中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (21): 3435-3444.doi: 10.12307/2022.656
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇
不同骨组织工程支架设计与骨传导性、骨诱导性及生物降解性变化的关系
汪雕雕1,2,孙雨阳3,田 壮1,2,张 矗2,李汉臣2,姚 琦1,2
- 1北京大学第九临床医学院,北京市 100038;2首都医科大学附属北京世纪坛医院关节外科,北京市 100038;3北京市创伤骨科研究所,北京市 100035
-
收稿日期:2021-08-10接受日期:2021-08-17出版日期:2022-07-28发布日期:2022-01-28 -
通讯作者:姚琦,教授,主任医师,博士生导师,首都医科大学附属北京世纪坛医院关节外科主任,北京大学第九临床医学院,北京市 100038;首都医科大学附属北京世纪坛医院关节外科,北京市 100038 -
作者简介:汪雕雕,男,1995年生,陕西省安康市人,汉族,北京大学医学部在读硕士,主要从事骨质疏松临床研究以及骨组织工程的基础研究。 孙雨阳,女,1996年生,北京市人,汉族,北京市创伤骨科研究所在读硕士。 -
基金资助:首都医科大学附属北京世纪坛医院突发事件紧急医学救援专项基金(2019-JJ03),项目负责人:姚琦;北京市百千万人才项目(2019BQW),项目负责人:姚琦
Relationship of the design of different bone tissue engineering scaffolds with the changes of osteoconduction, osteoinductivity and biodegradability
Wang Diaodiao1, 2, Sun Yuyang3, Tian Zhuang1, 2, Zhang Chu2, Li Hanchen2, Yao Qi1, 2
- 1Ninth Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing 100038, China; 2Department of Joint Surgery, Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China; 3Beijing Institute of Traumatic Orthopedics, Beijing 100035, China
-
Received:2021-08-10Accepted:2021-08-17Online:2022-07-28Published:2022-01-28 -
Contact:Yao Qi, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Ninth Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing 100038, China; Department of Joint Surgery, Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China -
About author:Wang Diaodiao, Master candidate, Ninth Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing 100038, China; Department of Joint Surgery, Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China Sun Yuyang, Master candidate, Beijing Institute of Traumatic Orthopedics, Beijing 100035, China Wang Diaodiao and Sun Yuyang contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Special Fund for Emergency Medical Rescue of Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, No. 2019-JJ03 (to YQ); Beijing Hundred Thousand Million Talents Project, No. 2019BQW (to YQ)
摘要:
文题释义:
骨组织工程支架:使用可植入生物材料作为干细胞的支架,以暂时保持骨组织在再生过程中的功能、生长和组织修复。
生物学特性:不同的材料能够通过其本身的物理、化学和结构特性等影响细胞生物学功能的性质。
背景:骨移植是临床中骨缺损治疗的主要方法,由于自体移植及异体移植的限制,组织工程骨作为替代品变得尤为重要。理想的组织工程骨需具有良好的生物学特性,这取决于支架材料的微观结构及化学性质等因素。
目的:骨组织工程支架的不同设计如何影响支架的骨传导性、骨诱导性及生物降解性3种生物学特性。
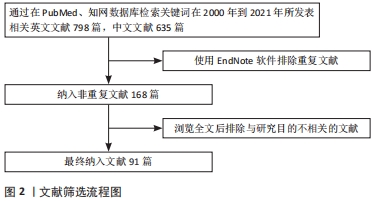
方法:以“骨组织工程、骨传导性、骨诱导性、黏附、扩散、物理特性、化学特性、结构特性、生长因子、离子、生物降解性、聚合物、无机材料、金属”为中文检索词检索中国知网数据库;以“bone tissue engineering,osteoconduction,osteoinductivity,adhesion,diffusion, physical characteristics,chemical characteristics,structural characteristics,growth factors,ions,biological degradability,polymer,inorganic material,metal”为英文检索词检索PubMed数据库,收集2000年1月至2021年7月时间段与骨组织工程支架生物学特性相关的文献,最终共纳入91篇文章进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①支架的骨传导性及骨诱导性的影响因素主要包括物理因素,如支架刚度及表面亲水性、生化因素、表面生化结构、结构因素、孔隙结构和表面形貌,此外,影响骨诱导性的因素还包括诱导分化物质的递送等。②对于骨传导性及骨诱导性的设计,可通过改善上述多种因素,进而通过促进蛋白的黏附、调节细胞-支架间的相互作用等机制促进骨再生过程。③支架的生物降解性主要与材料性质有关,聚合物、无机材料和金属等不同种类的材料具有不同降解特性和机械性能。④骨组织工程支架设计时,可通过结合不同性质的材料,以促进支架的降解性,同时平衡材料的降解性与机械性能间的关系。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6277-2290 (汪雕雕);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1975-2937(孙雨阳);https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6381-9871(姚琦)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
汪雕雕, 孙雨阳, 田 壮, 张 矗, 李汉臣, 姚 琦. 不同骨组织工程支架设计与骨传导性、骨诱导性及生物降解性变化的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(21): 3435-3444.
Wang Diaodiao, Sun Yuyang, Tian Zhuang, Zhang Chu, Li Hanchen, Yao Qi. Relationship of the design of different bone tissue engineering scaffolds with the changes of osteoconduction, osteoinductivity and biodegradability[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3435-3444.
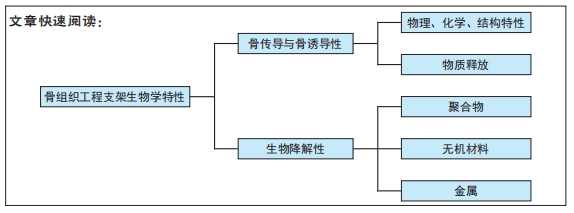
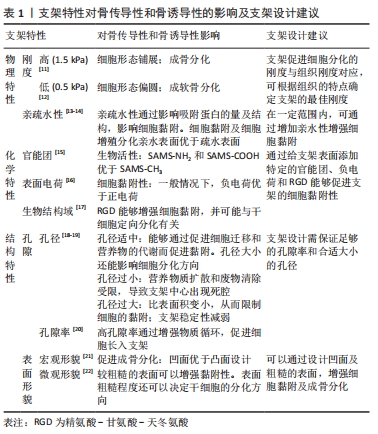
骨传导性被定义为一种生物材料特性,可促进新骨向表面或一定体积内的生长[7]。骨传导作用取决于生物材料与宿主组织的相互作用,这个过程涉及细胞在骨骼上附着、生长和迁移等细胞行为。因此,支架是通过自身的物理化学特性及结构特性影响细胞的行为,进而影响支架的骨传导性的。支架材料的刚度、湿润性、表面生化结构、孔隙结构和表面形貌等因素都影响着细胞黏附及扩散[11-22],见表1。
骨诱导性是干细胞受到所在微环境中的一些因素的刺激并向成骨细胞系分化的过程,骨诱导过程的成败直接决定了骨再生过程的成败。骨组织工程支架除了可以通过上述支架的物理化学和结构特性促进干细胞分化,还可以通过在微环境中产生诱导分化的物质促进干细胞定向分化。诱导分化物质的来源主要有2种:一种是支架材料本身析出成分的作用,多见于无机材料的离子析出,比如含锶羟基磷灰石支架降解产生的的锶离子可以诱导间充质干细胞的分化[8];另一种是支架作为递送载体,运输生长因子或药物等促成骨物质诱导干细胞分化,骨形态发生蛋白和血管内皮生长因子等生长因子已被证明可促进支架的骨诱导性[9-10]。然而,单纯某种因素对干细胞分化的影响有限,因此现今骨组织工程的支架设计大部分是综合了以上多种因素,从多方面增强了支架的骨诱导性[11-22]。
2.1.1 细胞黏附和扩散的机制 细胞黏附和扩散的机制主要取决于支架的物理、化学特性及支架的结构。细胞黏附过程中,宿主细胞并不直接与支架表面相互作用,而是与血浆和组织中吸附的蛋白质相互作用。细胞质外基质中的蛋白,通过整联蛋白受体物理偶联至细胞收缩性肌动蛋白细胞骨架来介导细胞锚定,而锚定处的亚细胞结构被称为黏着斑。对于成骨细胞黏附相关的重要蛋白是纤连蛋白。底物的物理化学组成也是决定吸附的细胞黏附蛋白的数量和构象的关键因素[23]。黏附的强度和类型,由吸附在支架的蛋白质与细胞产生的蛋白质共同决定,而吸附蛋白的性质及其构象取决于支架表面性质及其对基质的亲和力[24]。
细胞扩散的机制主要取决于支架的结构。当细胞在孔隙间距较密的支架迁移时,细胞利用架桥机制,从而利用邻近的细胞作为支持,跨过比单个细胞更大的孔。但是,如果支架孔隙间距明显超过细胞,细胞只能沿支杆扩散,这会影响细胞迁移和迁移速度[25]。因此,细胞的扩散主要取决于支架的结构特性。支架的物理、化学特性和支架结构共同决定了细胞黏附和细胞扩散,如支架材料的刚度、湿润性、表面生化结构、孔隙结构和表面形貌等因素。
