[1] SILVESTRE C, MAC-THIONG JM, HILMI R, et al. Complications and Morbidities of Mini-open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in 179 Patients. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(2):89-97.
[2] MEHREN C, MAYER HM, ZANDANELL C, et al. The Oblique Anterolateral Approach to the Lumbar Spine Provides Access to the Lumbar Spine With Few Early Complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(9): 2020-2027.
[3] ABBASI A, KHAGHANY K, ORANDI V, et al. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Oblique Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Cureus. 2019; 11(2):e4029.
[4] KRAIWATTANAPONG C, ARNUNTASUPAKUL V, KANTAWAN R, et al. Malposition of Cage in Minimally Invasive Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Case Rep Orthop. 2018;2018:9142074.
[5] CHUNG NS, LEE HD, JEON CH. Accuracy of the lateral cage placement under intraoperative C-arm fluoroscopy in oblique lateral interbody fusion. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(6):918-922.
[6] 郑召民, 王建儒. 开展侧方入路腰椎间融合术应思考的几个问题[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(5):385-388.
[7] LIU J, DING W, YANG D, et al. Modic Changes (MCs) Associated with Endplate Sclerosis Can Prevent Cage Subsidence in Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF) Stand-Alone. World Neurosurg. 2020;138: e160-e168.
[8] LIU X, MA J, PARK P, et al. Biomechanical comparison of multilevel lateral interbody fusion with and without supplementary instrumentation: a three-dimensional finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):63.
[9] ZENG ZY, XU ZW, HE DW, et al. Complications and Prevention Strategies of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Technique. Orthop Surg. 2018; 10(2):98-106.
[10] LU T, LU Y. Comparison of Biomechanical Performance Among Posterolateral Fusion and Transforaminal, Extreme, and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;129:e890-e899.
[11] XU H, JU W, XU N, et al. Biomechanical comparison of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with 1 or 2 cages by finite-element analysis. Neurosurgery. 2013;73(2 Suppl Operative):s198-s205,s205.
[12] REIS MT, REYES PM, ALTUN I, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of lateral lumbar interbody fusion with secondary augmentation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(6):720-726.
[13] LV QB, GAO X, PAN XX, et al. Biomechanical properties of novel transpedicular transdiscal screw fixation with interbody arthrodesis technique in lumbar spine: A finite element study. J Orthop Translat. 2018;15:50-58.
[14] NATARAJAN RN, WATANABE K, HASEGAWA K. Biomechanical Analysis of a Long-Segment Fusion in a Lumbar Spine-A Finite Element Model Study. J Biomech Eng. 2018;140(9).doi:10.1115/1.4039989.
[15] LI QY, KIM HJ, SON J, et al. Biomechanical analysis of lumbar decompression surgery in relation to degenerative changes in the lumbar spine - Validated finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2017;89:512-519.
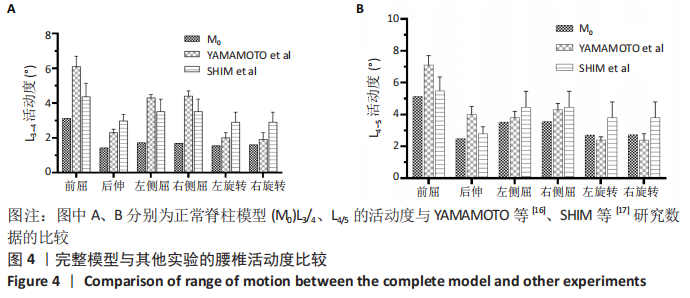
[16] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[17] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(22):E820-E827.
[18] WANG HW, HU YC, WU ZY, et al. Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Unilateral Fixation for Degenerative Lumbar Disease. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(3):277-283.
[19] JIN C, JAISWAL MS, JEUN SS, et al. Outcomes of oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease in patients under or over 65 years of age. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):38.
[20] OHTORI S, ORITA S, YAMAUCHI K, et al. Mini-Open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Spinal Degeneration Disease. Yonsei Med J. 2015; 56(4):1051-1059.
[21] OHTORI S, MANNOJI C, ORITA S, et al. Mini-Open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Degenerated Lumbar Spinal Kyphoscoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(4):565-572.
[22] HE W, HE D, SUN Y, et al. Quantitative analysis of paraspinal muscle atrophy after oblique lateral interbody fusion alone vs. combined with percutaneous pedicle screw fixation in patients with spondylolisthesis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):30.
[23] KRETZER RM, MOLINA C, HU N, et al. A Comparative Biomechanical Analysis of Stand Alone Versus Facet Screw and Pedicle Screw Augmented Lateral Interbody Arthrodesis: An In Vitro Human Cadaveric Model. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(7):E336-E343.
[24] FUJIBAYASHI S, KAWAKAMI N, ASAZUMA T, et al. Complications Associated With Lateral Interbody Fusion: Nationwide Survey of 2998 Cases During the First 2 Years of Its Use in Japan. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(19):1478-1484.
[25] GODZIK J, MARTINEZ-DEL-CAMPO E, NEWCOMB A, et al. Biomechanical Stability Afforded by Unilateral Versus Bilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation with and without Interbody Support Using Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion. World Neurosurg. 2018;113:e439-e445.
[26] DOULGERIS JJ, AGHAYEV K, GONZALEZ-BLOHM SA, et al. Biomechanical comparison of an interspinous fusion device and bilateral pedicle screw system as additional fixation for lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(2):205-210.
[27] FOGEL GR, PARIKH RD, RYU SI, et al. Biomechanics of lateral lumbar interbody fusion constructs with lateral and posterior plate fixation: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(3):291-297.
[28] TOWERS WS, KURTOM KH. Stand-alone LLIF Lateral Cage Migration: A Case Report. Cureus. 2015;7(10):e347.
[29] CHEN JF, LEE ST. The polymethyl methacrylate cervical cage for treatment of cervical disk disease Part III. Biomechanical properties. Surg Neurol. 2006;66(4):367-370,370.
[30] DAFFNER SD, WANG JC. Migrated XLIF cage: case report and discussion of surgical technique. Orthopedics. 2010;33(7):518.
(责任编辑:GD,ZN,ZH)
|