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Finite Element Study. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(11):1238.
[29] LEE HJ, LEE SJ, JUNG JM, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Various Fixation Options for Adjacent Segment Degeneration: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023;173:e156-e167.
[30] WANG T, ZHAO Y, CAI Z, et al. Effect of osteoporosis on internal fixation after spinal osteotomy: A finite element analysis. Clin Biomech. 2019; 69:178-183.
[31] ZHANG S, LIU Z, LU C, et al. Oblique lateral interbody fusion combined with different internal fixations for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spine disease: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):206.
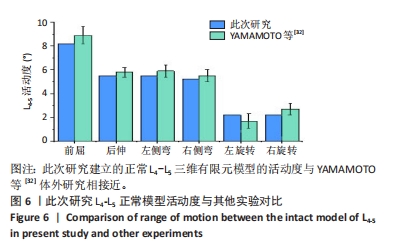
[32] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[33] TAO EX, ZHANG RJ, ZHANG B, et al. Biomechanical changes of oblique lumbar interbody fusion with different fixation techniques in degenerative spondylolisthesis lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):664.
[34] 唐福波,钟远鸣,李智斐.不同钉棒内固定方式在腰椎侧路融合中的有限元力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3293-3298.
[35] CHOI YH, KWON SW, MOON JH, et al. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion and in Situ Screw Fixation for Rostral Adjacent Segment Stenosis of the Lumbar Spine. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(6):755-762.
|