| [1]Brennan-Calanan RM,Genco RJ,Wilding GE,et al. Osteoporosis and oral infection: Independent risk factors for oral bone loss.J Dent Res.2008;87(4):323-327.[2]Prank K,Nowlan SJ,Harms HM,et al.Time series prediction of plasma hormone concentration. Evidence for differences in predictability of parathyroid hormone secretion between osteoporoctic patients and normal controls.J Clin Invest.1995; 95(6):2910-2919.[3]Blind E,Raue F,Knappe V,et al.Cyclic AMP formation in rat bone and kidney cells is stimulated equally by parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) 1-34 and PTH 1-34. Exp Clin Endocrinol.1993;101(3):150-155.[4]四川美康医药软件研究开发有限公司.药物临床信息参考[M].成都:四川科学技术出版社,2007:1507-1508.[5]Yu XH,Wang LP,Jiang X,et al.Biomimetic CaP coating incorporated with parathyroid hormone improves the osseointegration of titanium implant.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(9):2177-2186.[6]Brnemark PI,Hansson BO,Adell R,et al. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw.Experience from a 10-year period.Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Suppl. 1977;16:1-132.[7]Marquezan M,Osorio A,Sant’ Anna E,et al. Does bone mineral density influence the primary stability of dental implants? A systematic review.Clin Oral Implants Res.2012;23(7):767~774.[8]中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2011, 4(1):2-17.[9]Binte AR,Tanaka M,Kohno S,et al.Relationship between porotic changes in alveolar bone and spinal osteoporosis.J Dent Res.2007;86(1):52-57.[10]Khosla S,Westendorf JJ,Oursler MJ. Building bone to reverse osteoporosis and repair fractures.J Clin Invest. 2008;118(2): 421-428.[11]梁红.内源性及外源性甲状旁腺激素对小鼠拔牙创骨愈合的影响[D].南京医科大学,2010.[12]Tang ZL,Zhang WJ,Wang DX,et al.An experimental study addressing the promotion of mandibular defect repair through the intermittent subcutaneous injection of parathyroid hormone.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2014;72(2):419-430.[13]Deshpande SS,Gallagher KK,Donneys A,et al.Parathyroid hormone therapy mollifies radiation-induced biomechanical degradation in murine distraction osteogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg.2013;132(1):91-100.[14]Reynolds DG,Takahata M,Lerner AL,et al.Teriparatide therapy enhances devitalized femoral allograft osseointegration and biomechanics in a murine model. Bone.2011;48(3):562-570.[15]Hodsman AB,Bauer DC,Dempster DW,et al.Parathyroid hormone and teriparatide for the treatment of osteoporosis: a review of the evidence and suggested guidelines for its use. Endocr Rev.2005;26(5):688-703.[16]Jilka RL,Weinstein RS,Bellido T,et al.Increased bone formation by prevention of osteoblast apoptosis with parathyroid hormone.J Clin Invest.1999;104(4):439-446. [17]Chen HL,Demiralp B,Schneider A,et al.Parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related protein exert both pro- and anti-apoptotic effects in mesenchymal cells.J Biol Chem.2002; 277(22):19374-19381.[18]Dobnig H,Turner RT.Evidence that intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone increase bone formation in adult rats by activation of bone lining cells. Endocrinology.1995;136(8): 3632-3638.[19]Gasser JA,Kneissel M,Thomsen JS,et al. PTH and interactions with bisphoshonates.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.2000;1(1):53-56.[20]Hodsman AB,Steer BM.Early histomorphometric changes in response to parathyroid hormone therapy in osteoporosis: Evidence for de novo bone formation on quiescent cancellous surfaces.Bone.1993;14(3):523-527.[21]Jilka RL,O'Brien CA,Ali AA,et al.Intermittent PTH stimulates periosteal bone formation by actions on post-mitotic preosteoblasts.Bone.2009;44(2):275-286.