[1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(6):573-611.
[2] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Clinical application of bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells to repair skeletal tissue. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9759.
[3] OLSEN TK, BARYAWNO N. Introduction to single-cell RNA sequencing. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2018;122(1):e57.
[4] SLOVIN S, CARISSIMO A, PANARIELLO F, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis: a step-by-step overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2284:343-365.
[5] ANAPARTHY N, HO YJ, MARTELOTTO L. Single-cell applications of next-generation sequencing. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019;9:a026898.
[6] NEFTEL C, LAFFY J, FILBIN MG, et al. An integrative model of cellular states, plasticity, and genetics for glioblastoma. Cell. 2019;178(4):835-849.
[7] BONORA G, RAMANI V, SINGH R, et al. Single-cell landscape of nuclear configuration and gene expression during stem cell differentiation and X inactivation. Genome Biol. 2021;22(1):279.
[8] TUCKER NR, CHAFFIN M, FLEMING SJ, et al. Transcriptional and cellular diversity of the human heart. Circulation. 2020;142(5):466-482.
[9] SAULER M, MCDONOUGH JE, ADAMS TS, et al. Characterization of the COPD alveolar niche using single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):494.
[10] YEO AT, RAWAL S, DELCUZE B, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals evolution of immune landscape during glioblastoma progression. Nat Immunol. 2022;23:971-984.
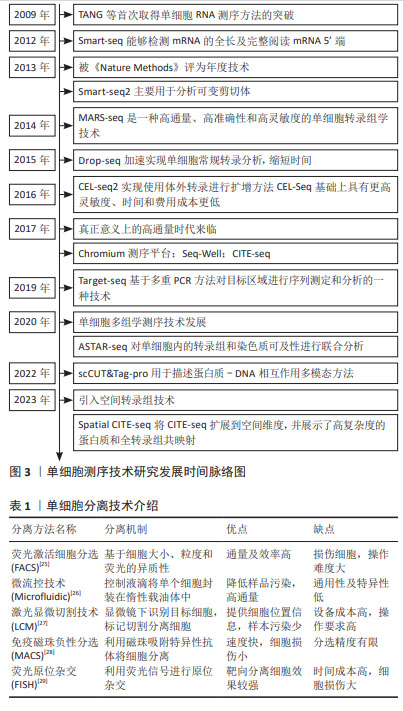
[11] TANG F, BARBACIORU C, WANG Y, et al. mRNA-Seq whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nat Methods. 2009;6(5):377-382.
[12] PICELLI S, BJÖRKLUND ÅK, FARIDANI OR, et al. Smart-seq2 for sensitive full-length transcriptome profiling in single cells. Nat Methods. 2013;10(11): 1096-1098.
[13] SEIRUP M, CHU LF, SENGUPTA S, et al. Reproducibility across single-cell RNA-seq protocols for spatial ordering analysis. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0239711.
[14] JAITIN DA, KENIGSBERG E, KEREN-SHAUL H, et al. Massively parallel single-cell RNA-seq for marker-free decomposition of tissues into cell types. Science. 2014;343(6172):776-779.
[15] MACOSKO EZ, BASU A, SATIJA R, et al. Highly parallel genome-wide expression profiling of individual cells using nanoliter droplets. Cell. 2015; 161(5):1202-1214.
[16] HASHIMSHONY T, SENDEROVICH N, AVITAL G, et al. CEL-Seq2: sensitive highly-multiplexed single-cell RNA-Seq. Genome Biol. 2016;17:77.
[17] ZHENG GX, TERRY JM, BELGRADER P, et al. Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14049.
[18] GIERAHN TM, WADSWORTH MH 2ND, HUGHES TK, et al. Seq-Well: portable, low-cost RNA sequencing of single cells at high throughput. Nat Methods. 2017;14(4):395-398.
[19] STOECKIUS M, HAFEMEISTER C, STEPHENSON W, et al. Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nat Methods. 2017;14(9):865-868.
[20] RODRIGUEZ-MEIRA A, BUCK G, CLARK SA, et al. Unravelling intratumoral heterogeneity through high-sensitivity single-cell mutational analysis and parallel RNA sequencing. Mol Cell. 2019;73(6):1292-1305.e8.
[21] XING QR, FARRAN CAE, ZENG YY, et al. Parallel bimodal single-cell sequencing of transcriptome and chromatin accessibility. Genome Res. 2020;30(7):1027-1039.