2.1.2 支架的物理、化学、结构特性支架骨传导性和骨诱导性的影响
刚度:支架刚度可以影响细胞的形态。刚性的支架上,细胞的形态铺展,纤维厚而紧,黏附斑块紧凑并且组装良好。例如成纤维细胞在较硬的基质上会形成更宽、更平坦的形态[11]。相反,柔软的支架上,则细胞的散布面积将变小,并且细胞倾向于是圆形的,并且黏附斑块的形成也较差[12]。然而有研究认为,对细胞黏附来讲,很大程度上取决于细胞表型和细胞与基底结合的黏附受体的性质,而非刚度[26]。
支架刚度还可以决定细胞分化方向。MURPHY等[27]发现,间充质干细胞在不同刚度的胶原-糖胺多糖支架上向不同方向分化,刚度最高的支架(1.5 kPa)诱导间充质干细胞向成骨细胞系分化,而刚度最低的支架(0.5 kPa)诱导间充质干细胞向软骨方向分化。有研究认为是因为较硬的基质对间充质干细胞产生的机械刺激激活了RhoA信号传导,从而促进了成骨过程,而抑制了软骨形成过程[28]。还有研究发现,当间充质干细胞在模仿肌肉弹性的凝胶上生长时,可观察到间充质干细胞向成肌谱系分化[29]。然而,TRAPPMANN等[30]则认为,决定细胞分化命运的机制是由干细胞与支架材料的相互作用力,而不是凝胶本身的刚度。
亲疏水性:材料的表面亲疏水性是决定细胞黏附行为的重要因素之一。亲疏水性同样影响着细胞的形态,在亲水表面上,细胞通常表现出良好的铺展、增殖和分化。具有较高亲水性的表面能够增加黏附蛋白的吸附能力,从而促进细胞的黏附[31]。有研究通过增加钛支架表面亲水性,促进了层粘连蛋白和纤连蛋白等蛋白的黏附,而成骨细胞的黏附水平也随着纤连蛋白的量增加而增加[13]。然而,亲疏水性对细胞行为的影响可能不仅限于支架预吸附蛋白量对细胞的影响,还可能取决于吸附蛋白的结构。HASAN等[14]研究中观察到,吸附的纤连蛋白的 β-转角含量随着表面疏水性的增加而增加,而在纤连蛋白中,精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸(arginine-glycine-aspartate,RGD) 环位于β-转角,因此黏附细胞率的增加随着β-转角含量的增加而增加。因此,润湿性决定了吸附蛋白的量及结构,进而影响细胞黏附。
表面生化结构:细胞对人造表面的黏附不仅取决于其润湿性,还取决于支架表面上的生化结构,如官能团种类、表面电荷和表面生物结构域。支架表面的官能团的种类可以影响细胞的黏附[32]。有研究团队发现,官能团种类可以通过影响纤连蛋白的吸附,影响骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附力变化[15]。研究发现SAMS-CH3的疏水表面虽然可以吸附纤连蛋白,但由于RGD/PHSRN基序的低暴露和纤连蛋白的变形导致较差的生物活性,而SAMS-NH2和SAMS-COOH通过范德华相互作用、静电相互作用等作用吸附纤连蛋白,并由于生物活性基序的高暴露显示出优异的生物活性。
除了官能团的种类,表面电荷也可以影响细胞的行为。首先是表面电荷的数量,随着聚(苯乙烯-丙烯酸)电荷密度的增加,观察到更多的细胞黏附和增殖[33]。其次是表面电荷的正负性,有研究认为,负电荷的掺入可以促进蛋白的吸附,进而促进细胞的黏附[16]。但也有研究证明了,与负电荷或中性电荷相比,掺有正电荷的HEMA水凝胶支持更多的细胞附着和成骨细胞和成纤维细胞的扩散[34]。
材料表面的生物结构域也是影响材料骨传导性的重要因素。成骨细胞可以通过焦点接触附着在生物材料表面[35]。这些细胞附着点的主要跨膜成分是整联蛋白超家族,整联蛋白作为细胞表面黏附受体家族,它主要利用RGD序列识别并结合其配体。在诸多生物材料中,天然细胞外基质材料,如胶原蛋白合成的支架,具有天然的与RGD序列结合的这些配体,而由合成材料制成的支架则需要将配体整合到支架上,结合方法有蛋白质吸附等[36]。已有许多研究表明,RGD修饰的表面聚合物或其他材料可以增强无血清培养基中的细胞黏附[37]。而GELAIN等[17]的研究团队认为,具有RGD的支架不仅能够增强细胞黏附,促进细胞与底物之间更好的相互作用,而且还增加了干细胞向特定谱系的受控分化。
孔隙结构:在组织工程中支架的使用中,遇到的一个常见问题是,细胞在支架外边缘的快速附着和增殖,这限制了细胞向支架中心的渗透,从而导致了支架中心易形成坏死腔隙。解决此问题的一种选择是优化支架的设计,改善营养物和细胞向支架中心的转移,常用的方法之一就是改善支架的孔隙,如孔径和孔隙率。支架需要设计足够的孔隙率,以保证渗透率。渗透率是允许液体(如营养物质)在支架中循环的能力,渗透率可随孔隙率的增加而增加。而支架的互联性也与渗透性相关,具有明确互连孔的支架能够以更有效的方式允许营养物流入和代谢废物流出,是更好的细胞向内生长支架[38]。
已有研究观察到孔大小对支架材料骨传导性的影响。由于孔的大小决定了提供表面支撑的大小和可用于细胞黏附的配体的密度,因此,随着孔径的减小,细胞会黏附更多的比表面积。但是如果孔径过小,细胞迁移则会受到限制,因而营养物质的扩散和废物的清除也会受到限制,导致支架中心出现死腔。相反,如果孔径过大,支架的比表面积就会变小,从而限制细胞的黏附,且孔径过大也会削弱支架的稳定性。因此,寻找到最佳孔径的支架是骨组织工程一直以来的研究方向。O'BRIEN等[18]发现,胶原蛋白-糖胺多糖支架孔径在96-150 μm时,细胞附着随着孔径的增加而降低。而MURPHY等[19]发现支架孔径在85-325 μm时,随孔径变化,细胞黏附规律呈现双峰特点。因此,可以推测孔径在一定范围内时,随着孔径的增加,即使比表面积减少,也会由于互联性的提高促进了细胞迁移和营养物的代谢,而使细胞的黏附增加。
孔结构对于支架材料的骨诱导性也很重要。DAVISON等[39]将无微孔和有微孔的生物陶瓷支架分别植入狗的背肌中,发现具有微孔的生物陶瓷支架诱导了骨形成,说明孔结构有促进干细胞向成骨方向分化的能力。不同孔径和孔隙率的支架对干细胞分化方向和分化程度的影响也是不同的。首先是孔径对干细胞分化的影响,GEORGE等[40]的研究表明,直径90-110 μm的小孔可诱导干细胞发生软骨内骨化而成骨,而直径350 μm的大孔则可通过膜内成骨直接生成新骨,说明不同孔径大小可以影响细胞的分化方向。而孔隙率对干细胞分化的影响主要是对其分化程度的影响,有研究表明,较高孔隙度(超过65%)的β-磷酸三钙支架的成骨细胞分化程度明显高于较低孔隙度的相同材料支架[20]。
表面形貌:研究发现,支架的表面形貌可以直接影响细胞黏附、凋亡、分化、遗传表达、迁移、形态、方向和增殖[41]。根据材料表面形貌的粗糙程度,可以分为宏观和微观两种特征的形貌。
宏观表面形貌结构主要是支架表面的凸起与凹陷。有研究发现,3D凹形底物可促进更快的细胞迁移,而凸形底物则偏向诱导成骨分化[42]。然而,GRAZIANO等[43]的研究却发现骨形成总是发生在凹面上,而不是在凸面上,材料的凹槽表面上的成骨细胞优先在凹腔内而不是在平坦表面上矿化,说明凹腔有一定的促成骨能力。关于凹面促进成骨及矿化的机制,有研究认为是由于矿化程度与表面曲率之间存在相关性,与凸面的表面相比,凹面更多的表面促进了成骨细胞的分化和矿化[21]。成骨细胞在支架上通过表面凹槽而非化学线索排列,进一步证明了形貌对细胞定向行为的影响[44]。
微观表面形貌结构,指材料表面的微米和纳米级形貌。因为粗糙的纳米表面具有更好的吸附黏附蛋白的能力,因此,成骨细胞对纳米粗糙表面(如纤维)表现出更高的效力和更强的附着力。通过增加纳米级(10-102 nm)生物材料的表面粗糙度,可以增强人静脉内皮细胞在其表面上的黏附和生长[22]。除促进黏附及增殖外,微观表面形貌结构还可以决定干细胞的命运,促进干细胞向成骨细胞谱系的分化。MASSUMI等[45]发现,小鼠胚胎干细胞在不同表面粗糙度的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米纤维支架上,可分别向成骨与内皮谱系、神经和心肌几个不同的方向分化。
2.1.3 支架的物质释放对骨诱导性的影响
递送生长因子的支架设计:仅依靠骨再生支架本身结构或降解产物的骨诱导能力,促进成骨的效果可能依然较弱,因此骨再生支架可与一些促成骨的物质结合,如生长因子、激素和药物等,以进一步提高支架的骨诱导性。关于骨诱导性支架的研究中,较多的是研究与生长因子相结合的支架。如今已有许多生长因子都在骨修复应用中取得了一定的成功,其中包括血小板衍生的生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白等。生长因子可与各种不同材料相结合形成骨诱导性支架,生长因子与材料的结合主要有以下2种方式,一是非共价结合,包括表面吸附、物理包埋、亲和结合和离子络合;二是共价结合,如化学共轭。而结合的方式则取决于支架理化性质和生长因子之间的相互作用。
虽然通过支架对生长因子的递送可以促进干细胞向成骨方向分化,但是由于有些支架对生长因子作用时间和作用剂量的不可控性,可能造成生长因子初始时期的爆发性释放和不能持续释放,阻碍骨诱导过程,因此现在的研究正在优化支架以期达到体外生长因子能够完全模拟体内生长因子释放的效果。为实现生长因子能够以仿生的方式诱导骨再生,即生长因子按时按量释放和多种生长因子的协同作用,已有许多关于控释支架的研究。控释支架的设计方式主要分为2种,一种是聚合物包封生长因子,另一种是多层支架使生长因子逐层释放,见图3。
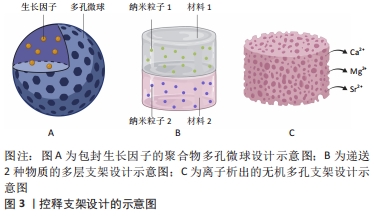
(1)聚合物包封生长因子支架:用于包封生长因子的聚合物可以是天然聚合物,如水凝胶和壳聚糖,也可以是合成聚合物。DONG等[46]开发了包封有骨形态发生蛋白2的壳聚糖-聚己内酯支架,支架在体外持续释放的骨形态发生蛋白2促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,说明聚合物包封生长因子的方法首先可以保证生长因子免受降解,其次其达到了持续性释放生长因子的目的。
然而,递送单个生长因子有时可因剂量过大等问题而产生副反应,如骨形态发生蛋白2过量导致的异位成骨[47],因此递送多个生长因子,通过生长因子间的协同作用可避免这一限制。有研究将负载骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子的硫酸化壳聚糖纳米粒子嵌入明胶海绵中植入兔股骨,与单独的骨形态发生蛋白2的作用相比,递送两种生长因子显着增强了骨再生[48]。递送多种生长因子的另一个方法是将包封了一种生长因子的微球,植入包封了另一生长因子的材料中。有研究将冻干的血管内皮生长因子与聚(D,L-乳酸-co-乙醇酸)颗粒混合,而将血小板衍生生长因子封装在聚(D,L-乳酸-co-乙醇酸)微球中,结果发现2种生长因子以不同速度释放,血管内皮生长因子可从材料表面快速释放,而在微球中的血小板衍生因子则释放缓慢[49]。这种设计不仅实现了同时递送多种生长因子,而且实现了不同生长因子按不同释放速度递送的目的,见图3A。
