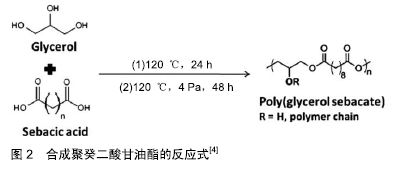
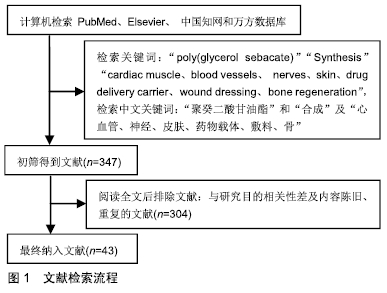
[1] LIU Q, TIAN M, SHI R, et al. Structure and properties of thermoplastic poly (glycerol sebacate) elastomers originating from prepolymers with different molecular weights.J Appl Polym Sci.2007;104(2):1131-1137.
[2] SFAKIS L, KAMALDINOV T, KHMALADZE A, et al.Mesenchymal Cells Affect Salivary Epithelial Cell Morphology on PGS/PLGA Core/Shell Nanofibers.Int J Mol Sci.2018;19(4):1031.
[3] LIANG SL, COOK WD, THOUAS GA, et al.The mechanical characteristics and in vitro biocompatibility of poly (glycerol sebacate)-Bioglass elastomeric composites.Biomaterials.2010;31(33): 8516-8529.
[4] WANG Y, AMEER GA, SHEPPARD BJ, et al.A tough biodegradable elastomer.Nat Biotechnol.2002;20(6):602-606.
[5] RAI R, TALLAWI M, GRIGORE A, et al.Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of poly (glycerol sebacate)(PGS): a review. Prog Polym Sci.2012;37(8):1051-1078.
[6] LI Y, COOK WD, MOORHOFF C, et al.Synthesis, characterization and properties of biocompatible poly (glycerol sebacate) pre-polymer and gel.Polym Int.2013;62(4):534-547.
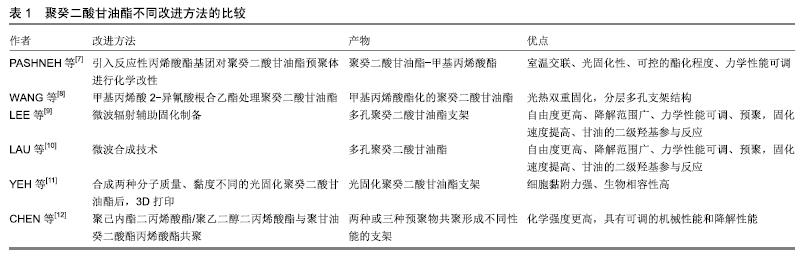
[7] PASHNEH-TALA S, OWEN R, BAHMAEE H, et al.Synthesis, characterization and 3D micro-structuring via 2-photon polymerization of poly (glycerol sebacate)-methacrylate-an elastomeric degradable polymer.Front Phys-Beijing.2018;6(41):ISSN 2296.
[8] WANG M, LEI D, LIU Z, et al.A(glycerol sebacate) based photo/thermo dual curable biodegradable and biocompatible polymer for biomedical applications.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2017;28(15):1728-1739.
[9] LEE SH, LEE KW, GADE, PS, et al.Microwave-assisted facile fabrication of porous poly (glycerol sebacate) scaffolds.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(7-9):907-916.
[10] LAU CC.A comprehensive study on synthesis and bioapplication of calcium phosphates, poly (glycerol sebacate) and the biocomposite by microwave approaches.Ph.D.Thesis,University College London,US,2018.
[11] YEH YC, HIGHLEY CB, OUYANG L, et al.3D printing of photocurable poly (glycerol sebacate) elastomers.Biofabrication.2016;8(4):045004.