[22] ZHU C, ZHANG Y, LI YE, et al. Joint profiling of histone modifications and transcriptome in single cells from mouse brain. Nat Methods. 2021;18(3): 283-292.
[23] ZHANG B, SRIVASTAVA A, MIMITOU E, et al. Characterizing cellular heterogeneity in chromatin state with scCUT&Tag-pro. Nat Biotechnol. 2022;40(8):1220-1230.
[24] LIU Y, DISTASIO M, SU G, et al. High-plex protein and whole transcriptome co-mapping at cellular resolution with spatial CITE-seq. Nat Biotechnol. 2023; 41(10):1405-1409.
[25] KUROKI Y, AGATA K. Isolation of planarian viable cells using fluorescence-activated cell sorting for advancing single-cell transcriptome analysis. Genes Cells. 2023;28(11):800-810.
[26] ZHOU WM, YAN YY, GUO QR, et al. Microfluidics applications for high-throughput single cell sequencing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):312.
[27] DATTA S, MALHOTRA L, DICKERSON R, et al. Laser capture microdissection: big data from small samples. Histol Histopathol. 2015;30(11):1255-1269.
[28] WELZEL G, SEITZ D, SCHUSTER S. Magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) can be used as a large-scale method for establishing zebrafish neuronal cell cultures. Sci Rep. 2015;5:7959.
[29] AMANN RI, KRUMHOLZ L, STAHL DA. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental studies in microbiology. J Bacteriol. 1990;172(2):762-770.
[30] DEMONTIERO O, VIDAL C, DUQUE G. Aging and bone loss: new insights for the clinician. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(2):61-76.
[31] WANG Z, LI X, YANG J, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing deconvolutes the in vivo heterogeneity of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(15):4192-4206.
[32] SACCHETTI B, FUNARI A, MICHIENZI S, et al. Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment. Cell. 2007;131:324-336.
[33] LI H, GHAZANFARI R, ZACHARAKI D, et al. Low/negative expression of PDGFR-α identifies the candidate primary mesenchymal stromal cells in adult human bone marrow. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;3(6):965-974.
[34] MATSUSHITA Y, NAGATA M, KOZLOFF KM, et al. A Wnt-mediated transformation of the bone marrow stromal cell identity orchestrates skeletal regeneration. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):332.
[35] TIKHONOVA AN, DOLGALEV I, HU H, et al. The bone marrow microenvironment at single-cell resolution. Nature. 2019;569:222-228.
[36] JOSEPHSON AM, BRADASCHIA-CORREA V, LEE S, et al. Age-related inflammation triggers skeletal stem/progenitor cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116(14):6995-7004.
[37] AMBROSI TH, SCIALDONE A, GRAJA A, et al. Adipocyte accumulation in the bone marrow during obesity and aging impairs stem cell-based hematopoietic and bone regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(6):771-784.e6.
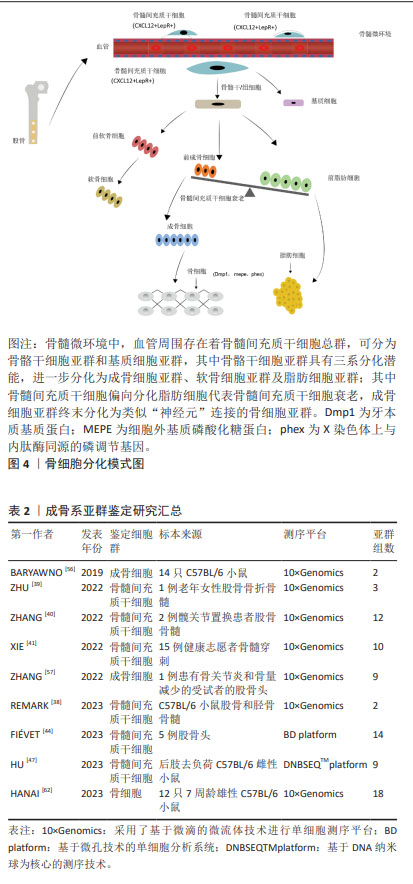
[38] REMARK LH, LECLERC K, RAMSUKH M, et al. Loss of Notch signaling in skeletal stem cells enhances bone formation with aging. Bone Res. 2023; 11(1):50.
[39] ZHU D, GAO J, TANG C, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from the elderly people. Int J Stem Cells. 2022; 15(2):173-182.