除了这些常用的天然和合成聚合物可作为包封材料外,近些年发现了一些聚合物可因外部环境的变化而发生性质的变化,如温敏型、pH敏感型和酶敏感型聚合物[50]。而骨缺损部位的温度和pH值都较正常组织不同,因此未来可使用刺激反应性聚合物包封生长因子,以实现按时、按需、按量释放,更加个性化。
(2)多层支架:逐层支架是指具有2个或多个并排层的支架,可在不同的层间嵌入生长因子,以实现根据不同的时间顺序递送多种生长因子,见图3B。逐层支架的形式有两种,分层支架和多层涂层支架。
逐层支架的第一种形式是分层支架,分层支架不同层的组成可以是相同材料,也可以是不同材料。一项研究中使用了3D打印方法制造出了一个两层交联程度不同的明胶分层支架,两层分别嵌入骨形态发生蛋白2,发现交联程度低的明胶层在第1天达到释放峰值,而交联程度高的明胶层在第6天才达到释放峰值[51],这个实验说明可通过制造不同交联程度的多层支架来控制生长因子释放的峰值时间。另一实验在藻酸盐相中掺入血管内皮生长因子,在聚乳酸相中较慢降解中掺入骨形态发生蛋白2,结果表明,血管内皮生长因子的释放速度更快,而骨形态发生蛋白2的释放则更缓慢和持久[52],此实验提示多层支架若想按不同时间递送不同的生长因子,可根据生长因子在不同材料中的释放特点,选用合适释放速度的材料制成分层支架。
逐层支架的另一种形式是作为涂层而非支架本体,来递送生长因子。一项研究在聚乳酸支架的表面用明胶和聚赖氨酸两种物质的涂层进行修饰,并分别嵌入了骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子,结果表明其设计促进了成骨分化和成血管分化[53]。
离子析出的支架设计:有些材料如磷酸钙材料,在不添加其他促成骨物质的情况下,其本身就具有一定的促成骨性能。其原因应是这些材料在植入体内后发生降解,降解产生的离子对干细胞具有骨诱导作用,见图3C。正如有研究发现较难溶的磷酸钙相比难溶的磷酸钙有更强的骨诱导性[54],说明一些离子的确参与了诱导干细胞成骨的过程。能够促进成骨的离子,除磷酸根和钙离子外,还有镁、硅和锶离子等。
有研究认为,磷酸钙材料具有骨诱导性的原因,可能是骨样生物碳酸盐磷灰石层是干细胞分化为成骨细胞谱系的物理和化学触发物。磷酸钙材料在最初的环境中提供了钙离子和磷酸根离子,形成了具有一定粗糙度的生物碳酸盐磷灰石层,其是磷酸钙沉淀的形成位点[55]。如一项研究所示,生物玻璃颗粒溶解导致了钠离子、钙离子和磷酸根离子的释放,并改善成骨细胞的分化[56]。其他一些研究通过在生物玻璃支架中添加了特定的金属离子来增强支架的生物活性和成骨分化能力,例如铜、锶、钛等[57]。有研究认为,金属离子是通过诱导干细胞成血管而促进其成骨分化的,如铜离子和锶离子可以上调缺氧诱导因子,诱导血管内皮生长因子表达。
2.2 改善生物降解性的支架设计
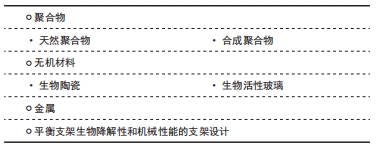
理想的骨组织工程支架并不是永久性的植入物,理想的支架需在前期具有完整性,为骨缺损部位提供机械支持、为成骨及破骨细胞等提供附着位点,在后期,支架需能降解或代谢,为新形成的骨组织让出足够的生长空间[58],最终使新形成的骨组织能够完全替代支架完成骨缺损部位的正常生理功能。因此,支架的生物降解性对于骨组织支架的长期成功是必不可少的,既避免了再次手术,又减少了支架作为异物产生炎症反应而导致的植入失败。具有降解性的支架,除了可为细胞浸润提供空间,还为药物和生长因子的运输和传递提供了另一种可能[58]。
对于生物降解性支架,需要满足3个要求。第一,材料的降解产物应具有生物相容性,不应对周围组织产生毒性作用和炎症[59];如一些合成聚合物,它们降解后产生酸性产物,可降低局部微环境的pH值,不利于伤口的愈合。第二,支架的降解速率需可控,支架具有合适的降解率对于骨组织工程的长期成功非常重要,因为支架的降解速度与组织的生长速度相匹配是骨组织工程植入物成功的基础。如果支架降解得太快,则可能会发生机械故障,因为植入的支架需要承载负荷,如果在形成新骨前无法提供骨缺损部位生理功能所需的机械支撑,则可能会发生骨折。相反,如果支架的降解过于缓慢,则可能会产生支架作为异物而导致的炎症反应,假性关节病等,从而损害组织再生,导致骨移植的失败[60]。第三,理想的生物降解性支架除了应具有合适的降解速度,还应考虑其作为载体的递送功能(如生长因子及蛋白),物质的递送要尽可能模拟体内正常生理的释放。例如,通过使用具有不同降解行为的聚合物分别加入生长因子,或通过控制微粒降解行为等方法,可以实现多种不同的释放曲线[61]。因此,设计具有生物降解性的支架必须要考虑到这3点。
2.2.1 聚合物
天然聚合物:其优势在于具有优异的生物活性、生物相容性,其表面上具有对细胞整合和分化有益的生物功能分子,因此可促进细胞黏附和生长。天然聚合物还具有生物降解性,其降解产物也是无毒的[62]。天然聚合物的降解方式是酶促降解,通过例如纤溶酶或基质金属蛋白酶等蛋白酶的切割完成的,这些蛋白酶可以切割细胞外基质蛋白中的特定肽序列。然而,天然聚合物的一些特性在骨组织工程的应用中也会受一些到限制,包括存在病原性杂质(例如内毒素)[63],降解速率过快和机械性能较差等[64]。因此,在应用时,通常将天然聚合物经过化学改性以改善其机械性能和降解速率,也常将其用于复合材料,以改善其他材料支架的一些特性,比如提高支架的酶促降解性及生物相容性等。已有许多天然聚合物应用于组织工程中,常用于组织工程骨再生修复的天然聚合物有胶原蛋白、壳聚糖、丝素蛋白等。
胶原蛋白占骨细胞外基质蛋白总质量的90%,且由于其生物相容性和生物降解性而被广泛用于骨组织工程支架。在诸多胶原蛋白分型中,Ⅰ型胶原蛋白具有低免疫反应性。然而胶原蛋白也有一些负面特性,比如机械性能的不足和较快的降解速度。因此,增强胶原蛋白的机械性能和降解性能的方法主要有2种,一种是在胶原蛋白中添加化学交联剂可以提高强度并降低降解速度,另一种是将其与骨组织工程中更坚固的材料结合使用,以形成复合支架。作为骨的主要无机成分,羟基磷灰石经常与胶原蛋白结合在复合支架中[66]。
壳聚糖是一种通常存在于甲壳类动物壳中的多糖,它不仅具有抗菌和生物黏附特性,还具有良好的生物相容性和生物降解性[67]。壳聚糖的降解主要是通过溶菌酶的酶解作用降解,其降解终产物是无毒、无免疫原性的葡糖胺[68]。因此,壳聚糖在骨组织工程中已有诸多应用,并已与多种材料结合在一起形成复合支架,包括磷酸钙、硫酸钙、羟基磷灰石和其他天然聚合物,如丝素蛋白[69-71]。由于壳聚糖良好的生物降解性,基于壳聚糖的微球也被用作细胞培养的微载体[72]。
丝素蛋白是一种主要由蚕和蜘蛛生产的天然蛋白质基聚合物,与其他天然生物材料相比,蚕丝具有更高的弹性模量和拉伸强度。因此,丝素蛋白支架解决了天然材料机械性能较差这个难题。丝素蛋白在体内的降解是通过蛋白水解作用缓慢发生,因此,其降解速度较慢。有研究表明,蚕丝纤维在植入体内后6周仍保留了大部分抗张强度和模量,作为对照的胶原蛋白交联制剂在此时间内已丧失了机械完整性[73]。可以通过控制加工溶剂、丝溶液浓度和支架孔径调节丝素蛋白的降解速率。
合成聚合物:近年来,合成聚合物支架比天然聚合物支架受到了更多的关注,因为它们可以生产特定的结构,并且可以通过改变聚合物本身或通过结合不同聚合物来控制支架的降解性。合成聚合物的降解基本模式分为:水解降解和酶促降解。水解降解是指生物体与可降解聚合物之间具有可水解的不稳定键的相互作用。酶促降解是具有某些化学键的材料,这些化学键需要催化才能在生理条件下发生有意义的降解。根据降解的基本模式,可知聚合物的生物降解速度主要取决于聚合物结构、表面积与体积比(孔隙率)[74]、聚合物组成等因素。因此,设计支架时可根据支架的具体应用选择合适的材料和结构设计。除此之外,聚酯类聚合物降解还会释放出酸性副产物,酸性副产物的积聚会导致局部环境pH值的下降,引发炎症反应,加剧纤维化反应和骨吸收[75]。解决这一局限性的方法之一是将聚合物与生物陶瓷或生物玻璃等材料相结合,生产复合支架。常用于骨组织工程中的可生物降解的合成聚合物包括:聚己内酯、聚乳酸和聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物等。
聚己内酯是一种脂肪族聚酯生物材料,已被美国食品药品监督管理局批准用于临床。这种聚酯的优势包括生物相容性,相对较慢的降解速度,分解产物的酸性较弱并且具有承重的潜力。但聚己内酯的细胞黏附性能差,已有许多研究进行了尝试来制备具有改善的生物活性的聚己内酯复合材料[76]。
聚乳酸也是一种可生物降解的热塑性聚酯,已被用于制造许多医疗植入物,包括接骨螺钉、固定装置和血管移植物[77]。由于聚丙交酯具有手性分子,所以聚乳酸有4种形式:左旋聚乳酸、右旋聚乳酸、外消旋聚乳酸以及内消旋聚乳酸。聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物是左旋聚乳酸和聚乙醇酸的合成共聚物,已获得临床应用的美国食品药品监督管理局批准。聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物可以通过改变共聚物中的单体比例来控制支架的物理性能和降解速率,根据左旋聚乳酸与聚乙醇酸的比例,聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物的降解速率可以从数周至数月不等[78]。由于聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物具有快速降解的特性,已被广泛用于药物递送应用中。聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物还具有出色的细胞黏附和增殖特性,也已有研究证明了聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物的3D打印能力[79]。
2.2.2 无机材料
生物陶瓷:生物陶瓷与骨骼矿物质相具有结构相似性,因此其具有较高的刚度和良好的生物相容性,常被用于骨组织工程中,最常用的是磷酸三钙和羟基磷灰石。生物陶瓷在体内的降解会产生钙离子和磷酸根离子等,这些离子可以诱导骨细胞活性,也可用作新骨形成的原料促进生物陶瓷支架表面上生物磷灰石沉淀的形成。然而,生物陶瓷材料通常降解速度很缓慢,可以持续数月或数年,这是阻碍其在大段骨缺损修复中应用的原因之一[80]。因此,创建降解速率可控的生物陶瓷支架仍然是骨缺损修复在生物材料领域的挑战。
羟基磷灰石作为骨骼的主要成分,具有公认的生物相容性、骨诱导性和骨传导特性,是骨组织工程中比较理想的植入物。然而,羟基磷灰石在体内的降解速度过慢限制了其在骨缺损修复中的应用。因此,羟基磷灰石可以与降解性强的材料形成复合材料,既解决了羟基磷灰石降解过缓的问题,也使复合材料具有良好的生物相容性和机械性能。现已研究了羟基磷灰石与胶原蛋白、β-磷酸三钙和其他聚合物等结合形成的复合材料[81-82]。
