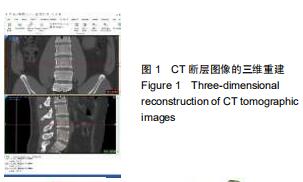
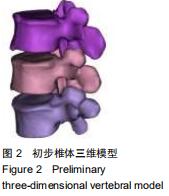
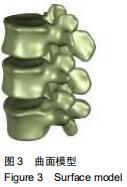
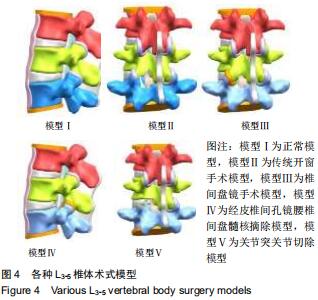
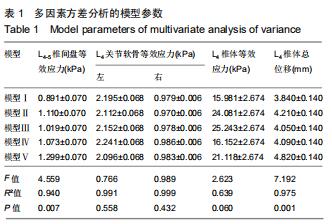
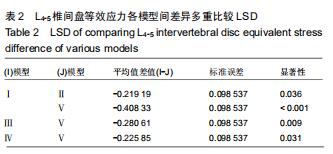
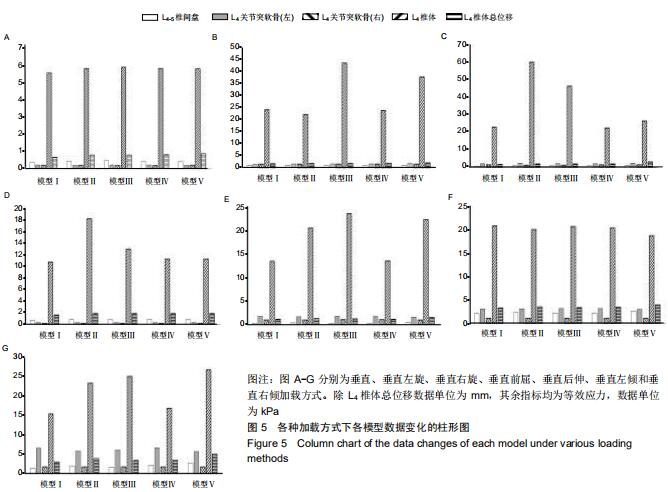
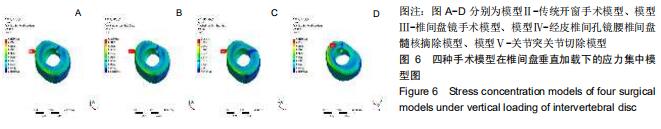
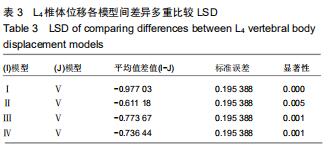
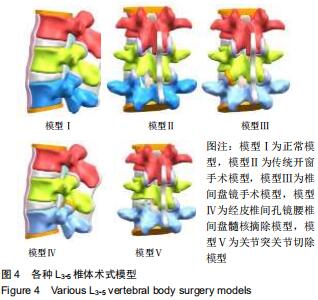
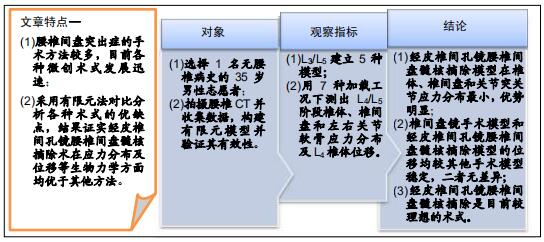
|
[1] PAN Z, HA Y, YI S, et al. Efficacy of transforaminal endoscopic spine system(TESSYS)technique in treating lumbar disc herniation. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:530-539.
[2] LI ZZ, HOU SX, SHANG WL, et al. Modified percutaneous lumbar foraminoplasty and percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: instrument design,technique notes, and 5 years follow-up. Pain Physician. 2017;20(1):E85-98.
[3] CHEN C, SHIH S. Biomechanical analysis of a new lumbar interspinous device with optimized topology. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(8):1333-1341.
