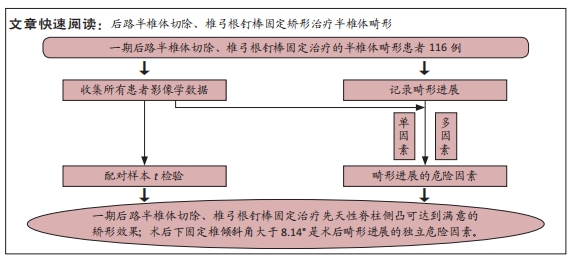
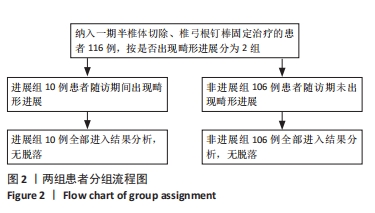
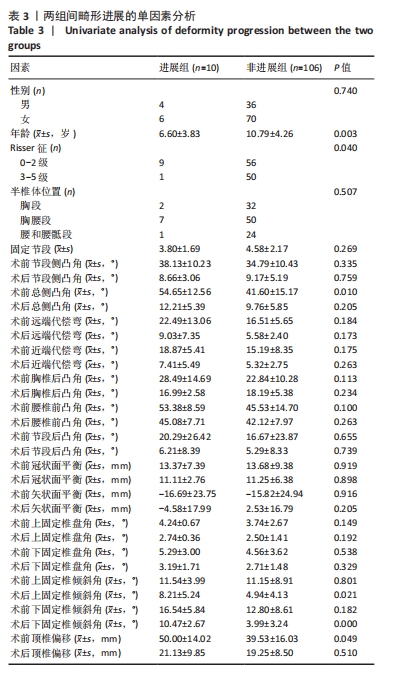
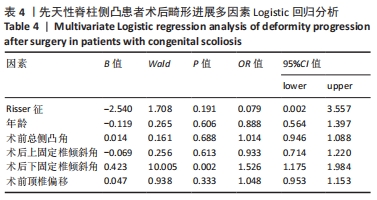
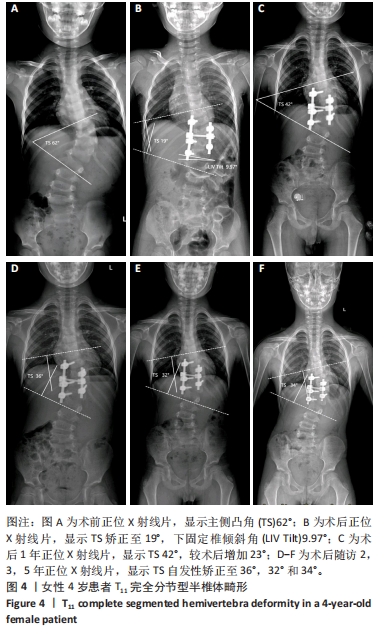
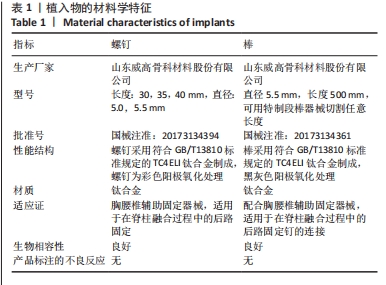
[1] MCMASTER MJ, SINGH H. Natural history of congenital kyphosis and kyphoscoliosis. A study of one hundred and twelve patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(10):1367-1383.
[2] MCMASTER MJ, DAVID CV. Hemivertebra as a cause of scoliosis. A study of 104 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(4):588-595.
[3] KAWAKAMI N, TSUJI T, IMAGAMA S, et al. Classification of congenital scoliosis and kyphosis: a new approach to the three-dimensional classification for progressive vertebral anomalies requiring operative treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(17):1756-1765.
[4] NASCA RJ, STILLING FR, STELL HH. Progression of congenital scoliosis due to hemivertebrae and hemivertebrae with bars. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57(4):456-466.
[5] MARKS DS, QAIMKHANI SA. The Natural History of Congenital Scoliosis and Kyphosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(17):1751-1755.
[6] JOHAL J, LOUKAS M, FISAHN C, et al. Hemivertebrae: a comprehensive review of embryology, imaging, classification, and management. Childs Nerv Syst. 2016;32(11):2105-2109.
[7] CHANG D, KIM J, HA K, et al. Posterior Hemivertebra Resection and Short Segment Fusion With Pedicle Screw Fixation for Congenital Scoliosis in Children Younger Than 10 Years : greater than 7-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(8):E484-E491.
[8] SHONO Y, ABUMI K, KANEDA K. One-stage posterior hemivertebra resection and correction using segmental posterior instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(7):752-757.
[9] YANG JH, CHANG DG, SUH SW, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of hemivertebra resection for congenital scoliosis in children under age 10 years: More than 5-year follow-up. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(32):e21720.
[10] OKSANEN HM, JALANKO T, HELENIUS IJ. Outcomes of early hemivertebrectomy in children with congenital scoliosis: A prospective follow-up study. Scand J Surg. 2021;110(4):542-549.
[11] LI H, CHEN Z, GAO B, et al. Surgical outcomes in children under 10 years old in the treatment of congenital scoliosis due to single nonincarcerated thoracolumbar hemivertebra: according to the age at surgery. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):721.
[12] CROSTELLI M, MAZZA O, MARIANI M, et al. Hemivertebra Resection and Spinal Arthrodesis by Single-Stage Posterior Approach in Congenital Scoliosis and Kyphoscoliosis: Results at 9.6 Years Mean Follow-up. Int J Spine Surg. 2022;16(1):194-201.
