中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (26): 4113-4118.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.26.003
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
人脱细胞羊膜与骨髓间充质干细胞复合体修复关节软骨缺损
姜良斌1,2,韦标方2,冯 志2,岳永彬1,2
- 1广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510006;2临沂市人民医院,山东省临沂市 276000
Repair of articular cartilage defects with human acellular amniotic membrane/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell composite
Jiang Liang-bin1, 2, Wei Biao-fang2, Feng Zhi2, Yue Yong-bin1, 2
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 2Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
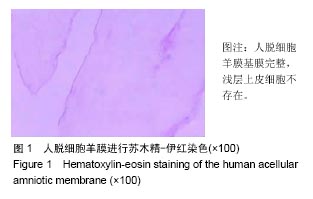
人羊膜:是一种半透明的生物膜,源于天然,主要特点如下:①含有促进细胞增殖及分化的成分,促贴壁物质(胶原蛋白和层粘连蛋白)等较多;②抗炎、抗微生物、抗纤维化、抗瘢痕形成,机械性能较合理,表达生长因子如转化生长因子,这为细胞增殖、分化提供了丰富的营养物质;③促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨转化。
软骨单位:是关节软骨最基本的解剖功能结构,它是软骨细胞与细胞外基质联系的重要“桥梁”,它由一个或几个软骨细胞与其细胞周围基质构成,是关节软骨的结构、功能和代谢的基础。
背景:骨髓间充质干细胞在软骨组织工程研究中作为一种常见的种子细胞被广泛应用于软骨缺损修复。
目的:以人脱细胞羊膜作为细胞支架负载兔骨髓间充质干细胞用以修复兔股骨髁间窝软骨缺损。
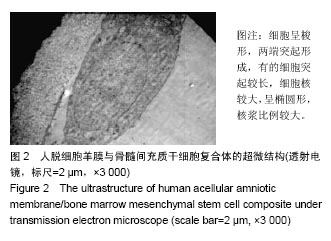
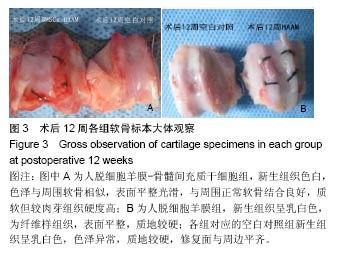
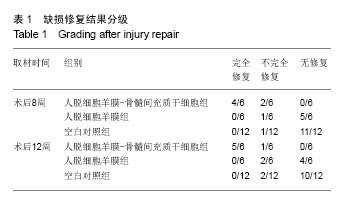
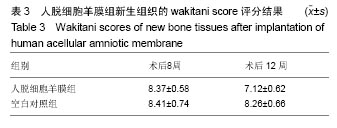
方法:将兔骨髓间充质干细胞接种于人脱细胞羊膜上,体外共培养2周。建立兔股骨髁间窝区关节软骨缺损模型,右膝软骨缺损处设为空白对照组,不植入任何材料,左膝软骨缺损处为实验侧,分别植入人脱细胞羊膜-骨髓间充质干细胞和单纯人脱细胞羊膜。术后第8,12周,取膝关节软骨缺损部位新生组织,行大体观察、组织学检测,评估新生软骨质量。
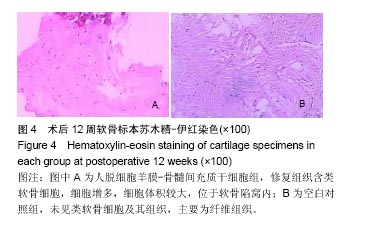
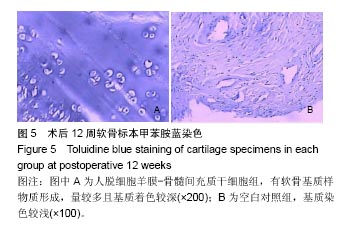
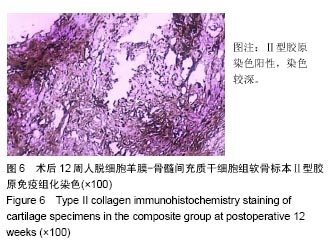
结果与结论:①大体观察结果:人脱细胞羊膜-骨髓间充质干细胞组有类软骨形成,质地较软,与周围正常软骨结合良好;人脱细胞羊膜组未形成软骨组织。空白对照组缺损区只由纤维样组织填充;②组织学观察结果:人脱细胞羊膜-骨髓间充质干细胞组新生出软骨细胞及软骨陷窝,并形成软骨基质,Ⅱ型胶原免疫组织化学染色呈阳性。软骨基质甲苯胺蓝染色较深。人脱细胞羊膜组仅有极少量的软骨细胞,甲苯胺蓝染色较浅,Ⅱ型胶原免疫组织化学染色呈阴性,无软骨基质形成。空白对照组为纤维组织修复,甲苯胺蓝染色较浅;③结果表明,人脱细胞羊膜有利于骨髓间充质干细胞的软骨化,软骨缺损处由类软骨组织填充,能够有效修复关节软骨缺损。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)