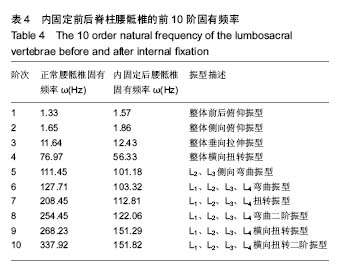
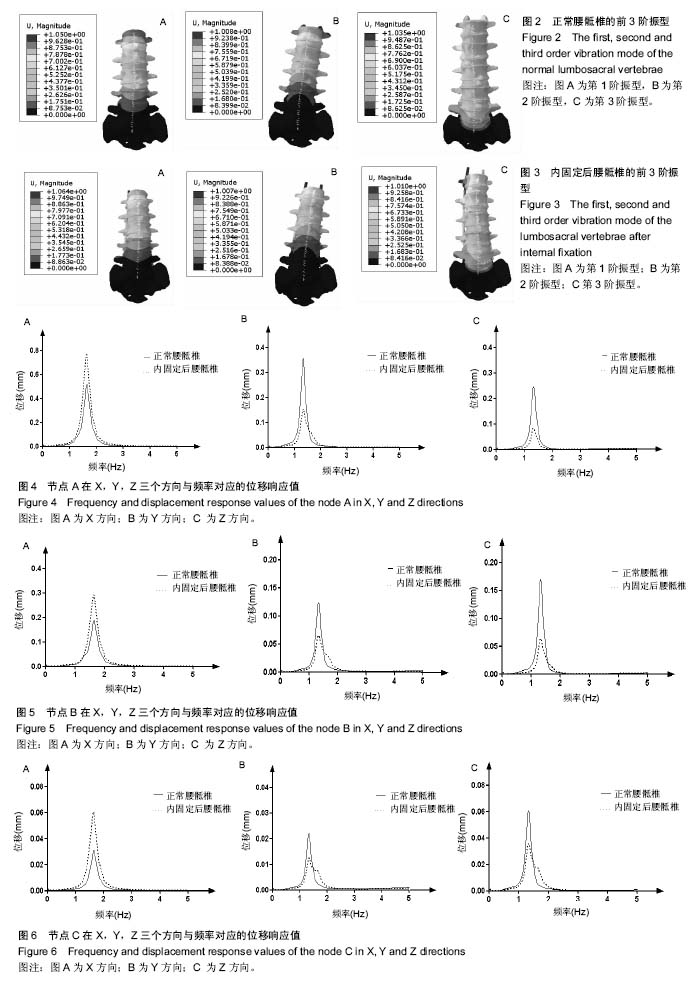
| [1] Li XF, Liu ZD, Dai LY, et al. Dynamic response of the idiopathic scoliotic spine to axial cyclic loads. Spine. 2011; 36(7): 521-528.[2] Guo LX, Teo EC, Lee KK, et al. Vibration characteristics of the human spine under axial cyclic loads: effect of frequency and damping. Spine. 2005;30(6): 631-637.[3] Kong WZ,Goel VK. Ability of the finite element models to predict response of the human spine to sinusoidal vertical vibration. Spine. 2003;28(28): 1961-1967.[4] Seidel H, Blüthner R, Hinz B. Application of finite-element models to predict forces acting on the lumbar spine during whole-body vibration. Clin Biomech. 2001;16Suppl 1(16 Suppl 1): S57-S63.[5] Kasra M, Shirazi-Adl A, Drouin G. Dynamics of human lumbar intervertebral joints. Experimental and finite-element investigations. Spine. 1992;17(1): 93-102.[6] 黄凯,刘展亮,刘少喻,等. 腰椎单侧与双侧椎弓根螺钉固定的生物力学对比性研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2015(22): 4143-4147.[7] 郝剑,姚进,朴哲,等. 腰椎坚强固定后邻近节段的有限元法生物力学分析[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2016,22(5):475-478.[8] Zhu R, Yu Y, Zeng ZL, et al. A Review of the Static Loads Applying on the Finite Element Models of the Lumbar Spine. J Med Imaging Health Informat. 2015.[9] Zafarparandeh I. Application of Finite Element Method in the human Spine Biomechanics. 2016.[10] Zhang Z, Yang L I, Liao Z, et al. Research Progress and Prospect of Applications of Finite Element Method in Lumbar Spine Biomechanics. J Biomed Eng. 2016.[11] 王端阳,奚春阳,杨辉,等. 有限元分析法在腰椎生物力学研究中的应用及新进展[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2015,15(9): 1794- 1797.[12] Zulkiflil A, Ariffinl AK, Rahman MM. Probabilistic finite element analysis of vertebrae of the lumbar spine under hyperextension loading. Int J Autom Mech Eng. 2011;3(1): 256-264.[13] Kavitha A, Sudhir G, Ranjani T S, et al. Implant Analysis on the Lumbar-Sacrum Vertebrae Using Finite Element Method. Springer Singapore, 2017.[14] Wang DY, Chun-Yang XI, Yang H, et al. New Progress and Application of Finite Element Analysis Technology in Lumbar Spine Biomechanics. Prog Mod Biomed. 2015.[15] Alonso-Rasgado MT, Martinez-Lozada FM, Bailey CG, et al. The effects of L4-L5 Fusion on the Adjacent Segments in Lumbar Spine: Finite Element Analysis. Int J Stroke. 2015; 10(2):269-274. [16] Li K, Zhang J, Jiang J, et al. Lumbar spinal finite element analysis in a gravity environment. in Eighth International Conference on Digital Image Processing. 