[13] HUANG Y, FENG G, LIU L, et al. Posterior hemivertebral resection for upper thoracic congenital scoliosis: be aware of high risk of complications. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2019;28(1):1-9.
[14] BAO B, SU Q, HAI Y, et al. Posterior thoracolumbar hemivertebra resection and short-segment fusion in congenital scoliosis: surgical outcomes and complications with more than 5-year follow-up. BMC Surg. 2021;21(1):165.
[15] PIANTONI L, FRANCHERI WILSON IA, TELLO CA, et al. Hemivertebra Resection With Instrumented Fusion by Posterior Approach in Children. Spine Deform. 2015;3(6):541-548.
[16] 涂志明, 王冰, 吕国华, 等. 先天性脊柱侧凸半椎体切除短节段融合术后失代偿的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(7): 648-651.
[17] YANG X, SONG Y, LIU L, et al. Emerging S-shaped curves in congenital scoliosis after hemivertebra resection and short segmental fusion. Spine J. 2016;16(10):1214-1220.
[18] LI S, CHEN Z, QIU Y, et al. Coronal Decompensation After Posterior-only Thoracolumbar Hemivertebra Resection and Short Fusion in Young Children With Congenital Scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(9):654-660.
[19] BAO B, YAN H, TANG J. A review of the hemivertebrae and hemivertebra resection. Br J Neurosurg. 2022;36(5):546-554.
[20] KAROL LA. The Natural History of Early-onset Scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2019;39((Issue 6, Supplement 1 Suppl 1):S38-S43.
[21] MACKEL CE, JADA A, SAMDANI AF, et al. A comprehensive review of the diagnosis and management of congenital scoliosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018;34(11):2155-2171.
[22] GAO R, ZHANG X, GUO D, et al. Medium-term and Long-term Follow-up Surgical Outcomes of the 1-stage Posterior-only Lumbosacral Hemivertebra Resection With Short-segment Fusion in Children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2023;43(2):e120-e126.
[23] XUE X, ZHAO S. Posterior hemivertebra resection with unilateral instrumented fusion in children less than 10 years old: preliminary results at minimum 5-year follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018; 13(1):240.
[24] BARIK S, MISHRA D, GUPTA T, et al. Surgical outcomes following hemivertebrectomy in congenital scoliosis: a systematic review and observational meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(7):1835-1847.
[25] WANG Y, LIU Z, DU C, et al. The radiological outcomes of one-stage posterior-only hemivertebra resection and short segmental fusion for lumbosacral hemivertebra: a minimum of 5 years of follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):426.
[26] 张福勇,王晓东,甄允方,等.后路半椎体切除短节段固定儿童先天性脊柱畸形[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(7):650-653.
[27] GUO J, ZHANG J, WANG S, et al. Surgical outcomes and complications of posterior hemivertebra resection in children younger than 5 years old. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):48.
[28] SÁNCHEZ-MÁRQUEZ JM, PIZONES J, MARTÍN-BUITRAGO MP, et al. Midterm Results of Hemivertebrae Resection and Transpedicular Short Fusion in Patients Younger Than 5 Years: How Do Thoracolumbar and Lumbosacral Curves Compare? Spine Deform. 2019;7(2):267-274.
[29] WANG S, ZHANG J, QIU G, et al. Posterior-only Hemivertebra Resection With Anterior Structural Reconstruction With Titanium Mesh Cage and Short Segmental Fusion for the Treatment of Congenital Scoliokyphosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(22):1687-1692.
[30] ZHUANG Q, ZHANG J, LI S, et al. One-stage posterior-only lumbosacral hemivertebra resection with short segmental fusion: a more than 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(5):1567-1574.
[31] 王升儒, 林莞锋, 杨阳, 等. 后路一期半椎体切除治疗先天性脊柱侧凸的疗效及并发症研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020, 13(12):976-981.
[32] SHI BL, LI Y, ZHU ZZ, et al. Failed Primary Surgery in Congenital Scoliosis Caused by a Single Hemivertebra: Reasons and Revision Strategies. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(2):349-355.
[33] XU Y, LI J, LI D, et al. Presence of compensatory curve predicts postoperative curve progression in congenital scoliosis after thoracolumbar hemivertebra resection and short fusion. Eur Spine J. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08398-0.
[34] 杨曦, 宋跃明, 刘立岷, 等. 先天性半椎体切除术后新发侧凸畸形的临床分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(7):586-592.
[35] 蒋彬, 王冰, 吕国华, 等. 上胸段半椎体切除术后远端冠状面S畸形进展的危险因素[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021,31(5):394-401.
[36] WANG Y, SHI B, LIU Z, et al. The Upper Instrumented Vertebra Horizontalization: An Essential Factor Predicting the Spontaneous Correction of Compensatory Curve After Lumbosacral Hemivertebra Resection and Short Fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(19): E1272-E1278.
[37] 曹隽,张学军,白云松,等.后路半椎体切除短节段融合固定术治疗儿童腰骶段半椎体畸形及近端代偿侧凸自发矫正的影响因素[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021,31(5):408-415.
[38] CHANG D, YANG J, LEE J, et al. Congenital scoliosis treated with posterior vertebral column resection in patients younger than 18 years: longer than 10-year follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016; 25(2):225-233.
[39] 邹传奇,初同伟,周跃.一期经后路半椎体切除矫治先天性脊柱半椎体侧后凸畸形研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014, 28(7):909-912.
[40] 刘威,陈文昊.先天性脊柱侧弯半椎体切除的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(19):1776-1779+1785. |