[12] CHEN JY, HWANG J, AO-IEONG WS, et al.Study of Physical and Degradation Properties of 3D-Printed Biodegradable, Photocurable Copolymers, PGSA-co-PEGDA and PGSA-co-PCLDA. Polymers. 2018;10(11):1263.
[13] SUNDBACK CA, SHYU JY, WANG Y, et al.Biocompatibility analysis of poly (glycerol sebacate) as a nerve guide material.Biomaterials. 2005; 26(27):5454-5464.
[14] HU T, WU Y, ZHAO X, et al.Micropatterned, electroactive, and biodegradable poly (glycerol sebacate)-aniline trimer elastomer for cardiac tissue engineering.Chem Eng J .2019;366:208.
[15] KHARAZI AZ, ATARI M, VATANKHAH E, et al.A nanofibrous bilayered scaffold for tissue engineering of small-diameter blood vessels.Polym Adv Technol.2018;29(12):3151.
[16] FERRARI PF, ALIAKBARIAN B, LAGAZZO A, et al.Tailored electrospun small-diameter graft for vascular prosthesis.Int J Polym Mater Po. 2017;66(12):635-643.
[17] LEE KW, GADE PS, DONG L, et al.A biodegradable synthetic graft for small arteries matches the performance of autologous vein in rat carotid arteries.Biomaterials.2018;181:67-80.
[18] WU HJ, HU MH, TUAN-MU HY, et al.Preparation of aligned poly (glycerol sebacate) fibrous membranes for anisotropic tissue engineering.Mat Sci eng C.2019;100:30.
[19] MERLE B, KRAUS X, TALLAWI M, et al.Dynamic mechanical characterization of poly (glycerol sebacate)/poly (butylene succinate-butylene dilinoleate) blends for cardiac tissue engineering by flat punch nanoindentation.Mater Lett .2018;221:115-118.
[20] HSIEH YK, CHANG CT, JEN IH, et al.Use of Gold Nanoparticles to Investigate the Drug Embedding and Releasing Performance in Biodegradable Poly (glycerol sebacate).Acs Appl Mater.2018;1(9): 4474-4482.
[21] NAGHIZADEH S, HASSANZADEH NEMATI N, HASSANI NAJAFABADI A, et al.Controlled release of fluorouracil (5-FU) from chitosan-co-poly (ethylene glycol)/poly (glycerol sebacate)-co-poly (ethylene glycol)-coated iron oxide.Int J Polym Mater Po. 2018;67(4): 212-220.
[22] DESAI P, VENKATARAMANAN A, SCHNEIDER R, et al. Self-assembled,ellipsoidal polymeric nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of therapeutics.J Biomed Mater Res A.2018;106(7): 2048-2058.
[23] MOLLAZADEH-MOGHADDAM K, REZAEI NEJAD H, CHEN AZ, et al. Fracture-Resistant and Bioresorbable Drug-Eluting Poly (glycerol Sebacate) Coils.Adv Therapeutics.2019;2(3):1800109.
[24] WANG Z, MA Y, WANG Y, et al. Urethane-based low-temperature curing, highly-customized and multifunctional poly (glycerol sebacate)- co-poly (ethylene glycol) copolymers.Acta Biomater.2018;71:279-292.
[25] HU J, KAI D, YE H, et al.Electrospinning of poly (glycerol sebacate)- based nanofibers for nerve tissue engineering.Mat Sci Eng C.2017;70: 1089-1094.
[26] SINGH D, HARDING AJ, ALBADAWI E, et al.Additive manufactured biodegradable poly (glycerol sebacate methacrylate) nerve guidance conduit.Acta Biomater.2018;78:48-63.
[27] ZARGAR KHARAZI A, DINI G, NASER R, et al.Fabrication and evaluation of a nerve guidance conduit capable of Ca2+ ion release to accelerate axon extension in peripheral nerve regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2018;106(8):2181-2189.
[28] SARAVANI S, EBRAHIMIAN-HOSSEINABADI M, MOHEBBI-KALHORI D.Polyglycerol sebacate/chitosan/gelatin nano-composite scaffolds for engineering neural construct .Mater Chem Phys.2019;222:147-151.
