| [1] Chen S, Huang Y, Chen W, et al. Protective effects of Tougu Xiaotong capsule on morphology and osteoprotegrin/nuclear factor-κB ligand expression in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(1):419-425.[2] Li X, Zhen Z, Tang G, et al. MiR-29a and MiR-140 Protect Chondrocytes against the anti-proliferation and cell matrix signaling changes by IL-1β. Mol Cells. 2016;39(2):103-110.[3] 刘献祥.基于陈可冀学术思想之骨性关节炎研究[J].康复学报, 2016,26(1):2-5.[4] 林洁,付长龙,李俐,等.电针治疗膝骨性关节炎疗效的系统评价[J].康复学报,2016,26(4):52-58.[5] Wu MX, Li XH, Lin MN, et al. Clinical study on the treatment of knee osteoarthritis of Shen-Sui insufficiency syndrome type by electroacupuncture. Chin J Integr Med. 2010;16(4): 291-297.[6] Ye J, Wu G, Li X, et al. Millimeter wave treatment inhibits apoptosis of chondrocytes via regulation dynamic equilibrium of intracellular free Ca2+. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:464161.[7] 吴明霞,李西海,吴广文,等.电针后血清对肿瘤坏死因子α诱导软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(46):8551-8555.[8] Wang X, Li F, Fan C, et al. Effects and relationship of ERK 1 and ERK 2 ininterleukin-1-induced alterations in MMP3, MMP13, typeII collagen and aggrecan expression in human chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2011;27(4):583-589.[9] Karnoub AE, Weinberg RA. Ras oncogenes: split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(7):517-531.[10] Roskoski R. ERK1/2 MAP kinases: structure,function,and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 2012; 66(2):105-143.[11] 李西海,梁文娜,党传鹏,等.补肾壮筋汤抑制炎性细胞因子表达延缓骨关节炎软骨退变的研究[J].风湿病与关节炎, 2014,3(5): 20-25.[12] 陈后煌,邵翔,李俐,等.肿瘤坏死因子α诱导大鼠软骨细胞凋亡模型的建立及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(4):527-531.[13] Fu CL, Zheng CS, Lin J, et al. Cibotium barometz polysaccharides stimulate chondrocyte proliferation in vitro by promoting G1/S cell cycle transition. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(5): 3027-3034.[14] 林木南,林艳红,刘献祥,等.温热疏密波对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨细胞RAS/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路的影响[J].中医正骨, 2016,28(2):81-86.[15] 高世超,殷海波,刘宏潇,等.MAPK信号通路在骨关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(5):441-444.[16] O'Neill E, Kolch W. Conferring specificity on the ubiquitous Raf/MEK signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 2004;90(2): 283-288.[17] Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, et al. Sorafenib blocks the raf/mek/erk pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006;66(24):11851-11858.[18] 蒋成英,戴广海.Ras/Raf/Mek/Erk信号传导通路在肝细胞癌发生中的作用机制及在靶向治疗中的应用[J].中国肿瘤临床, 2008, 35(23):1377-1380.[19] Karnoub AE, Weinberg RA. Ras oncogenes: split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(7):517-531.[20] Roskoski R. ERK1 /2 MAP kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 2012;66(2):105-143.[21] Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:626-634.[22] Wang X, Li F, Fan C, et al. Effects and relationship of ERK 1 and ERK 2 in interleukin-1β-induced alterations in MMP3,MMP13, type II collagen and aggrecan expression in human chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2011;27(4):583-589.[23] 李冠,甘丽娇,钟妙容.TNF-α与β1,4- GalT-I在骨关节炎滑膜炎症过程中的关系研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2016,15(2): 137-139.[24] 朱芳晓,周润华,石宇红,等.小白菊内酯对兔膝骨关节炎血清IL-1β及TNF-α的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2013,33(10): 1382-1384.