[40] ZHANG Z, ZHANG T, ZHOU L, et al. Identification of diagnostic genes and effective drugs associated with osteoporosis treatment by single-cell RNA-seq analysis and network pharmacology. Mediators Inflamm. 2022; 2022:6830635.
[41] XIE Z, YU W, YE G, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and functional subpopulation identification. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(4):483-492.
[42] HONG SH, LEE MH, KOO MA, et al. Stem cell passage affects directional migration of stem cells in electrotaxis. Stem Cell Res. 2019;38:101475.
[43] YANG YK, OGANDO CR, WANG SEE C, et al. Changes in phenotype and differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells aging in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):131.
[44] FIÉVET L, ESPAGNOLLE N, GEROVSKA D, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing of human non-hematopoietic bone marrow cells reveals a unique set of inter-species conserved biomarkers for native mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):229.
[45] WANG Z, LI X, YANG J, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing deconvolutes the in vivo heterogeneity of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(15):4192-4206.
[46] 李莉莉,魏琦岩,王艳芳,等.FGF/FGFR信号调控成骨细胞分化的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2017,37(6):107-113.
[47] HU Y, TIAN H, CHEN W, et al. The critical role of the Piezo1/β-catenin/ATF4 axis on the stemness of Gli1+ BMSCs during simulated microgravity-induced bone loss. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(32):e2303375.
[48] 黄浩然,卫杨文祥,章家皓,等.Piezo1介导的机械应力刺激在抗骨质疏松中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(17):2716-2722
[49] ZHU X, BAI W, ZHENG H. Twelve years of GWAS discoveries for osteoporosis and related traits:advances, challenges and applications. Bone Res. 2021; 9(1):23.
[50] WU D, LI L, WEN Z, et al. Romosozumab in osteoporosis: yesterday, today and tomorrow. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):668.
[51] REID IR, BILLINGTON EO. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet. 2022;399(10329):1080-1092.
[52] DOOLITTLE ML, KHOSLA S, SAUL D. Single-cell integration of BMD GWAS results prioritize candidate genes influencing age-related bone loss. JBMR Plus. 2023;7(10):e10795.
[53] CAPULLI M, PAONE R, RUCCI N. Osteoblast and osteocyte:games without frontiers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;561:3-12.
[54] LONG F. Building strong bones: molecular regulation of the osteoblast lineage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;13(1):27-38.
[55] JENSEN ED, GOPALAKRISHNAN R, WESTENDORF JJ. Regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts. Biofactors. 2010;36(1):25-32.
[56] BARYAWNO N, PRZYBYLSKI D, KOWALCZYK MS, et al. A cellular taxonomy of the bone marrow stroma in homeostasis and leukemia. Cell. 2019;177(7): 1915-1932.e16.
[57] ZHANG HX, CAO C, LI XH, et al. Imputation of human primary osteoblast single cell RNA-seq data identified three novel osteoblastic subtypes. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022;27(10):295.
[58] KONTOGEORGOS G, KRANTZ E, TRIMPOU P, et al. Teriparatide treatment in severe osteoporosis-a controlled 10-year follow-up study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):1011.
[59] SHI Y, LIAO X, LONG JY, et al. Gli1+ progenitors mediate bone anabolic function of teriparatide via Hh and Igf signaling. Cell Rep. 2021;36(7):109542.
[60] 高远,张长青,陶诗聪.骨细胞与骨衰老[J].国际骨科学杂志,2023, 44(1):1-4.
[61] ROBLING AG. BONEWALD LF. The osteocyte:new insights. Annu Rev Physiol. 2020;82:485-506.
[62] HANAI A, KAWABATA A, NAKAJIMA K, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies Fgf23-expressing osteocytes in response to 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1102751.
[63] WANG JS, WEIN MN. Pathways controlling formation and maintenance of the osteocyte dendrite network. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2022;20(6):493-504.
[64] BONEWALD LF. The amazing osteocyte. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(2): 229-238.
[65] TIEDE-LEWIS LM, DALLAS SL. Changes in the osteocyte lacunocanalicular network with aging. Bone. 2019;122:101-113.
[66] FABRE S, FUNCK-BRENTANO T, COHEN-SOLAL M. Anti-sclerostin antibodies in osteoporosis and other bone diseases. J Clin Med. 2020;9(11):3439.
[67] TSUKASAKI M, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology:evolving concepts in bone-immune interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(10):626-642.
[68] OKAMOTO K, NAKASHIMA T, SHINOHARA M, et al. Osteoimmunology: the conceptual framework unifying the immune and skeletal systems. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1295-1349.