磷酸钙类陶瓷支架目前最常用的是磷酸三钙陶瓷。磷酸三钙比包括羟基磷灰石在内的其他生物陶瓷材料具有更好的生物降解性,有实验证明,在切除骨肿瘤后的骨缺损中植入不同的生物陶瓷材料,结果磷酸三钙几乎所有都被新形成的骨吸收并替代,而羟基磷灰石甚至在术后130个月也没有明显的生物降解迹象[83]。在磷酸三钙支架中,最受关注的是β-磷酸三钙支架,除了出色的生物相容性、生物活性、还有优异的降解性。然而,虽然β-磷酸三钙的弯曲强度和断裂韧性优于羟基磷灰石生物陶瓷支架,但仍低于人体皮质骨的机械强度,因此β-磷酸三钙生物陶瓷支架不能作为植入物。而且有时纯β-磷酸三钙陶瓷降解速度与新骨生成速率不匹配,也可能会导致植入的失败。因此,常常将β-磷酸三钙和羟基磷灰石结合,形成复合支架双相磷酸钙陶瓷。得益于β-磷酸三钙优异的生物降解性和羟基磷灰石的高度生物相容性,双相磷酸钙陶瓷不仅具有良好生物相容性、生物活性和骨传导性,与纯羟基磷灰石和纯β-磷酸三钙支架相比,双相磷酸钙陶瓷具有可控的降解速率,更好的生物相容性和更强的促进骨再生的能力[84]。
生物活性玻璃:其拥有优异的骨传导性、生物活性和生物可降解性,常用的包括硅酸盐玻璃和硼酸盐玻璃。然而,生物活性玻璃的脆性限制了其在临床中的应用,仅可用于非承重骨中。
控制支架降解性和增强机械性能是生物活性玻璃设计的重点,改善方法有2种。首先,由于生物玻璃降解的机制涉及材料与环境中的离子交换及释放和表面二氧化硅层、磷酸钙层的形成[85],所以生物活性玻璃的降解性与支架物理结构有关,如支架孔隙率。因为高孔隙率可使支架的比表面积的增加,有利于环境与材料中离子的交换及生物活性玻璃的溶解,因此可以加快支架的降解速度[86]。其次,生物活性玻璃还可以通过与不同材料相结合形成复合支架,来控制降解速率并增强机械性能。GAO等[87]利用3D生物打印技术创建的聚己内酯-生物活性玻璃复合支架,在14 d时由于生物活性玻璃的受控降解,支架质量损失约1/4,可见生物活性玻璃的添加明显提高了聚己内酯支架的降解速度。另有研究发现,将聚己内酯添加到生物活性玻璃中形成复合支架后,支架的脆性显著降低了[88],可见聚己内酯的添加改善了生物活性玻璃的机械性能。
2.2.3 金属 金属植入物由于其优异的机械性能,在承重方面是理想的骨修复材料,因此金属材料在骨科修复中是应用最广泛的植入物材料。然而由于其缺乏生物活性,难以与组织黏附,可导致植入物松动;金属材料较低的降解率还导致需进行二次手术将植入物移除;且金属材料释放出的金属离子积聚也可能会产生毒性反应。因此,综合来讲金属材料并不是非常理想的可降解骨组织工程生物材料。
然而,镁及其合金由于其良好的生物相容性、生物活性和生物降解性,受到了极大的关注。在LIU等[89]的研究中,镁支架与羟基磷灰石支架同时植入兔股骨3个月后,两支架都表现出了理想的生物相容性,而镁支架的降解程度要远大于基本无降解的羟基磷灰石支架,且相比于羟基磷灰石支架,镁支架还明显促进了新骨向内生长。因此可见,镁支架是值得深入研究的生物可降解材料。
2.2.4 平衡支架生物降解性和机械性能的支架设计 由于降解性与机械性能密切相关,因此在设计支架时,降解性与机械性能的平衡十分重要。首先需要保证支架的机械性能,以完成骨的支撑功能,然后在保证机械性能的前提下,提高降解速度,以促进组织再生。
降解速率过快或过慢都不是骨再生支架的理想选择。降解性过强的材料,如以胶原蛋白为代表的天然聚合物,往往存在降解速率过快与骨再生过程不符和机械性能较差的问题。降解速率过慢的材料,如无机材料中的羟基磷灰石,虽然拥有良好的机械性能,但长时间不降解会阻碍骨修复。因此,多种材料结合形成复合支架的设计是迄今较为主流的做法[66],将降解速率过快和过慢的材料结合形成复合材料的支架设计,既解决了降解速率的问题,又改善了支架的机械性能,见表2。

除此之外,对于一些合成聚合物材料,如聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物,还可以通过调节其不同单体的比例[78],以达到兼顾机械性能和降解速率的目的。其他用于平衡降解速率和机械性能的手段还包括控制支架的物理结构、添加化学交联剂等。

| [1] ANSARI M. Bone tissue regeneration: biology, strategies and interface studies. Prog Biomater. 2019;8(4):223-237. [2] HAUGEN HJ, LYNGSTADAAS SP, ROSSI F, et al. Bone grafts: which is the ideal biomaterial? J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21:92-102. [3] JO SH, KIM YK, CHOI YH. Histological evaluation of the healing process of various bone graft materials after engraftment into the human body. Materials. 2018;11(5):714. [4] LEE JW, CHO DW. 3D Printing technology over a drug delivery for tissue engineering. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(12):1606-1617. [5] HONG H, SEO YB, KIM DY, et al. Digital light processing 3D printed silk fibroin hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2020; 232:119679. [6] QIAN Y, ZHOU X, ZHANG F, et al. Triple PLGA/PCL scaffold modification including silver impregnation, collagen coating, and electrospinning significantly improve biocompatibility, antimicrobial, and osteogenic properties for orofacial tissue regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(41):37381-37396. [7] XU HH, WANG P, WANG L, et al. Calcium phosphate cements for bone engineering and their biological properties. Bone Res. 2017;5:17056. [8] WU Q, WANG X, JIANG F, et al. Study of Sr-Ca-Si-based scaffolds for bone regeneration in osteoporotic models. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):25. [9] VAN HOUDT CIA, KOOLEN MKE, LOPEZ-PEREZ PM, et al. Regenerating critical size rat segmental bone defects with a self-healing hybrid nanocomposite hydrogel: effect of bone condition and BMP-2 incorporation. Macromol Biosci 21:e2100088. [10] GUREL PEKOZER G, ABAY AKAR N, CUMBUL A, et al. Investigation of Vasculogenesis Inducing Biphasic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(4):1526-1538. [11] YANG L, GAO Q, GE L, et al. Topography induced stiffness alteration of stem cells influences osteogenic differentiation. Biomater Sci. 2020; 8(9):2638-2352. [12] CHEN H, LIU Y, JIANG Z, et al. Cell-scaffold interaction within engineered tissue. Exp Cell Res. 2014;323(2):346-351. [13] ISOSHIMA K, UENO T, ARAI Y, et al. The change of surface charge by lithium ion coating enhances protein adsorption on titanium. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;100:103393. [14] HASAN A, SAXENA V, PANDEY LM. Surface functionalization of Ti6Al4V via self-assembled monolayers for improved protein adsorption and fibroblast adhesion. Langmuir. 2018;34(11):3494-506. [15] HAO L, LI T, WANG L, et al. Mechanistic insights into the adsorption and bioactivity of fibronectin on surfaces with varying chemistries by a combination of experimental strategies and molecular simulations. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3125-3135. [16] GUO S, ZHU X, LI M, et al. Parallel control over surface charge and wettability using polyelectrolyte architecture: effect on protein adsorption and cell adhesion. ACS App Mater Int. 2016;8(44):30552-30563. [17] GELAIN F, BOTTAI D, VESCOVI A, et al. Designer self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds for adult mouse neural stem cell 3-dimensional cultures. PLoS One. 2006;1(1):e119. [18] O’BRIEN FJ, HARLEY BA, YANNAS IV, et al. The effect of pore size on cell adhesion in collagen-GAG scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2005;26(4):433-441. [19] MURPHY CM, HAUGH MG, O’BRIEN FJ. The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation and migration in collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(3):461-466. [20] MCDERMOTT AM, HERBERG S, MASON DE, et al. Recapitulating bone development through engineered mesenchymal condensations and mechanical cues for tissue regeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2019; 11(495):eaav7756. [21] VANDERBURGH JP, FERNANDO SJ, MERKEL AR, et al. Fabrication of trabecular bone-templated tissue-engineered constructs by 3D inkjet printing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700369. [22] KUKUMBERG M, YAO Y, GOH SH, et al. Evaluation of the topographical influence on the cellular behavior of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Adv Biosyst. 2018;2(6):1700217. [23] KAFI MA, AKTAR MK, PHANNY Y, et al. Adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cell on chitosan/collagen composite scaffold. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(12):131. [24] KAFI MA, AKTAR K, TODO M, et al. Engineered chitosan for improved 3D tissue growth through Paxillin-FAK-ERK activation. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(2):141-151. [25] MAJI K, DASGUPTA S, KUNDU B, et al. Development of gelatin-chitosan-hydroxyapatite based bioactive bone scaffold with controlled pore size and mechanical strength. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 2015;26(16):1190-1209. [26] SANYOUR H, CHILDS J, MEININGER GA, et al. Spontaneous oscillation in cell adhesion and stiffness measured using atomic force microscopy. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2899. [27] MURPHY CM, MATSIKO A, HAUGH MG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell fate is regulated by the composition and mechanical properties of collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;11:53-62. [28] MIDGLEY AC, WOODS EL, JENKINS RH, et al. Hyaluronidase-2 regulates RhoA signaling, myofibroblast contractility, and other key profibrotic myofibroblast functions. Am J Pathol. 2020;190(6):1236-1255. [29] WOSCZYNA MN, KONISHI CT, PEREZ CARBAJAL EE, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells are required for regeneration and homeostatic maintenance of skeletal muscle. Cell Rep. 2019;27(7):2029-2035.e5. [30] TRAPPMANN B, GAUTROT JE, CONNELLY JT, et al. Extracellular-matrix tethering regulates stem-cell fate. Nat Mater. 2012;11(7):642-649. [31] 路荣建.微纳形貌钽及钽/羟基磷灰石涂层对骨髓间充质干细胞生物学活性的影响[D].北京:中国人民解放军医学院,2015. [32] JURAK M, WIĄCEK AE, ŁADNIAK A, et al. What affects the biocompatibility of polymers? Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;294:102451. [33] TAN F, LIU J, LIU M, et al. Charge density is more important than charge polarity in enhancing osteoblast-like cell attachment on poly (ethylene glycol)-diacrylate hydrogel. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;76:330-339. [34] ARIAS CJ, SURMAITIS RL, SCHLENOFF JB. Cell adhesion and proliferation on the “living” surface of a polyelectrolyte multilayer. Langmuir. 2016; 32(21):5412-5421. [35] VERSTAPPEN JFM, JIN J, KOçER G, et al. RGD-functionalized supported lipid bilayers modulate pre-osteoblast adherence and promote osteogenic differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;108(4): 923-937. [36] SALIFU AA, OBAYEMI JD, UZONWANNE VO, et al. Mechanical stimulation improves osteogenesis and the mechanical properties of osteoblast-laden RGD-functionalized polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;108(12):2421-2434. [37] ABDULGHANI S, MITCHELL GR. Biomaterials for in situ tissue regeneration: a review. Biomolecules. 2019;9(11):750. [38] DENG Y, ZHANG M, CHEN X, et al. A novel akermanite/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) porous composite scaffold fabricated via a solvent casting-particulate leaching method improved by solvent self-proliferating process. Regen Biomater. 2017;4(4):233-242. [39] DAVISON N, YUAN H, DE BRUIJN JD, et al. In vivo performance of microstructured calcium phosphate formulated in novel water-free carriers. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(7):2759-2769. [40] GEORGE J, KUBOKI Y, MIYATA T. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts on honeycomb collagen scaffolds. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;95(3):404-411. [41] YANG L, GE L, VAN RIJN P. Synergistic Effect of Cell-Derived Extracellular Matrices and Topography on Osteogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS App Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(23):25591-25603. [42] ZHANG HQ, WANG LJ, LIU SH, et al. Adiponectin regulates bone mass in AIS osteopenia via RANKL/OPG and IL6 pathway. J Transl Med. 2019; 17(1):64. [43] GRAZIANO A, D’AQUINO R, CUSELLA-DE ANGELIS MG, et al. Scaffold’s surface geometry significantly affects human stem cell bone tissue engineering. J Cell Physiol. 2008;214(1):166-172. [44] RüDRICH U, LASGORCEIX M, CHAMPION E, et al. Pre-osteoblast cell colonization of porous silicon substituted hydroxyapatite bioceramics: Influence of microporosity and macropore design. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;97:510-528. [45] MASSUMI M, ABASI M, BABALOO H, et al. The effect of topography on differentiation fates of matrigel-coated mouse embryonic stem cells cultured on PLGA nanofibrous scaffolds. Tissue engineering Part A. 2012;18(5-6):609-620. [46] DONG L, WANG SJ, ZHAO XR, et al. 3D-printed poly (ε-caprolactone) scaffold integrated with cell-laden chitosan hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13412. [47] HASHIMOTO K, KAITO T, FURUYA M, et al. In vivo dynamic analysis of BMP-2-induced ectopic bone formation. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):4751. [48] CAO L, WANG J, HOU J, et al. Vascularization and bone regeneration in a critical sized defect using 2-N, 6-O-sulfated chitosan nanoparticles incorporating BMP-2. Biomaterials. 2014;35(2):684-698. [49] RICHARDSON TP, PETERS MC, ENNETT AB, et al. Polymeric system for dual growth factor delivery. Nat Biotechn. 2001;19(11):1029-1034. [50] JIANG Y, WANG Y, LI Q, et al. Natural polymer-based stimuli-responsive hydrogels. Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(16):2631-2357. [51] KIM K, LAM J, LU S, et al. Osteochondral tissue regeneration using a bilayered composite hydrogel with modulating dual growth factor release kinetics in a rabbit model. J Controlled Release. 2013;168(2): 166-178. [52] KANCZLER JM, GINTY PJ, WHITE L, et al. The effect of the delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenic protein-2 to osteoprogenitor cell populations on bone formation. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6):1242-1250. [53] CUI H, ZHU W, HOLMES B, et al. Biologically inspired smart release system based on 3d bioprinted perfused scaffold for vascularized tissue regeneration. Adv Sci. 2016;3(8):1600058. [54] YANG L, PEREZ-AMODIO S, BARRèRE-DE GROOT FY, et al. The effects of inorganic additives to calcium phosphate on in vitro behavior of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Biomaterials. 2010;31(11):2976-2989. [55] DHIVYA S, KESHAV NARAYAN A, LOGITH KUMAR R, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on scaffolds containing chitosan, calcium polyphosphate and pigeonite for bone tissue engineering. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(1):e12408. [56] VICHERY C, NEDELEC JM. Bioactive glass nanoparticles: from synthesis to materials design for biomedical applications. Materials. 2016;9(4):288. [57] MOHAN BG, SHENOY SJ, BABU SS, et al. Strontium calcium phosphate for the repair of leporine (Oryctolagus cuniculus) ulna segmental defect. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(1):261-271. [58] YANG D, XIAO J, WANG B, et al. The immune reaction and degradation fate of scaffold in cartilage/bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109927. [59] SHAH SS, LIANG H, PANDIT S, et al. Optimization of degradation profile for new scaffold in cartilage repair. Cartilage. 2018;9(4):438-449. [60] FAIRAG R, LI L, RAMIREZ-GARCIALUNA JL, et al. A composite lactide-mineral 3D-printed scaffold for bone repair and regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:654518. [61] CHEN L, LIU J, GUAN M, et al. Growth factor and its polymer scaffold-based delivery system for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6097-6111. [62] BHARADWAZ A, JAYASURIYA A C. Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110698. [63] TURNBULL G, CLARKE J, PICARD F, et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(3):278-314. [64] LIU X, MA PX. Polymeric scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004;32(3):477-486. [65] MARQUES CF, DIOGO GS, PINA S, et al. Collagen-based bioinks for hard tissue engineering applications: a comprehensive review. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(3):32. [66] VILLA MM, WANG L, HUANG J, et al. Bone tissue engineering with a collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold and culture expanded bone marrow stromal cells. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(2):243-253. [67] PELLá MCG, LIMA-TENóRIO MK, TENóRIO-NETO ET, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogels: from preparation to biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;196:233-245. [68] KIM S, FAN J, LEE C S, et al. Dual functional lysozyme-chitosan conjugate for tunable degradation and antibacterial activity. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(4):2334-2343. [69] DIAS LL, MANSUR HS, DONNICI CL, et al. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol-bioactive glass hybrid membranes. Biomatter. 2011;1(1):114-119. [70] MIAO Q, YANG S, DING H, et al. Controlled degradation of chitosan-coated strontium-doped calcium sulfate hemihydrate composite cement promotes bone defect repair in osteoporosis rats. Biomedical materials (Bristol, England). 2020;15(5):055039. [71] YOUNES I, RINAUDO M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar Drugs. 2015; 13(3):1133-1174. [72] TEDESCO MT, DI LISA D, MASSOBRIO P, et al. Soft chitosan microbeads scaffold for 3D functional neuronal networks. Biomaterials. 2018;156: 159-171. [73] ADELMAN DM, CORNWELL KG. Fundamentals of extracellular matrix biomaterial assimilation: effect of suture type on attachment strength and cell repopulation. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020;8(3):e2635. [74] LEVATO R, JUNGST T, SCHEURING RG, et al. From Shape to Function:The Next Step in Bioprinting. Adv Mater. 2020;32(12):e1906423. [75] ZARGAR KHARAZI A, FATHI MH, MANSHAEI M, et al. In-vivo evaluation of a partially resorbable poly l-lactic acid/ braided bioactive glass fibers reinforced composite for load bearing fracture fixation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(7):57. [76] CHENG Z, TEOH SH. Surface modification of ultra thin poly (epsilon-caprolactone) films using acrylic acid and collagen. Biomaterials. 2004; 25(11):1991-2001. [77] NAAHIDI S, JAFARI M, LOGAN M, et al. Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(5):530-544. [78] KENRY, LIU B. Recent advances in biodegradable conducting polymers and their biomedical applications.Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(6): 1783-1803. [79] ANDERSON JM. Reflections on the Journal of Biomedical Materials Research-Part A. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2021;109(4):394. [80] HETTICH G, SCHIERJOTT RA, EPPLE M, et al. Calcium phosphate bone graft substitutes with high mechanical load capacity and high degree of interconnecting porosity. Materials. 2019;12(21):3471. [81] PANDA NN, JONNALAGADDA S, PRAMANIK K. Development and evaluation of cross-linked collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(18):2031-2044. [82] ORYAN A, ALIDADI S, BIGHAM-SADEGH A, et al. Chitosan/gelatin/platelet gel enriched by a combination of hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate in healing of a radial bone defect model in rat. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;101:630-637. [83] DANG W, MA B, LI B, et al. 3D printing of metal-organic framework nanosheets-structured scaffolds with tumor therapy and bone construction. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025005. [84] SMITH BT, SANTORO M, GROSFELD EC, et al. Incorporation of fast dissolving glucose porogens into an injectable calcium phosphate cement for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017;50:68-77. [85] HAN R, BUCHANAN F, FORD L, et al. A comparison of the degradation behaviour of 3D printed PDLGA scaffolds incorporating bioglass or biosilica. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol App. 2021;120:111755. [86] HO-SHUI-LING A, BOLANDER J, RUSTOM LE, et al. Bone regeneration strategies: engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 2018;180:143-162. [87] GAO F, XU Z, LIANG Q, et al. Osteochondral regeneration with 3D-printed biodegradable high-strength supramolecular polymer reinforced-gelatin hydrogel scaffolds. Adv Sci. 2019;6(15):1900867. [88] LIU X, RAHAMAN MN, LIU Y, et al. Enhanced bone regeneration in rat calvarial defects implanted with surface-modified and BMP-loaded bioactive glass (13-93) scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7506-7517. [89] LIU YJ, YANG ZY, TAN LL, et al. An animal experimental study of porous magnesium scaffold degradation and osteogenesis. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(8):715-720. [90] HUANG W, TANG X, QIU Z, et al. Cellulose-based superhydrophobic surface decorated with functional groups showing distinct wetting abilities to manipulate water harvesting. ACS App Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(36):40968-40978. [91] MILLER AE, HU P, BARKER TH. Feeling things out: bidirectional signaling of the cell-ecm interface, implications in the mechanobiology of cell spreading, migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(8):e1901445. |
