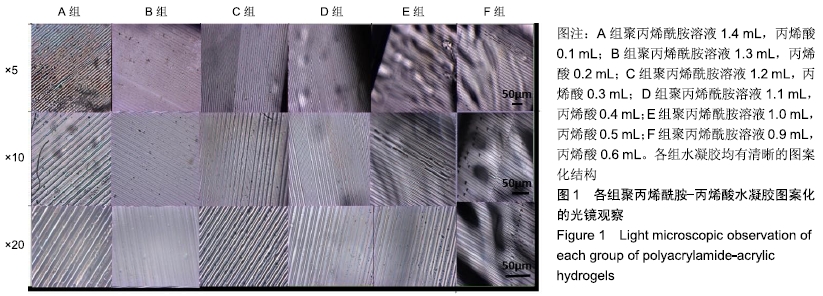
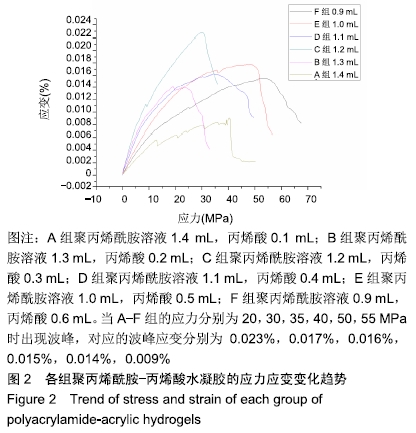
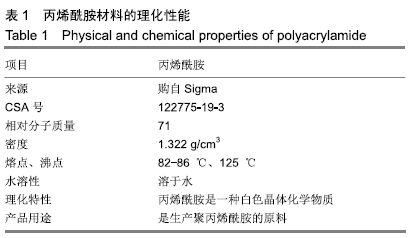
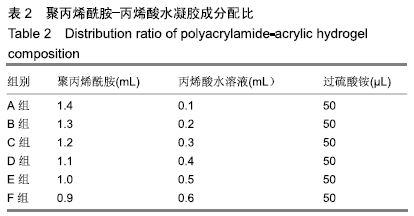
[1] ZHANG PX, LI-YA A, KOU YH, et al.Biological conduit small gap sleeve bridging method for peripheral nerve injury: regeneration law of nerve fibers in the conduit.Neural Regen Res.2015;10(1):71-78.
[2] LIU XN, LIU RL, CAO B, et al.Subcellular cell geometry on micropillars regulates stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials. 2016;111:27-39.
[3] FUJIMAKI H, UCHIDA K, INOUE G, et al.Oriented collagen tubes combined with basic fibroblast growth factor promote peripheral nerve regeneration in a 15 mm sciatic nerve defect rat model.J Biomed Mater Res A.2017;105(1):8-14.
[4] HSUEH YS, SAVITHA S, SADHASIVAM S, et al.Design and synthesis of elastin-like polypeptides for an ideal nerve conduit in peripheral nerve regeneration.Mater Sci Eng C. 2014;38(1):119-126.
[5] CHEN SL, CHEN ZG, HONG L, et al.Repair, protection and regeneration of peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(11):1777-1798.
[6] VISWANATHAN P, ONDECK MG, CHIRASATITSIN S, et al.3D surface topology guides stem cell adhesion and differentiation. Biomaterials. 2015;52(6):140-147.
[7] SAGAR N, KHANNA K, SARDESAI VS, et al.Bioconductive 3D nano-composite constructs with tunable elasticity to initiate stem cell growth and induce bone mineralization.Mater Sci Eng,C. 2016;69(1): 700-714.
[8] YE K, CAO LP, LI SY, et al.Interplay of Matrix Stiffness and Cell-Cell Contact in Regulating Differentiation of Stem Cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;34(8):21903-21913.
[9] HUANG L, DU XY, FAN S, et al.Bacterial cellulose nanofibers promote stress and fidelity of 3D-printed silk based hydrogel scaffold with hierarchical pores.Carbohydr Polym. 2019;221:146-156.
[10] ADEWUNMI AA, ISMAIL S, SULTAN AS, et al.Crosslinked Polyacrylamide Composite Hydrogels Impregnated with Fly Ash: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Application as Fractures Sealant for High Water Producing Zones in Oil and Gas Wells.J Polym Environ.2018;26(8):3294-3306.
[11] DUNCOMBE TA, KANG CC, MAITY S, et al.Hydrogel Pore-Size Modulation for Enhanced Single-Cell Western Blotting.Adv Mater. 2016;28(2):327-334.
