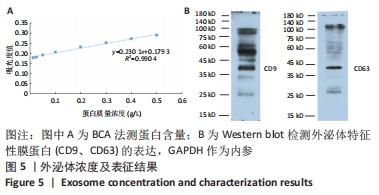
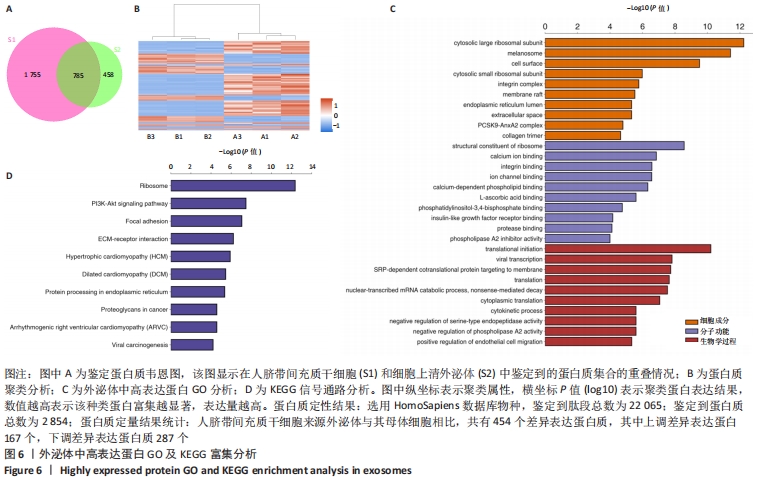
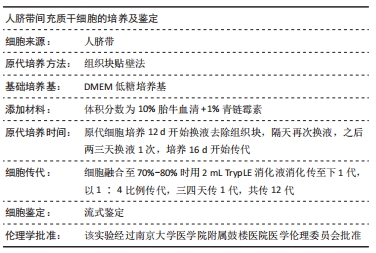
[1] DING DC, SHYU WC, LIN SZ. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(1):5-14.
[2] LAI RC, YEO RW, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88.
[3] PATHAN M, FONSEKA P, CHITTI SV, et al. Vesiclepedia 2019: a compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D516-D519.
[4] HE C, ZHENG S, LUO Y, et al. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):237-255.
[5] WEISS ML, TROYER DL. Stem cells in the umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev. 2006;2(2):155-162.
[6] DING DC, CHANG YH, SHYU WC, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(3):339-347.
[7] YAGHOUBI Y, MOVASSAGHPOUR A, ZAMANI M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes in diseases treatment. Life Sci. 2019;233:116733.
[8] MENDT M, REZVANI K, SHPALL E. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019;54(Suppl 2):789-792.
[9] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346.
[10] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[11] THÉRY C, ZITVOGEL L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(8):569-579.
[12] Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, et al. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347-360.
[13] FAROOQI AA, DESAI NN, QURESHI MZ, et al. Exosome biogenesis, bioactivities and functions as new delivery systems of natural compounds. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(1):328-334.
[14] LI T, XIA M, GAO Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an overview of their potential in cell-based therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(9):1293-1306.
[15] 王雨涵,程福,蒋汶学,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体的提取与鉴定[J].中国社区医师,2020,36(34):4-5.
[16] 徐燕,李长虹,孟恒星,等.人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养条件的优化及其生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(32):6289-6294.
[17] ZHANG B, SHEN L, SHI H, et al. Exosomes from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Identification, Purification, and Biological Characteristics. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1929536.
[18] 贾刚,唐秋莎.外泌体在肿瘤治疗中的应用研究进展[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2018,37(1):157-161.
[19] COX J, HEIN MY, LUBER CA, et al. Accurate proteome-wide label-free quantification by delayed normalization and maximal peptide ratio extraction, termed MaxLFQ. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014;13(9):2513-2526.
[20] COX J, NEUHAUSER N, MICHALSKI A, et al. Andromeda: a peptide search engine integrated into the MaxQuant environment. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(4):1794-1805.
[21] ASHBURNER M, BALL CA, BLAKE JA, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25-29.