[4] LI L, SHEN T, LI Y. A finite element analysis of stress distribution and disk displacement in response to lumbar rotation manipulation in the sitting and side-lying positions. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017;40(8):580-586.
[5] MOORE MK, FULOP S, TABIB-AZAR M, et al. Piezoresistive pressure sensors in the measurement of intervertebral disc hydrostatic pressure. Spine. 2009;12:120-134.
[6] 王沛,董强,雪原.腰椎间盘突出病变部的压力测定及病理学意义[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(3):129-133.
[7] 李勇,彭立阳,陈荣彬.三种纤维环处理方式对腰椎生物力学影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2019,25(4): 509-514.
[8] LEITE PMS, MENDONCA ARC, MACIEL LYS, et al. Does Electroacupuncture treatment reduce pain and change quantitative sensory testing responses in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain? A randomized controlled clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018: 8586746.
[9] LI J, HE J, LI H, et al. Proportion of neuropathic pain in the back region in chronic low back pain patients-a multicenter investigation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16537.
[10] CHOI KC, SHIM HK, PARK CJ, et al. Usefulness of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar foraminoplasty for lumbar disc herniation.World Neumsurg. 2017;106:484492.
[11] ZHANG JJ, CUI HP, DING Y, et al. Endoscopic foraminoplasty and neuro-ventral decompression for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation combining with lateral recess stenosis. J Spine. 2018; 7(2):412-417.
[12] OKOSUKA J, OSHIMA Y, KANEKO T, et al. Advantages and disadvantages of posterolateral approach for percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. J Spine Surg.2016;2(3): 158-166.
[13] ZHONG ZC, WEI SH, WANG JP, et al. Finite element anaylsis of the lumbar spine with a new cage using a topology optimization method. Med Eng Phys. 2006;1:90-98.
[14] WILCOX RK. The influence of material property and morphological parameters on specimen-specific finite element models of porcine vertebral bodies. J Biomech. 2007; 3:669-673.
[15] WHEELDON JA, PINTAR FA, KNOWLES S, et al. Experimenml flexion/extension data corridors for validation of finite element models of the young, normal cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006; 2:375-380.
[16] SAIRYO K, GOEL VK, VADAPALLI S, et al. Biomechanical comparison of lumbar spine with or without spina bifida occulta. A finite element analysis. Spinal Cord. 2006;7:440-444.
[17] 范建平,王传锋,魏显招,等.新型个体化三维矫形胸腰骶气囊支具的有限元研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(6):348-353.
[18] 黄宇峰,潘福敏,赵卫东,等.腰椎后外侧融合椎弓根钉对相邻节段椎间盘影响的三维有限元分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(6): 362-366.
[19] PANJABI MM, KRAG MH, CHUNG TQ. Effects of disc injury on mechanical behavior of the human spine. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1984;9(7):707-713.
[20] 文毅,苏峰,刘肃,等.L4-5椎体有限元模型建立及退变椎间盘力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究杂志,2019,23(8):1222-1227.
[21] 赵凡,刘正,王炳强,等.有限元模拟单节段腰椎小关节分级切除对腰椎稳定性的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2015,95(13):973-977.
[22] 阮朝阳,何永清,增强华,等.腰椎间孔成形幅度对关节突关节应力变化的有限元分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2017,15(6):357-365.
[23] 李振宙,侯树勋.经皮侧后路腰椎间孔成形与经椎间孔完全内镜下腰椎间盘摘除术[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2014,3(8):621-625.
[24] ABUMI K, PANJABI MM, KRAMER KM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of lumbar spinal stability after graded facetectomies. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15(11):1142-1147.
[25] 安民,袁野,曹虹,等.单双侧小关节分级切除的有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2002,20(6):473-474.
[26] 王小平,梁真娇,杨芳梅,等.齿突下软骨基质融合部对枢椎骨折类型影响的有限元分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(5):295-302.
[27] SHARMA M, LANGRANA NA, RODRIQUEZ J. Role of ligaments and facets in lumbar spinal stability. Spine.1995; 20(8):887-900.
[28] ADAMS MA. The resistance to flexion of the lumbar intervertebral joint. Spine.1980;5:245.
[29] 马剑雄,马信龙,骆巍,等.后部结构对腰椎前屈/后伸稳定性的影响[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2009,15(1):71-74.
|