| [1] 王磊,李兴.脂联素影响骨代谢致骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].现代药物与临床,2011,26(6):426-429.[2] 鲍晓雪,王娜,李玉坤.肥胖与骨质疏松症关系的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志,2015,9(14):2749-53.[3] Zhang Q, Riddle RC, Clemens TL. Bone and the regulation of global energy balance. J Int Med. 2015;277(6):681-689.[4] Gonnelli S, Caffarelli C, Nuti R. Obesity and fracture risk. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2014;11(1):9-14.[5] Fernandes TAP, Gonçalves LML, Brito JAA. Relationships between bone turnover and energy metabolism. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:9021314.[6] Chen T, Wu YW, Lu H, et al. Adiponectin enhances osteogenic differentiation in human adipose-derived stem cells by activating the APPL1-AMPK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;461(2):237-242.[7] Ding WX, Dong YB, Ding N, et al. Adiponectin protects rat heart from left ventricular remodeling induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia via inhibition of TGF-β/smad2/3 pathway. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(9):1278-1284.[8] Francin PJ, Abot A, Guillaume C, et al. Association between adiponectin and cartilage degrandation in human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(3):519-526.[9] 方曦,陈琳洁,谢长好,等.脂联素与脊柱关节炎的研究进展[J].中华全科医学,2016,14 (10):1732-1735.[10] Mendez-Sanchez N, Chavez-Tapia NC, Zamora-Valdes D, et al. Adiponectin, structure, function and pathophysiological implications in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006;6(6):651-656.[11] 陈栖栖,刘钢.脂联素在类风湿关节炎中的作用和进展[J].实用医院临床杂志,2016,13(2):174-177.[12] Wang QP, Li XP, Wang M, et al. Adiponectin exerts its negative effect on bone metabolism via OPG/RANKL pathway: an in vivo study. Endocrine. 2014. DOI: 10.1007 /s12020-014-0216-z.[13] 王峰,郑陆.脂联素、瘦素与运动及骨代谢的关系[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(2):221-227.[14] Elda L. Pacheco-Pantoja, Victoria J, et al. Adiponectin receptors are present in RANK-L-induced multinucleated osteoclast-like cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013. DOI: 10.3109/10799893.2013.828070.[15] Kanazawa I. Adiponectin in Metabolic Bone Disease. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19:5481-5492.[16] Pajvani UB, Du X, Combs TP, et al. Structure function studies of the adiponectin-secreted hormone Acrp30/adiponectin. Biol Chem. 2003;278(11):9073-9085.[17] Klein-Wieringa IR, Andersen SN, Herb-van Toorn L, et al. Are baseline high molecular weight adiponectin levels associated with radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2014;41(5):853-857.[18] Pajvani U B, Hankins M, Combs T P, et al. Complex distribution, not absolute amount of adiponectin, correlates with thizolidinedione-mediated mprovement in insulin sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(13):12152-12162. [19] Kalisz M, Baranowska B, Wolinska-Witort E, et al. Total and high molecular weight adiponectin levels and risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with high blood glucose levels. Atherosclerosis. 2013;229(1):222-227.[20] Huang ZH, Manickam B, Ryvkin V, et al. PCOS is associated with increased CD11c expression and crown-like structures in adipose tissue and increased central abdominal fat depots independent of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(1): E17-E24.[21] Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature. 2003;423(6941):762-769.[22] Kharroubi I, Rasschaert J, Eizirik DL, et al. Expression of adiponectin receptors in pancreatic beta cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;312(4):1118-1122.[23] Zhang ZL, He JW, Qin YJ, et al. Association between SNP and haplotypes in PPARGC1 and adiponectin genes and bone mineral density in Chinese nuclear families. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007; 28(2):287-295.[24] Hangen F, Drevon CA. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB by high molecular weight and globular adiponectin. Endocrinology. 