| [1] Bishara SE,Fehr DE.Ceramic brackets: Something old, something new, a review. Seminars in Orthodontics. 1997;3(3):178-188.
[2] Eliades T,Lekka M,Eliades G,et al. Surfacecharacterization of ceramic brackets: a multitechnique approach.Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop.1994;105(1):10-14
[3] Chang HS,Walsh LJ,Freer TJ.Enamel demineralization during orthodontic treatment. Aetiology and prevention. Aust Dent J.1997;42(5):322-327.
[4] Mizrahi E.Enamel demineralization following orthodontic treatment.Am J Orthod. 1982;82(1):62-67.
[5] Chatterjee R,Kleinberg I.Effect of orthodontic band placement on the chemical composition of human incisor tooth plaque.Arch Oral Biol.1979;24(2):97-100.
[6] Richter AE,Arruda AO,Peters MC,et al.Incidence of caries lesions among patients treated with comprehensive orthodontics.Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop.2011;139(5):657-664.
[7] Frey C,Yetkiner E,Stawarczyk B,et al.Effects of different chlorhexidine pretreatments on adhesion of metal brackets in vitro.Head Face Med.2012;8(36):1-5.
[8] Li F,Weir MD,Chen J,et al.Comparison of quaternary ammonium- containing with nano- silver- containing adhesive in antibacterial properties and cytotoxicity. Dent Mater.2013;29(4):450- 461.
[9] 张晟,麦理想,柳大烈,等.纳米Ag/ TiO2 涂层托槽的研制及力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(38):7047-7052.
[10] Grigorov KG,Oliveira IC,Maciel HS,et al.Optical and morphological properties of N-doped TiO2 thin films. Surf Sci.2011;605(7):775-782.
[11] Mattsson A,Lejon C,Bakardjieva S,et al. Characterisation, phase stability and surface chemical properties of photocatalytic active Zr and Y co-doped anatase TiO2 nanoparticles.J Solid State Chem. 2013; 199:212-223.
[12] Di Valentin C,Finazzi E,Pacchioni G,et al.N-doped TiO2: Theory and experiment.Chem Phys. 2007;339: 44-56.
[13] Jiang X,Wang Y,Pan C.High Concentration Substitutional N-Doped TiO2 Film: Preparation, Characterization, and Photocatalytic Property.J Am Ceram Soc. 2011;94(11):4078-4083.
[14] 李娜,曹宝成,王育华,等.掺氮TiO(2-x)Nx薄膜托槽的制备及其性能研究[J].功能材料,2011,42(B11):835-838.
[15] Li S,Hobson RS,Bai Y,et al.A method for producing controlled fluoride release from an orthodontic bracket. EurJ Orthod.2007;29(6):550-554.
[16] 束嫘,丁寅,曹勇,等.纳米陶瓷涂层托槽的研制[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2005, 21(2):252-255.
[17] Meng FM,Lu F.Chracterization and PhotocataIytic Activity of TiO2 Thin Films Prepared by RF Magnetron sputtering.Vacuum.2010;85(1):84-88.
[18] Studenikin SA,Golego N,Cocivera M.Carrier mobility and density contributions to photoconductivity transients in polycrystalline ZnO films.J Appl Phys. 2000;87:2413.
[19] Pradhan SS,Sahoo S,Pradhan SK.Influence of Annealing Temperatture on the Structual, Mechanical and Wetting Properyt of TiO2 Film Deposited by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Thin Solid Films. 2010;518(23):6904-6908.
[20] 唐伟忠.薄膜材料制备原理、技术及应用[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,2003.
[21] 田明波.薄膜技术与薄膜材料[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2006:247-253.
[22] Kilicoglu H,Yildirim M,Polater H.Comparison of the effectiveness of two types of toothbrushes on the oral hygiene of patients undergoing orthodontic treatment w ith fixed appliances.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1997;111(6):591-594 .
[23] Cal E,Güneri P,Kose T.Comparison of digital and spectrophotometric measurements of colour shade guides.J Oral Rehabil.2006;33(3):221-228.
[24] Shungin D,Olsson AI,Persson M.Orthodontic treatment-related white spot lesions: a 14- year prospective quantitative follow- up,including bonding material assessment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2010;138(2):136e1-8.
[25] Asahi R,Morikawa T,Ohwaki T,et al.Visible-Light Photocatalysis in Nitrogen-Doped Titanium Oxides. Science.2001;293(5528):269-271.
[26] Bu X,Zhang G,Zhang C.Effect of nitrogen doping on anatase–rutile phase transformation of TiO2.Appl Surf Sci. 2012;258(20):7997-8001.
[27] O'reilly M,Featherstone J.Demineralization and remineralization around orthodontic appliances: an in vivo study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthopedics. 1987;92(1):33-40.
[28] Lemos JA,Quivey RG,JrKoo H,et al.Streptococcus mutans: a new Gram-positive paradigm? Microbiology. 2013;59(Pt 3):436-445.
[29] 闫文娟,杨德鸿,吴补颌.变形链球菌8cp基因突变菌株的构建及鉴定[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2011,9(6):325-328
[30] Kleinegger CL,Lockhard SR,Vargas K,et al.Frequency, intensity species, and strainsofora Candida vary as a function of hostage.J Clin Microbiol.1996; 30(1): 2246-2254. |
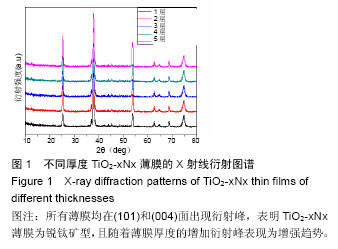
.jpg)
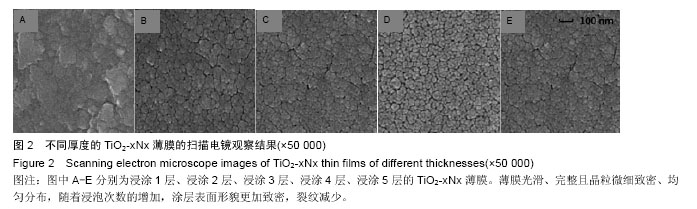
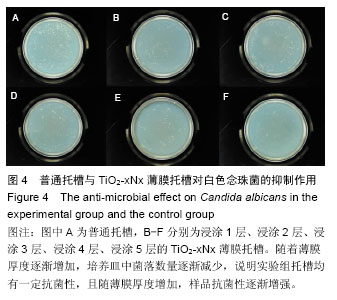
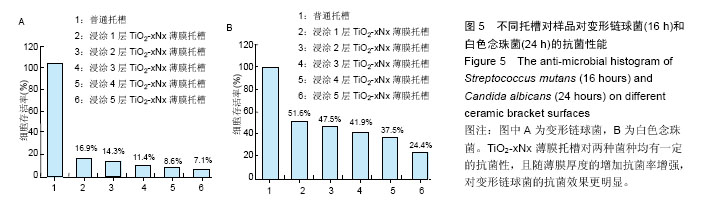
.jpg)
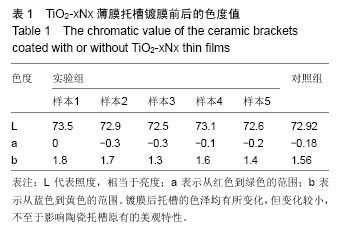
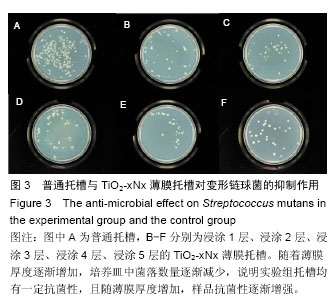
.jpg)