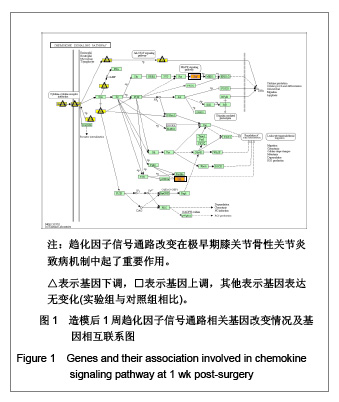
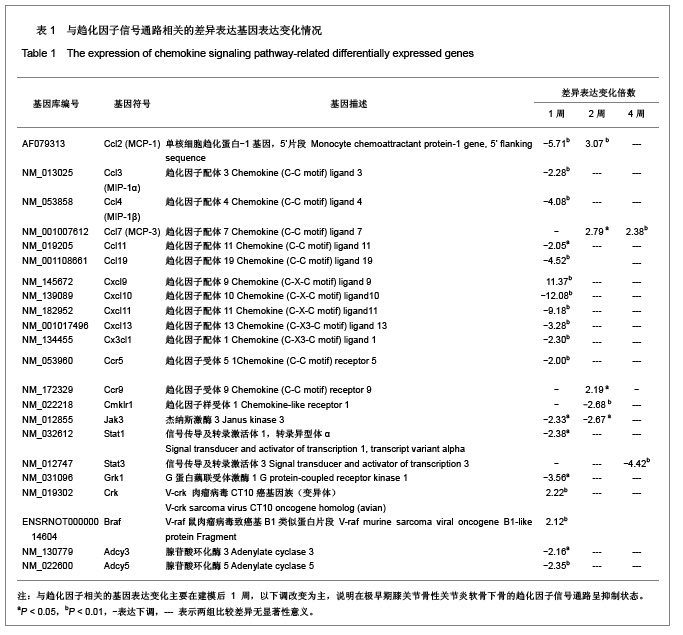
| [1] Felson DT, Neogi T. Osteoarthritis: is it a disease of cartilage or of bone? Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):341-344.[2] Lohmander LS. What can we do about osteoarthritis? Arthritis Res. 2000;2(2):95-100.[3] Henrotin Y, Pesesse L, Sanchez C. Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis physiopathology: state-of-the art and perspectives. Biomed Mater Eng. 2009;19(4-5):311-316.[4] Madry H, van Dijk CN, Mueller-Gerbl M. The basic science of the subchondral bone. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(4):419-433.[5] Roemer FW, Guermazi A, Javaid MK, et al. Change in MRI-detected subchondral bone marrow lesions is associated with cartilage loss: the MOST Study. A longitudinal multicentre study of knee osteoarthritis. Change in MRI-detected subchondral bone marrow lesions is associated with cartilage loss: the MOST Study. A longitudinal multicentre study of knee osteoarthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(9):1461-1465.[6] Shirai T, Kobayashi M, Nishitani K, et al. Chondroprotective effect of alendronate in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(10):1572-1577.[7] Kadri A, Funck-Brentano T, Lin H, et al. Inhibition of bone resorption blunts osteoarthritis in mice with high bone remodelling. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(8):1533-1538.[8] Hayami T, Pickarski M, Wesolowski GA, et al. The role of subchondral bone remodeling in osteoarthritis: reduction of cartilage degeneration and prevention of osteophyte formation by alendronate in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection model. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(4):1193-1206.[9] Shibakawa A, Yudoh K, Masuko-Hongo K, et al. The role of subchondral bone resorption pits in osteoarthritis: MMP production by cells derived from bone marrow. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2005;13(8):679-687.[10] Jiao K, Niu LN, Wang MQ. Subchondral bone loss following orthodontically induced cartilage degradation in the mandibular condyles of rats. Bone. 2011;48(2):362-371.[11] Lisignoli G, Toneguzzi S, Pozzi C,et al. Chemokine expression by subchondral bone marrow stromal cells isolated from osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999;116(2):371-378.[12] Endres M, Andreas K, Kalwitz G, et al. Chemokine profile of synovial fluid from normal, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis patients: CCL25, CXCL10 and XCL1 recruit human subchondral mesenchymal progenitor cells. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010;18(11):1458-1466. [13] Borzì RM, Mazzetti I, Cattini L, et al. Human chondrocytes express functional chemokine receptors and release matrix-degrading enzymes in response to C-X-C and C-C chemokines. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(8):1734-1741.[14] Yuan GH, Masuko-Hongo K, Sakata M,et al. The role of C-C chemokines and their receptors in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(5):1056-1070.[15] Lisignoli G, Toneguzzi S, Grassi F,et al. Different chemokines are expressed in human arthritic bone biopsies: IFN-gamma and IL-6 differently modulate IL-8, MCP-1 and rantes production by arthritic osteoblasts. Cytokine. 2002;20(5): 231-238. [16] Lande R, Giacomini E, Serafini B,et al. Characterization and recruitment of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in synovial fluid and tissue of patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol. 2004;173(4):2815-2824.[17] Hayami T, Pickarski M, Zhuo Y, et al. Characterization of articular cartilage and subchondral bone changes in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection and meniscectomized models of osteoarthritis. Bone. 2006;38(2):234-243.[18] van den Berg WB. Lessons from animal models of osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2008;10(1):26-29.[19] Appleton CTG, Pitelka V, Henry J, et al. Global analyses of gene expression in early experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(6):1854-1868.[20] Zhang RK, Fang H, Lu HD, et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2011;27(12):2391-2395. 张荣凯,方航,卢华定,等. Mmp3在早期骨关节炎模型软骨下骨的表达及其意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(12):2391-2395.[21] Zhang RK, Li GW, Fang H, et al. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi. 2012;29(4):767-768. 张荣凯,李国威,方航,等. 一种提取大鼠膝关节软骨下骨总RNA的方法[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(4):767-768.[22] Madry H, van Dijk CN, Mueller-Gerbl M. The basic science of the subchondral bone. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(4):419-433.[23] Rollins BJ. Chemokines. Blood. 1997;90(3):909-928.[24] Szekanecz Z, Koch AE, Tak PP. Chemokine and chemokine receptor blockade in arthritis, a prototype of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Neth J Med. 2011; 69(9):356-366.[25] Szekanecz Z, Vegvari A, Szabo Z,et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in arthritis. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010;1(2):153-167.[26] Tak PP. Chemokine inhibition in inflammatory arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006;20(5):929-939.[27] CE Vergunst, MGH van de Sande, MC Lebre, et al. The role of chemokines in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005;34(6):415-425.[28] Lisignoli G, Toneguzzi S, Piacentini A,et al.CXCL12 (SDF-1) and CXCL13 (BCA-1) chemokines significantly induce proliferation and collagen type I expression in osteoblasts from osteoarthritis patients. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(1):78-85.[29] Haringman JJ, Smeets TJM, Reinders-Blankert P, et al. Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in paired peripheral blood mononuclear cells and synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and reactive arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006;65(3):294-300.[30] Meikle MC, Bord S, Hembry RM,et al. Human osteoblasts in culture synthesize collagenase and other matrix metalloproteinases in response to osteotropic hormones and cytokines. J Cell Sci. 1992;103(Pt4):1093-1099. |