[69] TSUKASAKI M, HUYNH NC, OKAMOTO K, et al. Stepwise cell fate decision pathways during osteoclastogenesis at single-cell resolution. Nat Metab. 2020;2(12):1382-1390.
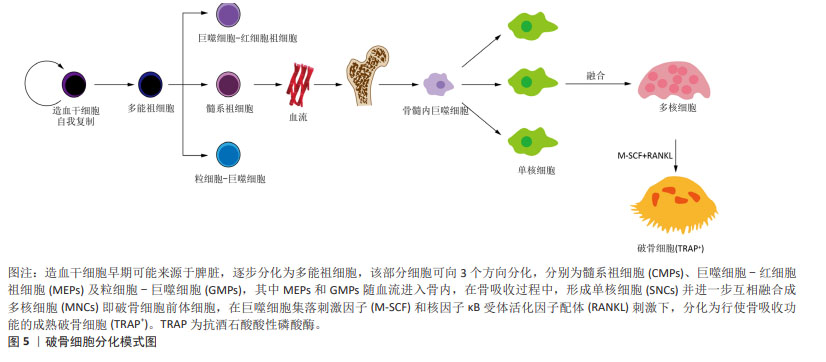
[70] OMATA Y, OKADA H, UEBE S, et al. Interspecies single-cell RNA-Seq analysis reveals the novel trajectory of osteoclast differentiation and therapeutic Targets. JBMR Plus. 2022;6(7):e10631.
[71] YAHARA Y, BARRIENTOS T, TANG YJ, et al. Erythromyeloid progenitors give rise to a population of osteoclasts that contribute to bone homeostasis and repair. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(1):49-59.
[72] GINHOUX F, JUNG S. Monocytes and macrophages: developmental pathways and tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(6):392-404.
[73] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):19-26.
[74] JIRUI W, WENCHAO W, MIN T, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals classical monocytes are the major precursors of rat osteoclasts. Biocell. 2022;46(3):655-665.
[75] KODAMA J, KAITO T. Osteoclast multinucleation: review of current literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5685.
[76] CHO E, CHEON S, DING M, et al. Identification of novel genes for cell fusion during osteoclast formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(12):6421.
[77] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Osteoimmunology-bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408(6812):535-536.
[78] SRIVASTAVA RK, DAR HY, MISHRA PK. Immunoporosis: immunology of osteoporosis-role of T cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:657.
[79] ZHOU Z, HUANG Z, KHAN HM, et al. Identification of 12 hub genes associated to the pathogenesis of osteoporosis based on microarray and single-cell RNA sequencing data. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023;23(2):186.
[80] GUO W, JIN P, LI R, et al. Dynamic network biomarker identifies cdkn1a-mediated bone mineralization in the triggering phase of osteoporosis. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55(1):81-94.
[81] SUN Y, WANG X, CHEN G, et al. miRNA-187-5p Regulates osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in mice by targeting ICAM1. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6139469.
[82] GUARANÁ WL, LIMA CAD, BARBOSA AD, et al. Can polymorphisms in NLRP3 inflammasome complex be associated with postmenopausal osteoporosis severity? Genes (Basel). 2022;13(12):2271.
[83] XU Y, HUANG S, LI Z, et al. Single-cell RNA landscape of osteoimmune microenvironment in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture and Kümmell’s disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1276098.
[84] WANG S, GREENBAUM J, QIU C, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals in vivo osteoimmunology interactions between the immune and skeletal systems. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1107511.
[85] ONO N, ONO W, MIZOGUCHI T, et al. Vasculature-associated cells expressing nestin in developing bones encompass early cells in the osteoblast and endothelial lineage. Dev Cell. 2014;29(3):330-339.
[86] IGA T, KOBAYASHI H, KUSUMOTO D, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of bone marrow endothelial cells unveils a distinct subtype in the epiphysis. Nat Cell Biol. 2023;25(10):1415-1425.
[87] TUCKERMANN J, ADAMS RH. The endothelium-bone axis in development, homeostasis and bone and joint disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(10): 608-620.
[88] 陈伟坚,姜涛,周宜,等.LC-MS联合单细胞测序分析探讨参苓白术散治疗原发性骨质疏松症的作用机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(10): 1458-1465.
[89] SALIBA AE, WESTERMANN AJ, GORSKI SA, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq: advances and future challenges. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(14):8845-8860.
|