[29] WU Y, WANG L, HU T, et al.Conductive micropatterned polyurethane films as tissue engineering scaffolds for Schwann cells and PC12 cells. J Colloid Interf Sci.2018;518:252-262.
[30] THANARAK J,MOHAMMED H,PASHNEH-TALA S,et al.Enhanced Collagen Production from Human Dermal Fibroblasts on Poly(glycerol sebacate)-methacrylate Scaffolds.In:2018 11th Biomedical Engineering International Conference(BMEiCON).Chiang Mai,Thailand.
[31] ZHANG X, JIA C, QIAO X, et al.Silk fibroin microfibers and chitosan modified poly (glycerol sebacate) composite scaffolds for skin tissue engineering.Polym Test.2017;62:88-95.
[32] KEIROUZ A, FORTUNATO G, CALLANAN A, et al.Needleless electrospinning of PVP/PGS fibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering applications.2018.DOI:10.31224/osf.io/xs64k
[33] HEYDARI P, VARSHOSAZ J, ZARGAR KHARAZI A, et al.Preparation and evaluation of poly glycerol sebacate/poly hydroxy butyrate core-shell electrospun nanofibers with sequentially release of ciprofloxacin and simvastatin in wound dressings.Polym Adv TechnoL. 2018;29(6):1795-1803.
[34] AYATI NAJAFABADI SA, SHIRAZAKI P, ZARGAR KHARAZI A, et al. Evaluation of sustained ciprofloxacin release of biodegradable electrospun gelatin/poly (glycerol sebacate) mat membranes for wound dressing applications.Asia-Pac J Chem Eng.2018;13(6):e2255.
[35] ABUDULA T, GZARA L, SIMONETTI G, et al.The Effect of Poly (Glycerol Sebacate) Incorporation within Hybrid Chitin–Lignin Sol–Gel Nanofibrous Scaffolds.Materials.2018;11(3):451.
[36] KEMPPAINEN JM, HOLLISTER SJ.Tailoring the mechanical properties of 3D-designed poly (glycerol sebacate) scaffolds for cartilage applications.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010; 94(1):9-18.
[37] ZAKY SH, LEE KW, GAO J, et al.Poly (glycerol sebacate) elastomer supports bone regeneration by its mechanical properties being closer to osteoid tissue rather than to mature bone.Acta Biomater. 2017;54: 95-106.
[38] LIU Y, TIAN K, HAO J, et al.Biomimetic poly (glycerol sebacate)/ polycaprolactone blend scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2019;30(5):53.
[39] TEVLEK A, HOSSEINIAN P, OGUTCU C, et al.Bi-layered constructs of poly (glycerol-sebacate)-β-tricalcium phosphate for bone-soft tissue interface applications.Mat Sci Eng C.2017;72:316-324.
[40] MA Y, ZHANG W, WANG Z, et al.PEGylated poly (glycerol sebacate)- modified calcium phosphate scaffolds with desirable mechanical behavior and enhanced osteogenic capacity.Acta Biomater. 2016;44: 110-124.
[41] JIANG L, JIANG Y, STIADLE J, et al.Electrospun nanofibrous thermoplastic polyurethane/poly (glycerol sebacate) hybrid scaffolds for vocal fold tissue engineering applications.Mat Sci Eng C. 2019;94: 740-749.
[42] YAN Y, POTTS M, JIANG Z, et al.Synthesis of highly-stretchable graphene–poly (glycerol sebacate) elastomeric nanocomposites piezoresistive sensors for human motion detection applications. Compos Sci Technol. 2018;16214-16222.
[43] CHEN S, HUANG T, ZUO H, et al.A Single Integrated 3D-Printing Process Customizes Elastic and Sustainable Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Wearable Electronics. Adv Funct Mater.2018; 28.46:1805108.
|