2007; 148(11):5478-5486.[25] Neumeier M, Weigert J, Schfiffier A, et al. Different effects of adiponectin isoforms in human monocytic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;79(4):803-808.[26] Sonmez A, Dogru T, Yilmaz MI, et al. Adiponectin and insulin resistance in young and healthy smokers. Endocr J. 2006;53(6): 729-734.[27] Koenig W, Khuseyinova N, Baumert J, et al. Serum concentrations of Adiponectin and risk of type 2diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease in apparently healthy middle-aged men: results from the 18-year follow-up of a large cohort from southern Germany. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(7):1369-1377.[28] Schulze MB, Shai I, Rimm EB, et al. Adiponectin and future coronary heart disease events among men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54(2):534-539.[29] Tajtakova M, Petrasova D, Petrovicova J, et al. Adiponectin as a biomarker of clinical manifestation of metabolic syndrome. Endocr Regul. 2006;40(1):15-19.[30] Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, et al. Adiponectin and AdipoQnectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(7):1784-1792.[31] Okada-Iwabu M, Yamauchi T, Iwabu M, et al. A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature. 2013;503:493-499.[32] Okada-Iwabu M, Iwabu M, Ueki K, et al. Perspective of small-molecule adipor agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39:363-372.[33] Dimitri P, Rosen C. The Central Nervous System and Bone Metabolism: An Evolving Story. Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;100(5): 476-485.[34] Xu C, Ochi H, Fukuda T, et al. Circadian clock regulates bone resorption in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(7):1344-1355.[35] Cao Y, Gomes SA, Rangel EB, et al. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase-dependent PPARγ denitrosylation participates in MSC-derived adipogenesis and osteogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(4):1679-1691.[36] Martin PJ, Haren N,Ghali O,et al. Adipogenic RNAs are transferred in osteoblasts via bone marrow adipocytes-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). BMC Cell Biol. 2015;16(1):1-10.[37] Su CM, Lee WL, Hsu CJ, et al. Adiponectin Induces Oncostatin M Expression in Osteoblasts through the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Adiponectin Induces Oncostatin M Expression in Osteoblasts through the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:29.[38] 邹晓玲,罗湘杭.脂联素研究进展[J].实用预防医学, 2010,17(11): 2338-2341.[39] Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, et al. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:26746-26749.[40] Huang CY, Lee CY, Chen MY, et al. Adiponectin increases BMP-2 expression in osteoblasts via AdipoR receptor signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2010;224(2):475-483.[41] Yamaguchi N, Kukita T, Li YJ, et al. Adiponectin inhibits osteoclast formation stimulated by lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007;49: 28-34.[42] Berner HS, Lygstadaas Sp, Spahr A, et al. Adiponeetin and its receptors are expressed in bone-forming cells. J Bone. 2004; 35(4):842-849.[43] 袁凌青,罗湘杭,谢辉,等.脂联素对人成骨细胞增殖作用的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006,12(2):135-137.[44] Oshima K, Nampei A, Matsuda M, et al.Adiponectin increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and activating osteoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;331(2):520-526.[45] Luo XH, Guo LJ, Yuan LQ, et al. Adiponectin stimulates human osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2005;309(1):99-109.[46] Luo XH, Guo LJ, Xie H, et al. Adiponectin stimulates RANKL and inhibits OPG expression in human osteoblasts through the MAPK signaling pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21(10):1648-1656.