[12] NIELSEN K, VORUM H, EHLERS N, et al.Tear film proteins deposited on high water content contact lenses identified with two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry.Acta Ophthalmol. 2015; 93(7):658-662.
[13] LI J, HAN D, ZHAO YP.Kinetic behaviour of the cells touching substrate: the interfacial stiffness guides cell spreading.Sci Rep.2014;28(4):3910.
[14] SALEHI M, BAGHER Z, KAMRAVA SM, et al.Alginate/chitosan hydrogel containing olfactory ectomesenchymal stem cells for sciatic nerve tissue engineering.J Cell Physiol. 2019,234:15357-15368.
[15] 徐雪峰,白艳华.聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶隆乳后的并发症及其临床验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(34):6429-6432.
[16] KIYAMA R, NONOYAMA T, WADA S, et al.Micro patterning of hydroxyapatite by soft lithography on hydrogels for selective osteoconduction.Acta Biomater.2018;81:60-69.
[17] 李志军,陈捷,杨黎明,等.聚丙烯酰胺/聚异丙基丙烯酰胺互穿网络水凝胶的制备与性能[J].化学研究,2005,16(4):6-9.
[18] 郝定均,谢恩,陈博等.修复脊髓损伤的仿生多孔水凝胶的制备研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(5):9-12.
[19] PRADHAN S, SALTER JH.Tunable hydrogels for controlling phenotypic cancer cell states to model breast cancer dormancy and reactivation. Biomaterials.2019;215:119-127.
[20] SEO Y, LEE H, LEE JW, et al.Hyaluronate-alginate hybrid hydrogels prepared with various linkers for chondrocyte encapsulation.Carbohydr Polym.2019;218:1-7.
[21] NARAYANAN KB, CHOI SM, HAN SS.Biofabrication of Lysinibacillus sphaericus-reduced graphene oxide in three-dimensional polyacrylamide/carbon nanocomposite hydrogels for skin tissue engineering. Colloids Surf,B. 2019;181:539-548.
[22] KLOXIN AM, KASKO AM, SALINAS CN, et al.Photodegradable hydrogels for dynamic tuning of physical and chemical properties. Science. 2009;324:59-63.
[23] MI HY, JIANG YC, XIN J, et al.Fabrication of triple-layered vascular grafts composed of silk fibers, polyacrylamide hydrogel,and polyurethane nanofibers with biomimetic mechanical properties.Mater Sci Eng,C. 2019;98:241-249.
[24] MANSOURI N, BAGHERI S.The influence of topography on tissue engineering perspective.Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;61(4):906-921.
[25] 何银亭,詹秀环,姚新建.聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J].河北化工,2010,33(9):28-29.
[26] 杨蓉,黄星,吴小蔚.聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶注射隆鼻后继发鼻畸形的分析与处理[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(26):5234-5236.
[27] HU WK, WANG ZJ, YU X, et al.Advances in crosslinking strategies of biomedical hydrogels.Biomater Sci. 2019;7:1179-1187.
[28] UEDA E, LEVKIN PA.Micropatterning hydrophobic liquid on a porous polymer surface for long-term selective cell-repellency. Adv Healthc Mater.2013;2(11):1425-1429.
[29] ALBERT PJ, SCHWARZ US.Optimizing micropattern geometries for cell shape and migration with genetic algorithms.Integr Biol. 2016; 8(7):741-750.
[30] OSORIO M, ORTIZ I, GANAN P, et al.Novel surface modification of three-dimensional bacterial nanocellulose with cell-derived adhesion proteins for soft tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;100: 697-705.
[31] BEDUER A, VIEU C, ARNAUDUC F, et al.Engineering of adult human neural stem cells differentiation through surface micropatterning. Biomaterials.2012;33(2):504-514.
[32] 孙艳花,宋建明,温文等.注射聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶隆乳后的乳腺病变[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(25):4623-4626.
[33] BENOIT DS, DURNEY AR, ANESTH KS.The effect of heparin-functionalized PEG hydrogels on three-dimensional human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Biomateials. 2007; 28(1):66-77.
[34] REHMANN MS, LUNA JI, MAVERAKIS E, et al.Tuning microenvironment modulus and biochemical composition promotes human mesenchymal stem cell tenogenic differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;144(5):1162-1174.
[35] YOON SH, KIM YK, HAN ED, et al.Passive control of cell locomotion using micropatterns: the effect of micropattern geometry on the migratory behavior of adherent cells.Lab Chip.2012;12(13):2391-2402.
|