2016.[17] 韩硕. 有限元分析在腰椎间盘生物力学中的应用研究[D]. 河北医科大学, 2016.[18] 曹丽君.正常及退变下腰椎在不同工况下三维有限元力学分析[D].河北医科大学, 2015.[19] 张伟,宫赫.振动载荷作用下人体腰椎多孔弹性有限元分析[C]//北京力学会学术年会. 2015.[20] 张振军,李阳,廖振华,等. 有限元法在腰椎生物力学应用中的研究进展和展望[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016,(6): 1196-1202.[21] 秦计生, 王昱, 彭雄奇, 等. 全腰椎三维有限元模型的建立及其有效性验证[J]. 医用生物力学, 2013, 28(3):321-325.[22] 黄菊英,李海云,吴浩. 腰椎间盘突出症力学特征的仿真计算方法[J]. 医用生物力学, 2012, 27(1): 4630-4631.[23] 苏晋,赵文志,陈秉智,等. 建立全腰椎有限元接触模型[J]. 医用生物力学, 2010, 25(3): 200-205.[24] 牛文鑫.人体振动生物力学响应的数学模型研究进展[J]. 2008.[25] 马亮,郭卫春.成年人腰椎-骨盆的三维有限元模型的建立及验证[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2016,(3): 229-235.[26] 魏峰. 基于CT图像的人体腰椎有限元模型构建与力学分析[D].南京理工大学, 2015.[27] 陈为坚,段扬,林周胜,等. 基于三维有限元法的腰椎动态稳定系统建立及生物力学行为初步分析[J]. 广东医学, 2015,36(10): 1497-1500.[28] 冯杰荣,殷海东,陈伟,等. T(12)椎体前缘不同压缩状态下相邻椎体终板应力的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(22): 3263-3271.[29] Pawlikowski M, Domański J, Suchocki C. Advanced finite element analysis of L4–L5 implanted spine segment. Cont Mech Ther. 2015;27(4): 571-582.[30] 吕永强,彭春政. 负重屈伸运动对腰椎受力的有限元分析[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报, 2016, 35(2): 92-97.[31] 陶勇,吴云乐,宗少晖,等. 基于有限元分析腰椎内固定的生物力学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(13): 1932-1938.[32] 胡迎春,赵舒婷,余兵浩. 人体腰椎模拟植入椎弓根螺钉的有限元分析[J]. 广西科技大学学报, 2014, 25(3): 10-13.[33] 任伟.基于人体腰椎有限元分析的乘坐舒适性研究[D].东北大学, 2010.[34] 申成刚. 基于人体腰椎动力学特性分析的高速列车座椅舒适性研究[D].东北大学, 2011.[35] 项嫔, 都承斐, 赵美雅, 等.全腰椎有限元模态分析[J]. 医用生物力学, 2014, 29(2): 154-160.[36] Kurutz M,Oroszváry L. Finite element analysis of weightbath hydrotraction treatment of degenerated lumbar spine segments in elastic phase. J Biomech. 2010;43(3): 433-441.[37] Chen CS, Chen WJ, Cheng CK, et al. Failure analysis of broken pedicle screws on spinal instrumentation. Med Eng Phys. 2005;27(6): 487-496.[38] 肖振平. 腰椎动态—非动态椎弓根钉内固定系统的有限元分析及初步临床应用[D].南华大学,2012.[39] Zhang QH,Teo EC. Finite element application in implant research for treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease. Med Eng Phys. 2008;30(10): 1246-1256.[40] 黄宇峰,潘福敏,赵卫东,等. 关于腰椎三维有限元模型的建模及有效性验证[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2015,12(5):16-19.[41] 董凡,侯筱魁.小关节在腰椎结构刚度中的作用[J]. 中华外科杂志,1993,31(7): 417-420.[42] Heth J, Hitchon P, Goel V, et al. A biomechanical comparison between anterior and transverse interbody fusion cages. Spine. 2001;26(12): e261-e267.[43] Yamamoto I, Panjabi M, Crisco T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine. Spine. 1989;14(11): 1256-1260. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)