[22] GÖTZ S, GARCÍA-GÓMEZ JM, TEROL J, et al. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(10):3420-3435.
[23] KANEHISA M, SATO Y, MORISHIMA K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(4):726-731.
[24] HUANG DA W, SHERMAN BT, LEMPICKI RA. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(1):1-13.
[25] HUANG DA W, SHERMAN BT, LEMPICKI RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44-57.
[26] CAN A, BALCI D. Isolation, culture, and characterization of human umbilical cord stroma-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;698:51-62.
[27] BATSALI AK, KASTRINAKI MC, PAPADAKI HA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton’s Jelly of the umbilical cord: biological properties and emerging clinical applications. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(2):144-155.
[28] MA Y, DONG L, ZHOU D, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve transection in rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(4): 2822-2835.
[29] SUN G, LI G, LI D, et al. hucMSC derived exosomes promote functional recovery in spinal cord injury mice via attenuating inflammation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:194-204.
[30] ZHANG Y, WANG WT, GONG CR, et al. Combination of olfactory ensheathing cells and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes sciatic nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(10):1903-1911.
[31] LI X, LIU LL, YAO JL, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inhibit Endometrial Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration through Delivery of Exogenous miR-302a. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:8108576.
[32] JIANG L, ZHANG S, HU H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute liver failure by reducing the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508(3):735-741.
[33] JIANG W, TAN Y, CAI M, et al. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:6079642.
[34] YIN S, JI C, WU P, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes: bioactive ways of tissue injury repair. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1230-1240.
[35] DING Y, CAO F, SUN H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells deliver exogenous miR-145-5p to inhibit pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression. Cancer Lett. 2019;442:351-361.
[36] LIU B, DING F, HU D, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium attenuates renal fibrosis by reducing inflammation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):7.
[37] JIA H, LIU W, ZHANG B, et al. HucMSC exosomes-delivered 14-3-3ζ enhanced autophagy via modulation of ATG16L in preventing cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(1):101-113.
[38] SHU L, NIU C, LI R, et al. Treatment of severe COVID-19 with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):361.
[39] ATLURI S, MANCHIKANTI L, HIRSCH JA. Expanded Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells (UC-MSCs) as a Therapeutic Strategy in Managing Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: The Case for Compassionate Use. Pain Physician. 2020;23(2):E71-E83.
[40] XIE K, LIU L, CHEN J, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via delivering miR-1246. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(24):3491-3501.
[41] CHO PS, MESSINA DJ, HIRSH EL, et al. Immunogenicity of umbilical cord tissue derived cells. Blood. 2008;111(1):430-438.
[42] LIU M, WANG J, LIU M, et al. Study of immunomodulatory function of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;95(32):2630-2633.
[43] WANG ZG, HE ZY, LIANG S, et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):511.
[44] DING M, SHEN Y, WANG P, et al. Exosomes Isolated From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Neuroinflammation and Reduce Amyloid-Beta Deposition by Modulating Microglial Activation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(11):2165-2177.
[45] THÉRY C, AMIGORENA S, RAPOSO G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22.
[46] DRAGOVIC RA, GARDINER C, BROOKS AS, et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomedicine. 2011;7(6):780-788.
[47] KEERTHIKUMAR S, CHISANGA D, ARIYARATNE D, et al. ExoCarta: A Web-Based Compendium of Exosomal Cargo. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(4):688-692.
[48] YOSHIOKA Y, KONISHI Y, KOSAKA N, et al. Comparative marker analysis of extracellular vesicles in different human cancer types. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2.
[49] SALUNKHE S, DHEERAJ, BASAK M, et al. Surface functionalization of exosomes for target-specific delivery and in vivo imaging & tracking: Strategies and significance. J Control Release. 2020;326:599-614.
[50] 宋玉仙,张东亚,许玉君,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可调控巨噬细胞的极化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(13):2002-2008.
[51] 郭莹,王秀伟,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体提取方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(9):1382-1388.
[52] WANG XL, ZHAO YY, SUN L, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve myocardial repair via upregulation of Smad7. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(5):3063-3072.
|