[25] 李迎雪,陈丹丹,张茹,等.双歧杆菌脂磷壁酸通过激活小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞MEK/ERK通路促进TNF-α表达[J].海南医学院学报, 2015,21(4):442-448.[26] 包飞,张燕,吴志宏,等.电针治疗膝骨关节炎疗效观察及对软骨磁共振T2图的影响[J].中国针灸,2013,33(3):193-197.[27] 刚嘉鸿,宓轶群,王华敏.电针与美洛昔康治疗早中期膝骨关节炎临床疗效比较随机对照研究[J].中国针灸,2016,36(5):467-470.[28] 吴明霞,李西海,李俐,等.电针后血清对TNF-α诱导凋亡软骨细胞MAPK信号通路的影响[J].福建中医药,2011,42(6):43-45.[29] 吴明霞,李西海,李俐,等.电针对骨性关节炎软骨细胞JAK-STAT信号通路表达的影响[J].福建中医药大学学报, 2011,21(6): 21-23.[30] Yang X, He H, Zhou Y, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field at different stages of knee osteoarthritis in rats induced by low-dose monosodium iodoacetate: Effect on subchondral trabecular bone microarchitecture and cartilage degradation. Bioelectromagnetics. 2017;38(3):227-238. [31] Baudi P, Catani F, Rebuzzi M, et al. Morphological Study: Ultrastructural Aspects of Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone in Patients Affected by Post-Traumatic Shoulder Instability. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017;300(7): 1208-1218. [32] Atik O?, Erdo?an D, Seymen CM, et al. Is there crosstalk between subchondral bone, cartilage, and meniscus in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis? Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2016;27(2):62-67. [33] Iijima H, Aoyama T, Tajino J, et al. Subchondral plate porosity colocalizes with the point of mechanical load during ambulation in a rat knee model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(2):354-363.[34] Kaderli S, Viguier E, Watrelot-Virieux D, et al. Efficacy study of two novel hyaluronic acid-based formulations for viscosupplementation therapy in an early osteoarthrosic rabbit model. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;96:388-395. [35] Prieto-Potin I, Largo R, Roman-Blas JA, et al. Characterization of multinucleated giant cells in synovium and subchondral bone in knee osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:226. [36] Tomatsu S, Alméciga-Díaz CJ, Montaño AM, et al. Therapies for the bone in mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol Genet Metab. 2015;114(2):94-109. [37] Asakawa-Tanne Y, Su S, Kunimatsu R, et al. Effects of enzymatic degradation after loading in temporomandibular joint. J Dent Res. 2015;94(2):337-343. [38] Cheleschi S, Cantarini L, Pascarelli NA, et al. Possible chondroprotective effect of canakinumab: an in vitro study on human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Cytokine. 2015;71(2): 165-172. [39] Neu CP, Novak T, Gilliland KF, et al. Optical clearing in collagen- and proteoglycan-rich osteochondral tissues. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(3):405-413. [40] Prokopovich P. Interactions between mammalian cells and nano- or micro-sized wear particles: physico-chemical views against biological approaches. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;213:36-47. [41] Yan JY, Tian FM, Wang WY, et al. Age dependent changes in cartilage matrix, subchondral bone mass, and estradiol levels in blood serum, in naturally occurring osteoarthritis in Guinea pigs. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(8):13578-12595. [42] Salzmann GM, Erdle B, Porichis S, et al. Long-term T2 and Qualitative MRI Morphology After First-Generation Knee Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation: Cartilage Ultrastructure Is Not Correlated to Clinical or Qualitative MRI Outcome. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(8):1832-1840. [43] Espino DM, Shepherd DE, Hukins DW. Viscoelastic properties of bovine knee joint articular cartilage: dependency on thickness and loading frequency. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:205.[44] Speirs AD, Beaulé PE, Ferguson SJ, et al. Stress distribution and consolidation in cartilage constituents is influenced by cyclic loading and osteoarthritic degeneration. J Biomech. 2014;47(10):2348-2353. [45] Roemer FW, Eckstein F, Hayashi D, et al. The role of imaging in osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28(1): 31-60. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路:Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路(ERK1/2通路),位于MAPK信号通路的下游,外界刺激首先激活Ras,诱发连锁反应,活化的Ras进一步激活Raf,Raf激活MEK1/2,进而活化ERK1/2,ERK1/2进入细胞核,激活转录因子的表达,促进软骨细胞的异常增殖及肥大分化,引起软骨钙化、增生,最终形成骨关节炎,因此,ERK1/2信号的活化是决定软骨细胞转归的关键。PD98059作为该信号通路的抑制剂,可通过选择性、非ATP竞争性抑制MEK,进而阻断该信号通路。
电针:电针具有通络舒筋、消肿止痛的功效其在治疗膝骨性关节炎上,具有疗效可靠,不良反应小并且操作方便等优点,可有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。
文题释义:
Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路:Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路(ERK1/2通路),位于MAPK信号通路的下游,外界刺激首先激活Ras,诱发连锁反应,活化的Ras进一步激活Raf,Raf激活MEK1/2,进而活化ERK1/2,ERK1/2进入细胞核,激活转录因子的表达,促进软骨细胞的异常增殖及肥大分化,引起软骨钙化、增生,最终形成骨关节炎,因此,ERK1/2信号的活化是决定软骨细胞转归的关键。PD98059作为该信号通路的抑制剂,可通过选择性、非ATP竞争性抑制MEK,进而阻断该信号通路。
电针:电针具有通络舒筋、消肿止痛的功效其在治疗膝骨性关节炎上,具有疗效可靠,不良反应小并且操作方便等优点,可有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。.jpg) 文题释义:
Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路:Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路(ERK1/2通路),位于MAPK信号通路的下游,外界刺激首先激活Ras,诱发连锁反应,活化的Ras进一步激活Raf,Raf激活MEK1/2,进而活化ERK1/2,ERK1/2进入细胞核,激活转录因子的表达,促进软骨细胞的异常增殖及肥大分化,引起软骨钙化、增生,最终形成骨关节炎,因此,ERK1/2信号的活化是决定软骨细胞转归的关键。PD98059作为该信号通路的抑制剂,可通过选择性、非ATP竞争性抑制MEK,进而阻断该信号通路。
电针:电针具有通络舒筋、消肿止痛的功效其在治疗膝骨性关节炎上,具有疗效可靠,不良反应小并且操作方便等优点,可有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。
文题释义:
Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路:Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路(ERK1/2通路),位于MAPK信号通路的下游,外界刺激首先激活Ras,诱发连锁反应,活化的Ras进一步激活Raf,Raf激活MEK1/2,进而活化ERK1/2,ERK1/2进入细胞核,激活转录因子的表达,促进软骨细胞的异常增殖及肥大分化,引起软骨钙化、增生,最终形成骨关节炎,因此,ERK1/2信号的活化是决定软骨细胞转归的关键。PD98059作为该信号通路的抑制剂,可通过选择性、非ATP竞争性抑制MEK,进而阻断该信号通路。
电针:电针具有通络舒筋、消肿止痛的功效其在治疗膝骨性关节炎上,具有疗效可靠,不良反应小并且操作方便等优点,可有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。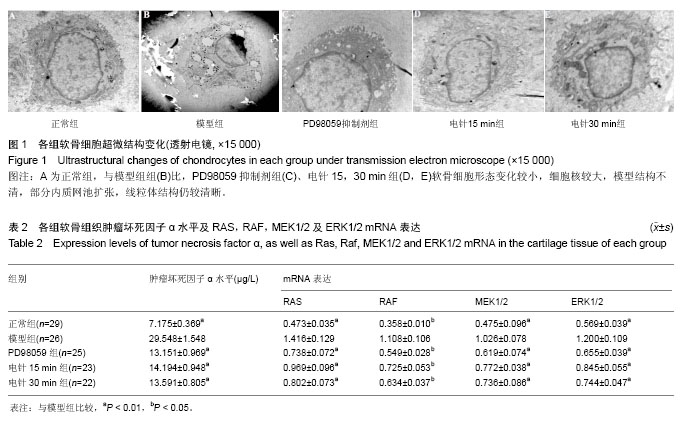
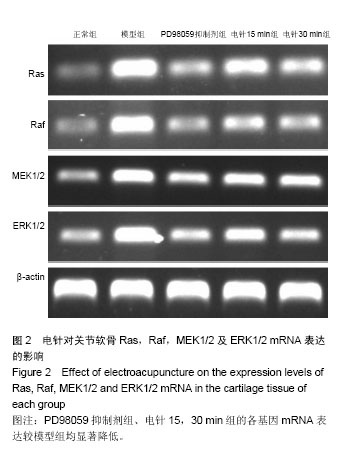
.jpg) 文题释义:
Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路:Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路(ERK1/2通路),位于MAPK信号通路的下游,外界刺激首先激活Ras,诱发连锁反应,活化的Ras进一步激活Raf,Raf激活MEK1/2,进而活化ERK1/2,ERK1/2进入细胞核,激活转录因子的表达,促进软骨细胞的异常增殖及肥大分化,引起软骨钙化、增生,最终形成骨关节炎,因此,ERK1/2信号的活化是决定软骨细胞转归的关键。PD98059作为该信号通路的抑制剂,可通过选择性、非ATP竞争性抑制MEK,进而阻断该信号通路。
电针:电针具有通络舒筋、消肿止痛的功效其在治疗膝骨性关节炎上,具有疗效可靠,不良反应小并且操作方便等优点,可有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。
文题释义:
Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路:Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路(ERK1/2通路),位于MAPK信号通路的下游,外界刺激首先激活Ras,诱发连锁反应,活化的Ras进一步激活Raf,Raf激活MEK1/2,进而活化ERK1/2,ERK1/2进入细胞核,激活转录因子的表达,促进软骨细胞的异常增殖及肥大分化,引起软骨钙化、增生,最终形成骨关节炎,因此,ERK1/2信号的活化是决定软骨细胞转归的关键。PD98059作为该信号通路的抑制剂,可通过选择性、非ATP竞争性抑制MEK,进而阻断该信号通路。
电针:电针具有通络舒筋、消肿止痛的功效其在治疗膝骨性关节炎上,具有疗效可靠,不良反应小并且操作方便等优点,可有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。