[22]Rickard DJ,Wang FL,Rodriguez-Rojas AM,et al.Intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone(PTH)as well as a non-peptide small molecule agonist of the PTH1 receptor inhibits adipocyte differentiation in human bone marrow stromal cells. Bone.2006;39(6):1361-1372. [23]唐雯菁,杜艳萍,洪维,等.甲状旁腺素对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化和旁分泌功能的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2014,7(1):42-47.[24]Frisch SM.cAMP takes controls.Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(9): E167-168.[25]Drake MT,Srinivasan B,Mdder UI,et al.Effects of intermittent parathyroid hormone treatment on osteoprogenitor cells in postmenopausal women.Bone.2011;49(3):349-355.[26]Neer M,Slovik DM,Daly M,et al.Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis with daily parathyroid hormone plus calcitriol. Osteoporos Int.1993;3(1):204-205.[27]Burr DB,Hirano T,Turner CH,et al.Intermittently administered human parathyroid hormone (1-34) treatment increases intracortical bone turnover and porosity without reducing bone strength in the humerus of ovariectomized cynomolgous monkeys.J Bone Miner Res.2001;16(1):157-165.[28]Sato M.Westmore M,Ma YL,et al.Teriparatide [PTH(1-34)] strengthens the proximal femur of onariectomized nonhuman primates despite increasing porosity.J Bone Miner Res. 2004; 19(4):623-629.[29]Datta NS,Abou-Samra AB.PTH and PTHrP signaling in osteoblasts.Cell Signal.2009; 21(8):1245-1254.[30]卫红艳,朱梅.甲状旁腺素治疗骨质疏松研究进展[J].药品评价, 2013,10(5):40-44.[31]王晶晶,孟维艳,张喆,等.负载 PTH(1-34) 聚乳酸微球体外促成骨分化作用的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2015,31(3):360-364.[32]于美娜.负载PTH(1-34)的温水凝胶的制备及细胞学研究[D].吉林大学,2013.[33]Valderrama P,Jung RE,Thoma DS,et al.Evaluation of parathyroid hormone bound to a synthetic matrix for guided bone regeneration around dental implants: A histomorphometric study in dogs.J Periodontol. 2010;81(5): 737-747.[34]Yu X,Wei M.Preparation and evaluation of parathyroid hormone incorporated CaP coating via a biomimetic method.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2011;97(2):345-354.[35]李德超,刘惠萍,李慕勤,等.具有微弧氧化-硅烷-褪黑素复合膜层钛合金种植体的体内骨结合[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(43):6438-6444.[36]Weng J,Wang M,Chen J.Plasma-sprayed calcium phosphate particles with high bioactivity and their use in bioactive scaffolds.Biomaterials.2002;23(13):2623-2629.[37]Milella E,Cosentino F,Licciulli A,et al.Preparation and characterisation of titania/hydroxyapatite composite coatings obtained by sol-gel process. Biomaterials. 2001;22(11): 1425-1431. [38]邓炜,王贻宁.仿生溶液生长法磷酸钙涂层种植体的研究进展[J].国外医学口腔医学分册,2001,28(2):76-78.[39]Junker R,Dimakis A,Thoneick M,et al.Effects of implant surface coatings and composition on bone integration: a systematic review.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(4): 185-206.[40]Luong LN,McFalls KM,Kohn DH.Gene delivery via DNA incorporation within a biomimetic apatite coating. Biomaterials. 2009;30(36):6996-7004.[41]Stigter M,Bezemer J,de Groot K,et al.Incorporation of different antibiotics into carbonated hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium implants, release and antibiotic efficacy.J Control Release.2004;99(1):127-137. [42]Liu Y,Li JP,Hunziker EB,et al.Incorporation of growth factors into medical devices via biomimetic coatings.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci.2006;364(1838):233-248.[43]Wang CX,Liu JJ,Xiao Y,et al.Study on preparation and activity of a novel recombinant human parathyroid hormone(1-34) analog with N-terminal Pro-Pro extension. Regul Pept.2007; 141(1-3):35-43. |
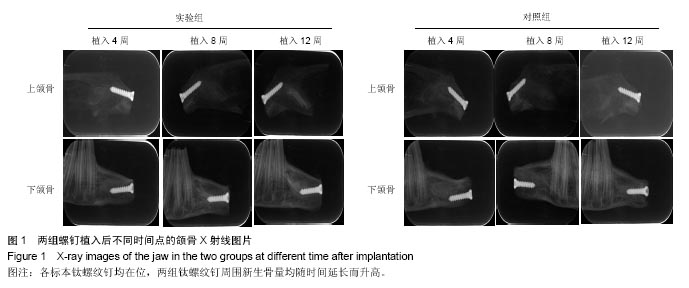
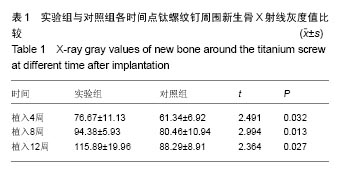
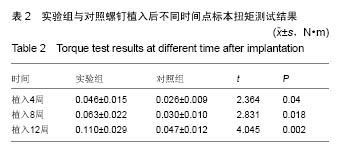
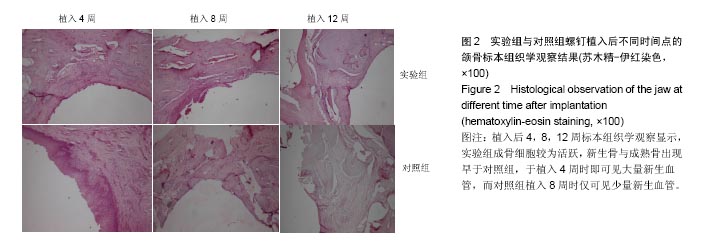
.jpg)
.jpg)