| [1] | 谭新访, 郭艳幸, 秦晓飞, 张斌清, 赵东亮, 潘琨琨, 李瑜卓, 陈皓宇. 顺轴疲劳运动对兔髌股关节软骨损伤的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | 许新忠, 吴钟汉, 余水生, 赵 耀, 徐春归, 张 鑫, 郑嵋戈, 荆珏华. 斯氏针置入股骨头不同方式的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | 魏国强, 李云峰, 王 一, 牛晓芬, 车丽芳, 王海燕, 李志军, 史国鹏, 白 灵, 莫 凯, 张晨晨, 许阳阳, 李筱贺. 非均匀材料股骨在不同负荷情况下的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [4] | 李 获, 王 鹏, 高健明, 蒋浩然, 鲁晓波, 彭 江. 股骨头坏死血运重建与内部微观结构改变的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [5] | 李 睿, 史 文, 杨士彩, 吕林蔚, 张春秋. 夹板外固定与散巴布剂对桡骨骨折模型兔骨愈合的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1329-1333. |
| [6] | 袁加斌, 朱宗东, 唐孝明, 魏 丹, 谭 波, 肖成伟, 赵淦琳炜, 廖 锋. 难复性股骨转子间骨折的解剖分型与复位策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1341-1345. |
| [7] | 张吉超, 董跃福, 牟志芳, 张 震, 李冰言, 徐祥钧, 李佳意, 任 梦, 董万鹏. 骨关节炎患者在不同步态角度下膝关节内部生物力学变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [8] | 刘 峰, 冯 毅. 步态周期下不同克氏针张力带治疗髌骨横行骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [9] | 姚晓玲, 彭建城, 许岳荣, 杨志东, 张顺聪. 可变角度零切迹前路椎间融合内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病:30个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [10] | 姜欢畅, 张兆飞, 梁 德, 江晓兵, 杨晓东, 刘志祥. 单侧多方向弯曲与直行椎体成形治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折优势的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [11] | 遇呈祥, 刘乐洪, 李文博, 陈金石, 冉春雷, 王忠平. 脊柱和骨盆矢状位参数与椎体成形治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折预后的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1412-1417. |
| [12] | 薛亚东, 周新社, 裴立家, 孟繁宇, 李 键, 王金子. 自体髂骨块联合钛板重建Paprosky Ⅲ型髋臼骨缺损为假体提供坚强的初始固定#br#[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [13] | 庄至坤, 吴荣凯, 林行会, 龚志兵, 张前进, 魏秋实, 张庆文, 吴昭克. 稳定增强型内衬髋关节系统在偏瘫老年股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [14] | 李灿辉, 吴征杰, 曾焰辉, 何影浩, 司徒晓鹏, 杜雪莲, 洪 石, 何家雄. 骨科手术机器人辅助与传统透视下经皮骶髂螺钉置入的优劣分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1434-1438. |
| [15] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 周 倩, 张 强, 陈 秋. 人体唾液成分与骨质疏松/骨量低下[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
良好的生物学特性是骨再生支架保持正常生理功能并引导新骨形成需具备的重要特性之一,主要包括:骨传导性、骨诱导性和生物降解性。迄今为止研究较多的促进骨再生支架的生物学特性的方法,大部分是围绕材料化学性质和支架功能设计对支架生物学特性的影响2个方面。然而,至今仍然没有一种理想的支架设计能够完全替代骨组织,主要原因为:①受限于支架制造技术,如传统制造工艺中不能控制支架的孔形状、几何形状及孔隙率等结构[4];然而,随着近年来支架制造技术的发展,出现了如3D打印技术等新型支架制造技术[5-6],不仅可以制造融合了多种材料的复合支架,而且使得支架复杂的形态结构可以得到精确的控制,突破了支架制造技术的瓶颈。②受限于对支架化学性质和功能设计指导骨再生机制的了解不够全面。
作为骨再生支架重要特性之一的生物学特性,受到多种因素的影响,深入了解支架材料的化学性质及支架功能设计等因素对于骨再生支架生物学特性的影响,对于设计理想的骨再生支架至关重要。为此,文章综述了聚合物、无机材料、金属等不同材料及支架的物理、化学、结构和物质递送等不同的功能设计,并阐述其如何促进骨再生支架的骨传导性、骨诱导性及生物降解性3种生物学特性,为未来研究中骨再生支架的生物学特性的设计提供思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2021年7月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 查阅2000年1月至2021年7月发表的文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“骨组织工程、骨传导性、骨诱导性、黏附、扩散、物理特性、化学特性、结构特性、生长因子、离子、生物降解性、聚合物、无机材料、金属”;英文检索词为“bone tissue engineering,osteoconduction,Osteoinduction,adhesion,diffusion,physical characteristics,chemical characteristics,structural characteristics, growth factors,ions,biological degradability,polymer,inorganic material,metal”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述和荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.1.8 检索文献量 初步检索英文文献798篇,中文文献635篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①文章内容与骨组织工程、支架设计、骨诱导性和生物降解性密切相关;②同一领域选择新发表的文献或在权威杂志上发表的文章。
1.2.2 排除标准 筛除重复性研究和与文章内容无关的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估 通过阅读标题及摘要初筛,排除与文章目的不符、年代久远及重复性研究,共入选文献91篇,见图2。
骨组织工程支架设计首要考虑支架的骨传导性。根据前文所述,影响骨传导性的因素主要分为物理、化学和结构特性。①亲疏水性和表面生化结构主要是支架表面性质,是通过改善材料对纤连蛋白等蛋白的吸附能力,进而增强细胞黏附,促进支架的骨传导性。因此改善支架表面亲疏水性、表面生化结构的主要手段是通过对支架材料表面进行改性,如增加亲水基团[90],增加RGD等生物结构域等[36]。②影响骨传导性的另一个因素是刚度,是通过改变细胞-支架间的相互作用,给支架传递机械信号,进而影响细胞黏附及分化[91]。因此,对于支架刚度的设计需考虑刚度与应用功能的匹配性以及刚度指导的细胞分化方向。刚度除可影响骨传导性外,还可影响骨诱导性,现有研究认为较低刚度可促进间充质干细胞向成软骨或成脂方向分化,而较高刚度则更有利于成骨[27]。因此在设计支架时应通过调整交联度或与刚度较高材料结合等手段,使支架达到促进成骨分化的刚度。③结构特性中孔隙结构是支架设计时需考虑的重要因素之一,孔隙大小及孔隙率都会影响成骨分化过程。近年来新兴的3D打印技术可以通过设计内部孔隙和通道结构制造结构复杂的支架,弥补了传统技术的单一性和不可控性,使支架制造标准化、精准化,也使得孔隙结构的构造可以更多样化。
骨组织工程支架的骨诱导性除会受到上述因素影响外,还会被支架释放的具有诱导作用的物质影响,如生长因子和具有促成骨作用的离子等。①对于生长因子促进骨诱导性的设计,现有的研究已通过直接吸附、聚合物包封和逐层技术等尝试进行生长因子递送,然而在持续释放时间和剂量依赖性生长因子释放技术方面,仍待解决。最近发现的温敏型、pH敏感型聚合物[50],也许是解决这一难题的方法之一。②输送具有诱导成骨能力的离子也是骨再生的策略之一,如硅、镁、锶等。离子递送的设计主要是通过将具有诱导成骨能力的离子与生物材料结合,尤其是与无机材料的结合,如羟基磷灰石和生物活性玻璃。多种离子的结合递送,也是手段之一。然而,关于离子的受控释放也是有待解决的挑战。
生物降解性的支架设计主要涉及对于降解速度的控制,然而迄今为止,支架材料生物降解的可控性仍是支架设计的难点,生长因子递送的时序问题就是现有研究仍存在的悬而未决的问题之一,如如何控制生长因子的早期爆发性释放和生长因子的持续性释放。现有的设计思路之一是将不同生长因子包封入具有不同生物降解性的材料中,根据不同材料降解性控制生长因子释放时间和持续时间[52]。除物质递送外,生物降解材料的机械力学性能也是支架设计的难点之一,由于具有较好生物降解性的材料常机械力学性能较差,导致支架材料无法达到作为骨移植物的机械强度。现有研究的设计思路是将具有较好机械强度的材料与具有较好生物降解性的材料相结合形成复合支架[87],然而仍无法达到理想的机械强度。
理想的支架设计,不应只采用单一因素或材料,应综合上述多种影响因素,从多方面增强支架的生物学特性才是未来骨组织工程支架设计的正确思路,如结合多种材料,以平衡单一材料的生物相容性、生物降解性和机械性能等限制。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:
骨组织工程支架:使用可植入生物材料作为干细胞的支架,以暂时保持骨组织在再生过程中的功能、生长和组织修复。
生物学特性:不同的材料能够通过其本身的物理、化学和结构特性等影响细胞生物学功能的性质。
骨移植是临床中骨缺损治疗的主要方法,由于自体移植及异体移植的限制,骨组织工程骨作为替代品变得尤为重要。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||