[47] Wang QP, Li XP, Wang, M, et al. Adiponectin exerts its negative effect on bone metabolism via OPG/RANKL pathway: an in vivo study. Endocrine. 2014;47(3):845-853.[48] Lee HW, Kim SY, Kim AY, et al. Adiponectin Stimulates Osteoblast Differentiation Through Induction of COX2 in Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells. 2009,27(9):2254-2262.[49] Berner HS, Lyngstadaas SP, Spahr A et al. Adiponectin and its receptors are expressed in bone-forming cells. Bone. 2004;35: 842-849.[50] Shinoda Y, Yamaguchi M, Ogata N, et al. Regulation of bone formation by adiponectin through autocrine/paracrine and endocrine pathways. Cell Biochem. 2006;99(1):196-208.[51] Jurimae J, Jurimae T, Plasma adiponectin concentration in healthy pre- and postmenopausal women: relationship with body composition, bone mineral, and metabolic variables. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293(1):42-47.[52] Lewiecki EM. RANK ligand inhibition with denosumab for the management of osteoporosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2006;6(10): 1041-1050.[53] Schett G, Hayer S, Zmerina J, et al. Mechanisms of Disease: the link between RANKL and arthritic bone disease. Nat Clin Pract Pheumatol. 2005;1(1):47-54.[54] Simonet WS, Laeey DL, Dunstan CR, et al. Osteporotegerin: a novel secreted pretein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997;89(2):309-319.[55] P. Szulc, P.D. Delmas, Biochemical markers of bone turnover: potential use in the investigation and management of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19(12): 1683-1704.[56] Yamauchi T; Kadowaki T. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in the integrated regulation of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Int J Obes. 2008;7;S13-S18.[57] Hong X, Arguelles LM, Tsai HJ, et al. Plasma adipokines, bone mass, and hip geometry in rural Chinese adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:1644-1652.[58] Kiechl S, Werner P, Knoflach M, et al. The osteoprotegerin/ RANK/RANK-L system: a bone key to vascular disease. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2006;4(6):801-811.[59] Kostenuik PJ. Osteoprotegerin and RANKL regulate bone resorption, density, geometry and strength. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5(6):618-625.[60] Krumbholz G, Junker S, Meier FMP, et al. Response of human rheumatoid arthritis osteoblasts and osteoclasts to adiponectin. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(3):406-414.[61] Zhang L, Meng S, Tu Q, et al. Adiponectin ameliorates experimental periodontitis in diet-induced obesity mice. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e97824. [62] 张平平,向川.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗骨关节炎:可能与未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6):968-973.[63] 贾懿劼,田京.干细胞治疗骨质疏松症的可能与可行[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(1):148-152. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
脂联素:主要是由成熟的脂肪细胞合成和分泌,具有一定的多功能激素蛋白。在动脉粥样硬化中,脂联素被认为是一种保护因子,而在一些自身免疫性疾病如类风湿性及风湿性关节炎中,则被认为具有前炎性因子的作用。
骨质疏松:是多种原因引起的一组骨病,骨组织有正常的钙化,钙盐与基质呈正常比例,以单位体积内骨组织量减少为特点的代谢性骨病变。
文题释义:
脂联素:主要是由成熟的脂肪细胞合成和分泌,具有一定的多功能激素蛋白。在动脉粥样硬化中,脂联素被认为是一种保护因子,而在一些自身免疫性疾病如类风湿性及风湿性关节炎中,则被认为具有前炎性因子的作用。
骨质疏松:是多种原因引起的一组骨病,骨组织有正常的钙化,钙盐与基质呈正常比例,以单位体积内骨组织量减少为特点的代谢性骨病变。.jpg) 文题释义:
脂联素:主要是由成熟的脂肪细胞合成和分泌,具有一定的多功能激素蛋白。在动脉粥样硬化中,脂联素被认为是一种保护因子,而在一些自身免疫性疾病如类风湿性及风湿性关节炎中,则被认为具有前炎性因子的作用。
骨质疏松:是多种原因引起的一组骨病,骨组织有正常的钙化,钙盐与基质呈正常比例,以单位体积内骨组织量减少为特点的代谢性骨病变。
文题释义:
脂联素:主要是由成熟的脂肪细胞合成和分泌,具有一定的多功能激素蛋白。在动脉粥样硬化中,脂联素被认为是一种保护因子,而在一些自身免疫性疾病如类风湿性及风湿性关节炎中,则被认为具有前炎性因子的作用。
骨质疏松:是多种原因引起的一组骨病,骨组织有正常的钙化,钙盐与基质呈正常比例,以单位体积内骨组织量减少为特点的代谢性骨病变。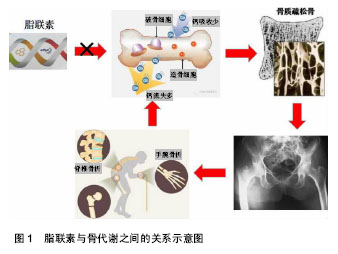
.jpg) 文题释义:
脂联素:主要是由成熟的脂肪细胞合成和分泌,具有一定的多功能激素蛋白。在动脉粥样硬化中,脂联素被认为是一种保护因子,而在一些自身免疫性疾病如类风湿性及风湿性关节炎中,则被认为具有前炎性因子的作用。
骨质疏松:是多种原因引起的一组骨病,骨组织有正常的钙化,钙盐与基质呈正常比例,以单位体积内骨组织量减少为特点的代谢性骨病变。
文题释义:
脂联素:主要是由成熟的脂肪细胞合成和分泌,具有一定的多功能激素蛋白。在动脉粥样硬化中,脂联素被认为是一种保护因子,而在一些自身免疫性疾病如类风湿性及风湿性关节炎中,则被认为具有前炎性因子的作用。
骨质疏松:是多种原因引起的一组骨病,骨组织有正常的钙化,钙盐与基质呈正常比例,以单位体积内骨组织量减少为特点的代谢性骨病变。